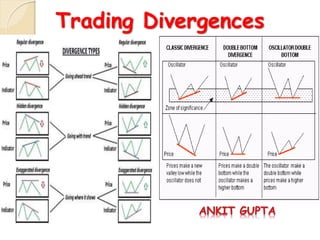
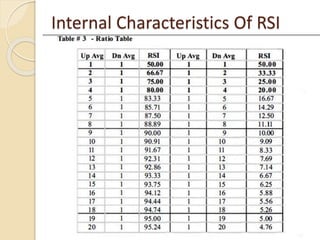
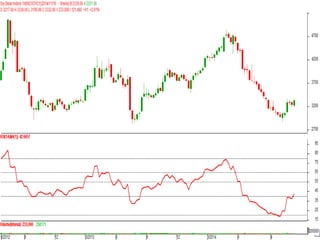
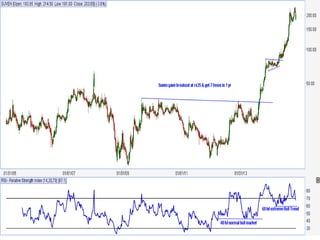
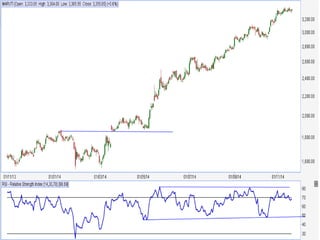
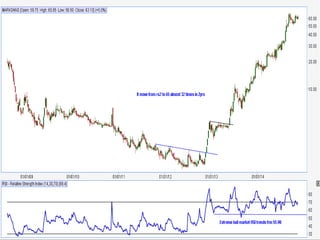
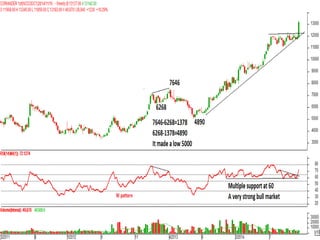
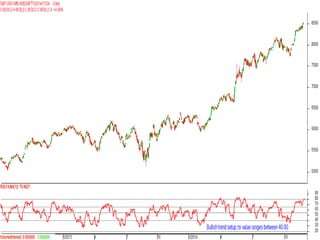
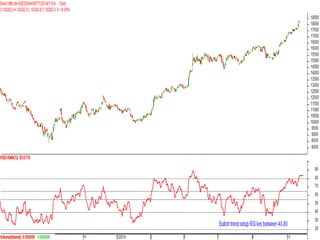
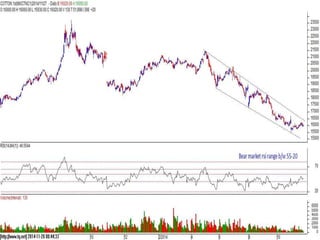
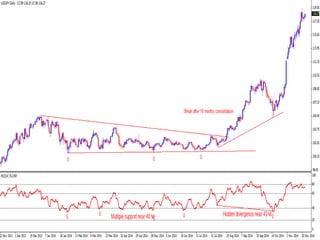
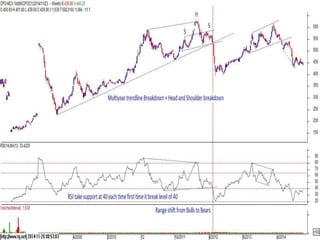
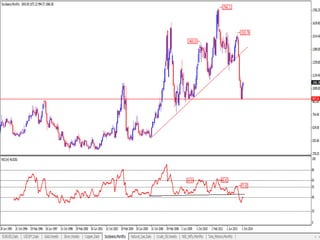
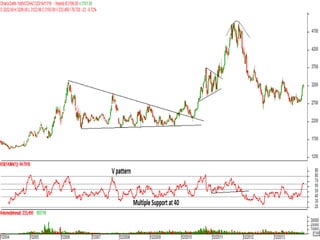
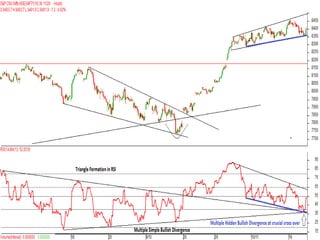
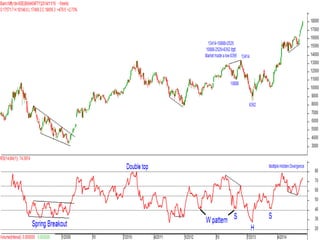
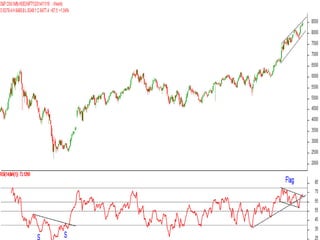
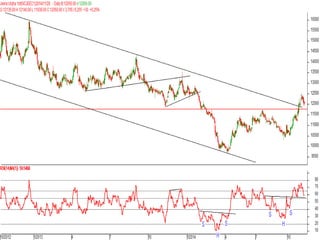
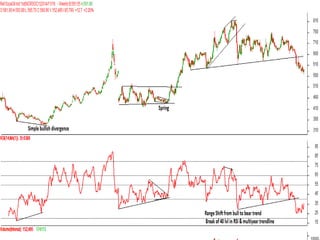
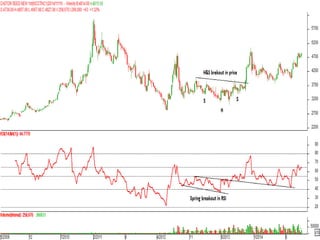
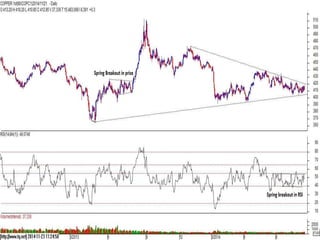
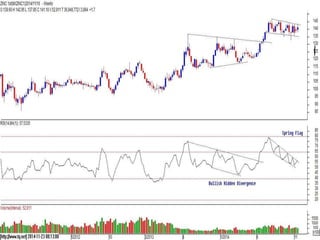
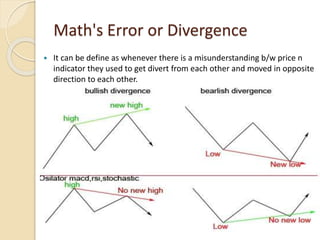
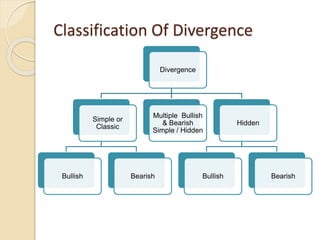
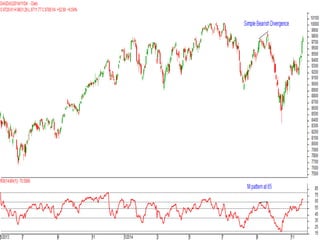
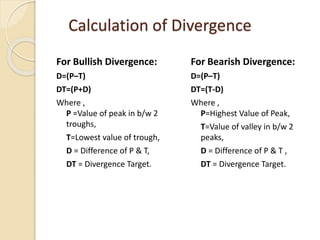
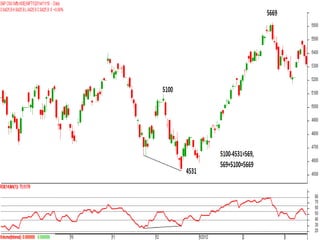
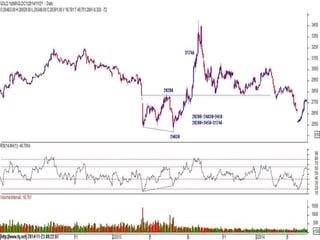
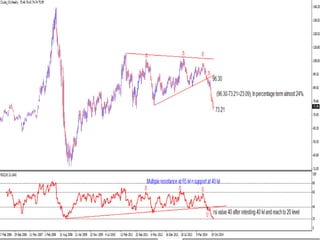
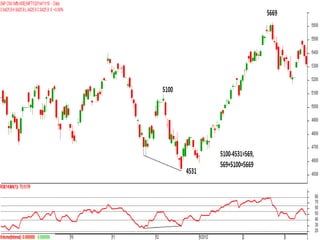
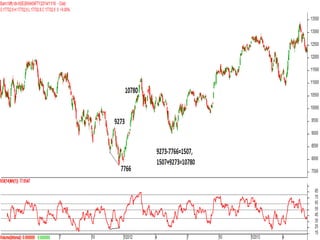
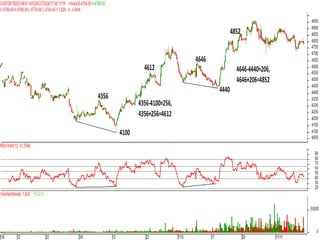
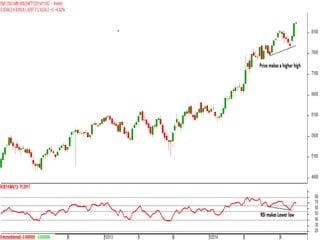
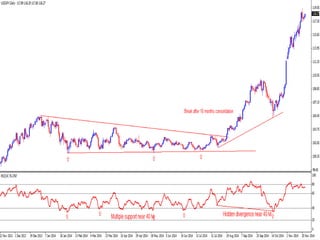
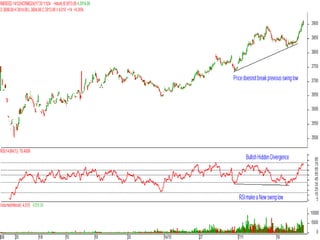
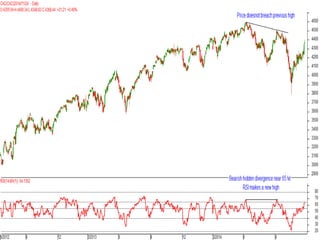
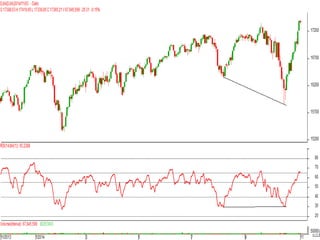
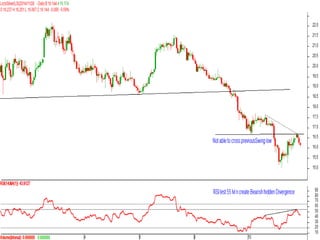
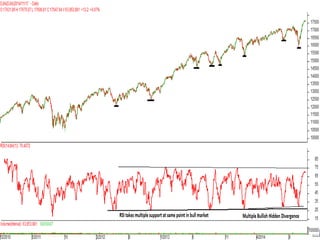
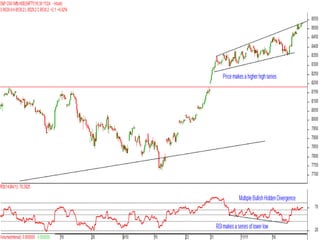
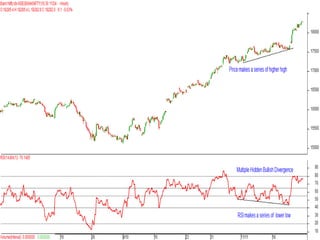
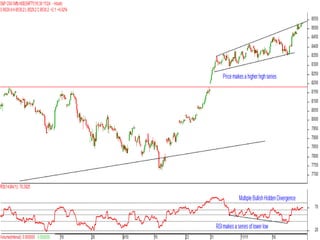
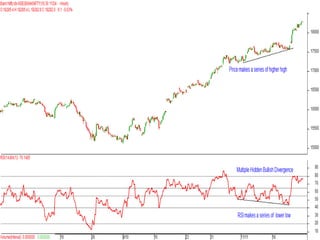
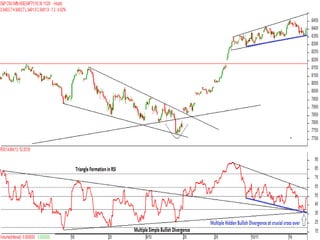
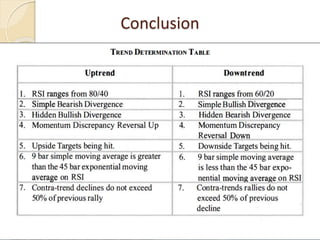
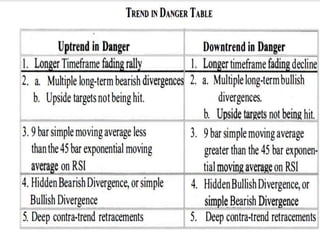
This document discusses different types of divergences that can occur between price and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicator. It defines simple, hidden, and multiple divergences and provides "cheat sheets" to identify them. Simple divergences occur when price and RSI make higher highs/lower lows that do not confirm each other. Hidden divergences occur when RSI makes higher highs/lower lows than price. Multiple divergences involve a series of non-confirming highs or lows between price and RSI. The document provides guidelines on when each type of divergence is most reliable based on RSI values and other technical patterns.