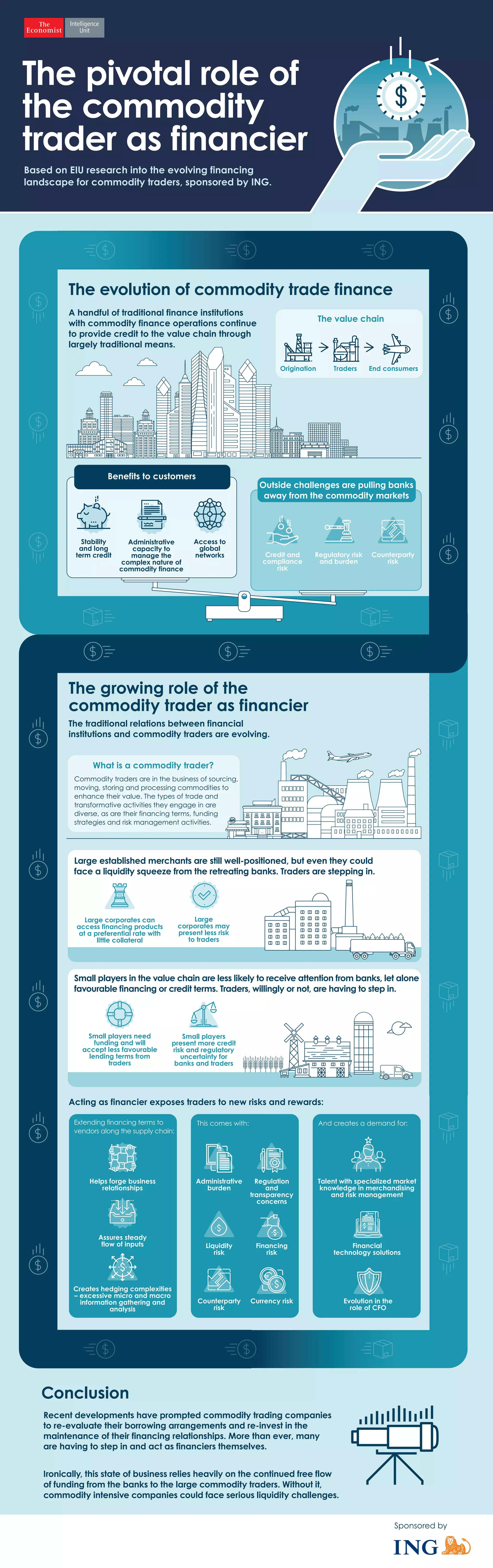
Recent developments have prompted commodity trading companies to re-evaluate their borrowing arrangements and take on more of a financing role. As banks pull back financing from commodity traders, the traders are having to step in as financiers themselves. While this relies on continued funding from banks, without it commodity companies could face serious liquidity challenges.