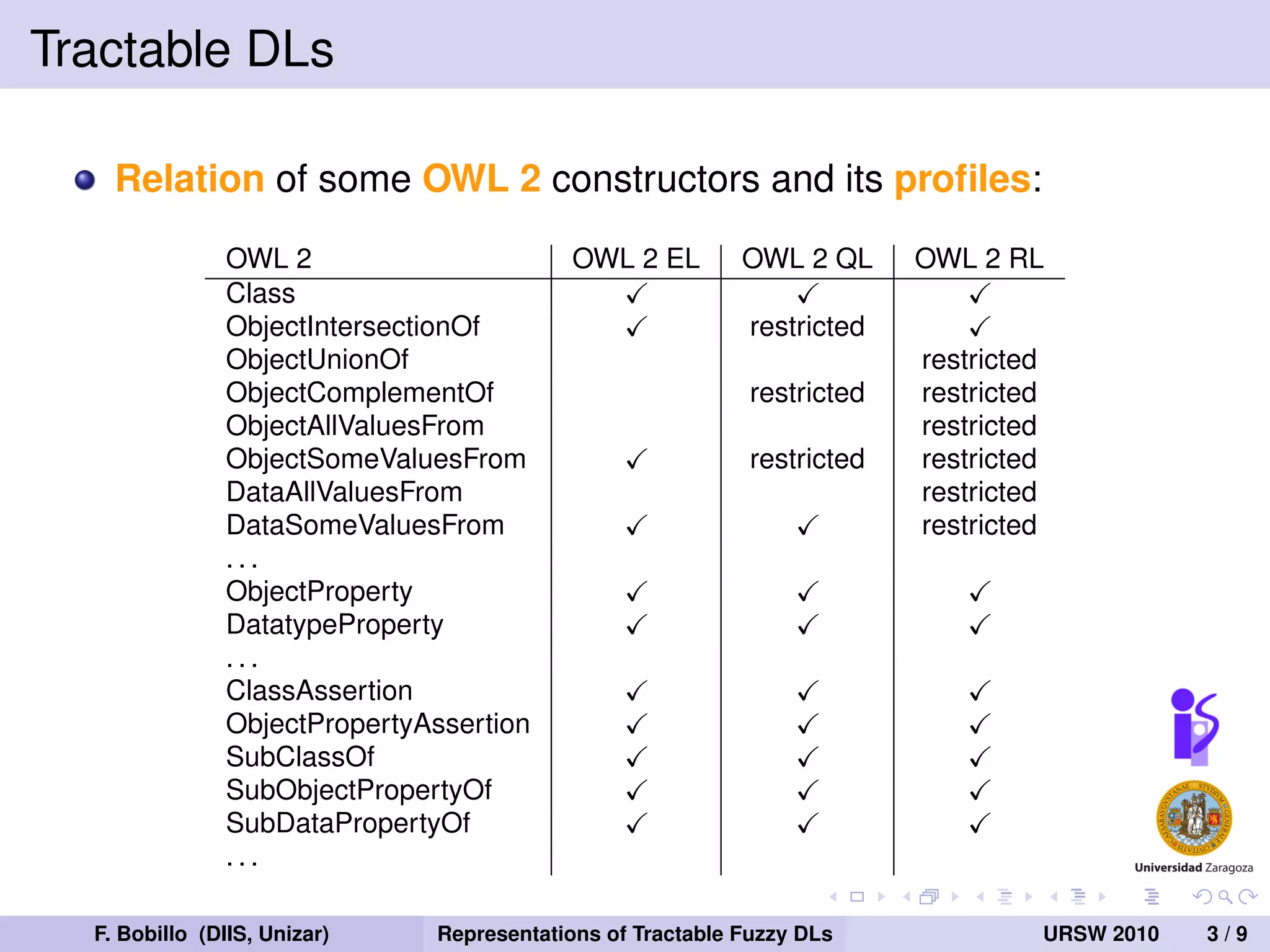
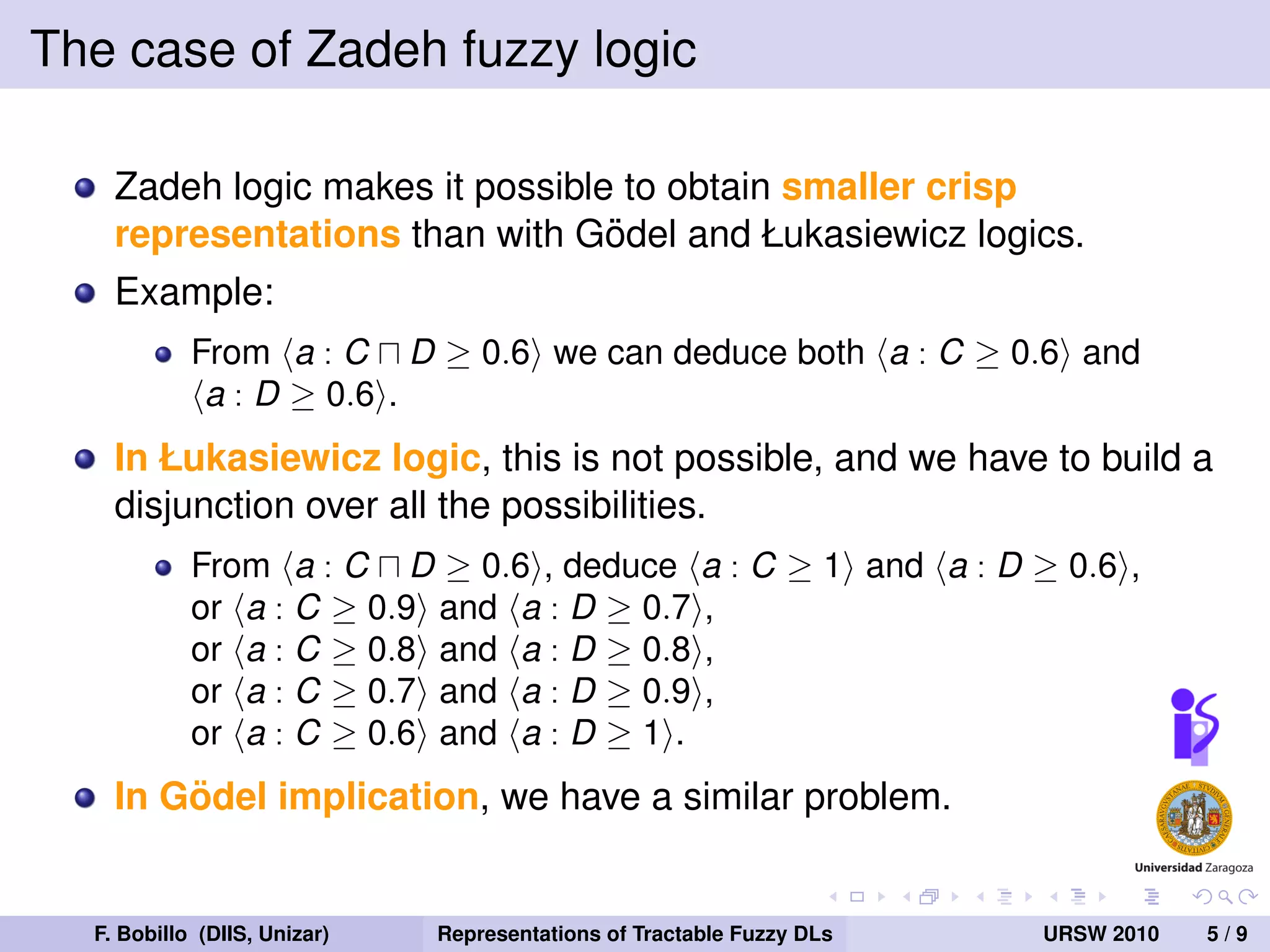
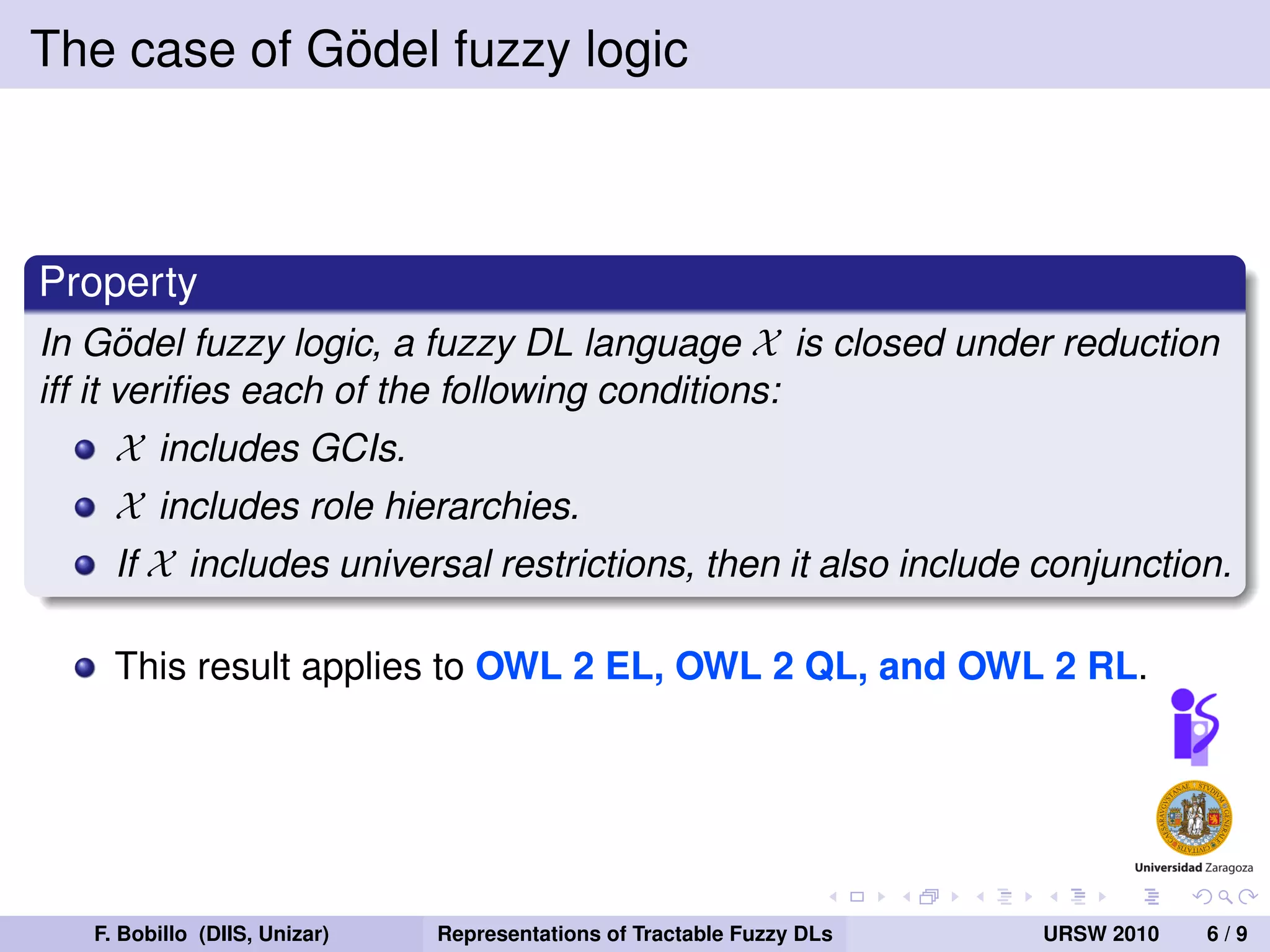
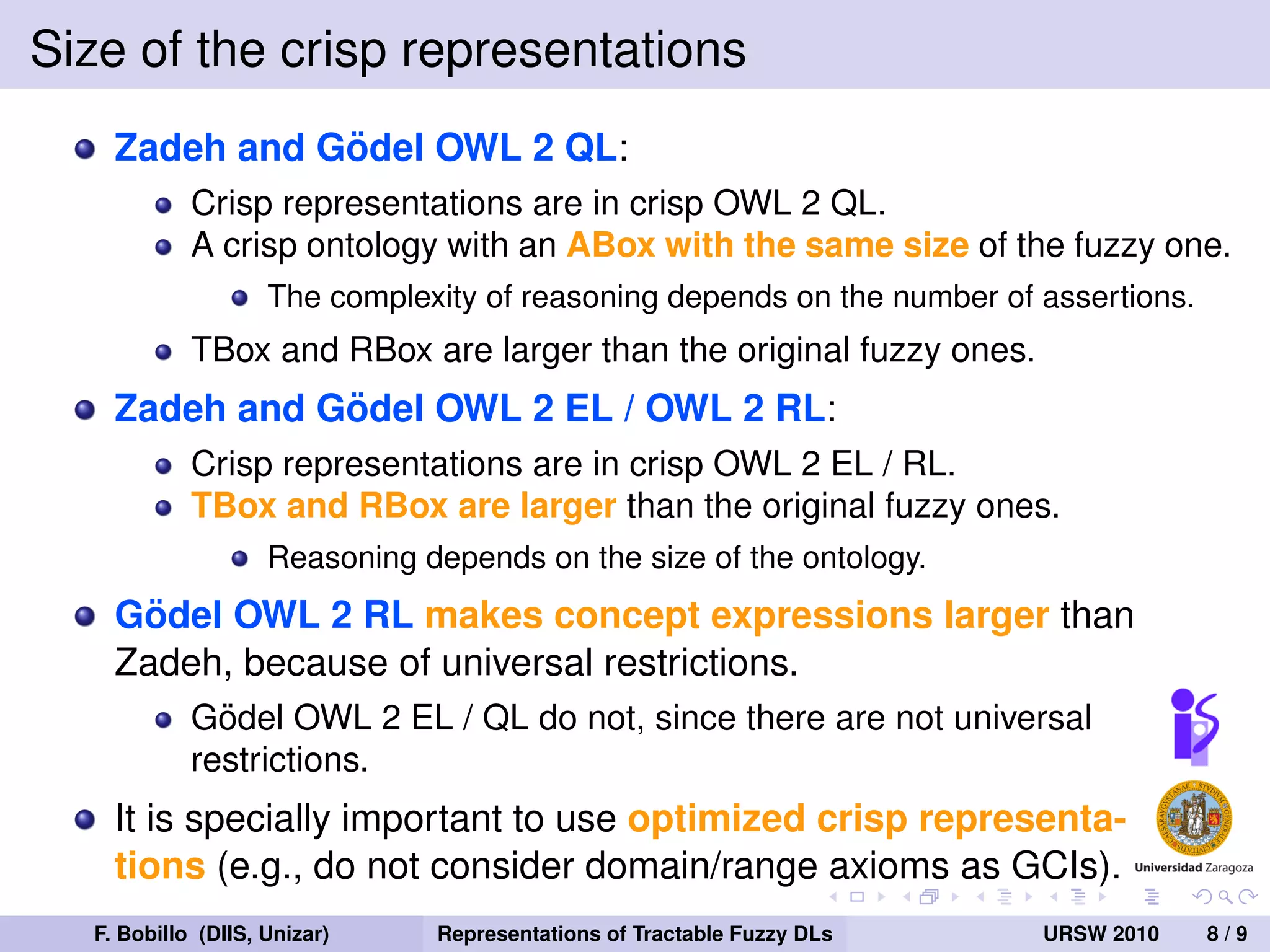
The document discusses the tractability of crisp representations of fuzzy description logics and their applicability in reasoning due to vagueness in knowledge representation. It evaluates different fuzzy logics, specifically Zadeh, Godel, and Łukasiewicz, and their closure under reduction conditions. The findings indicate that Zadeh fuzzy logic offers smaller crisp representations, while Godel and Łukasiewicz have varying requirements impacting their tractability.