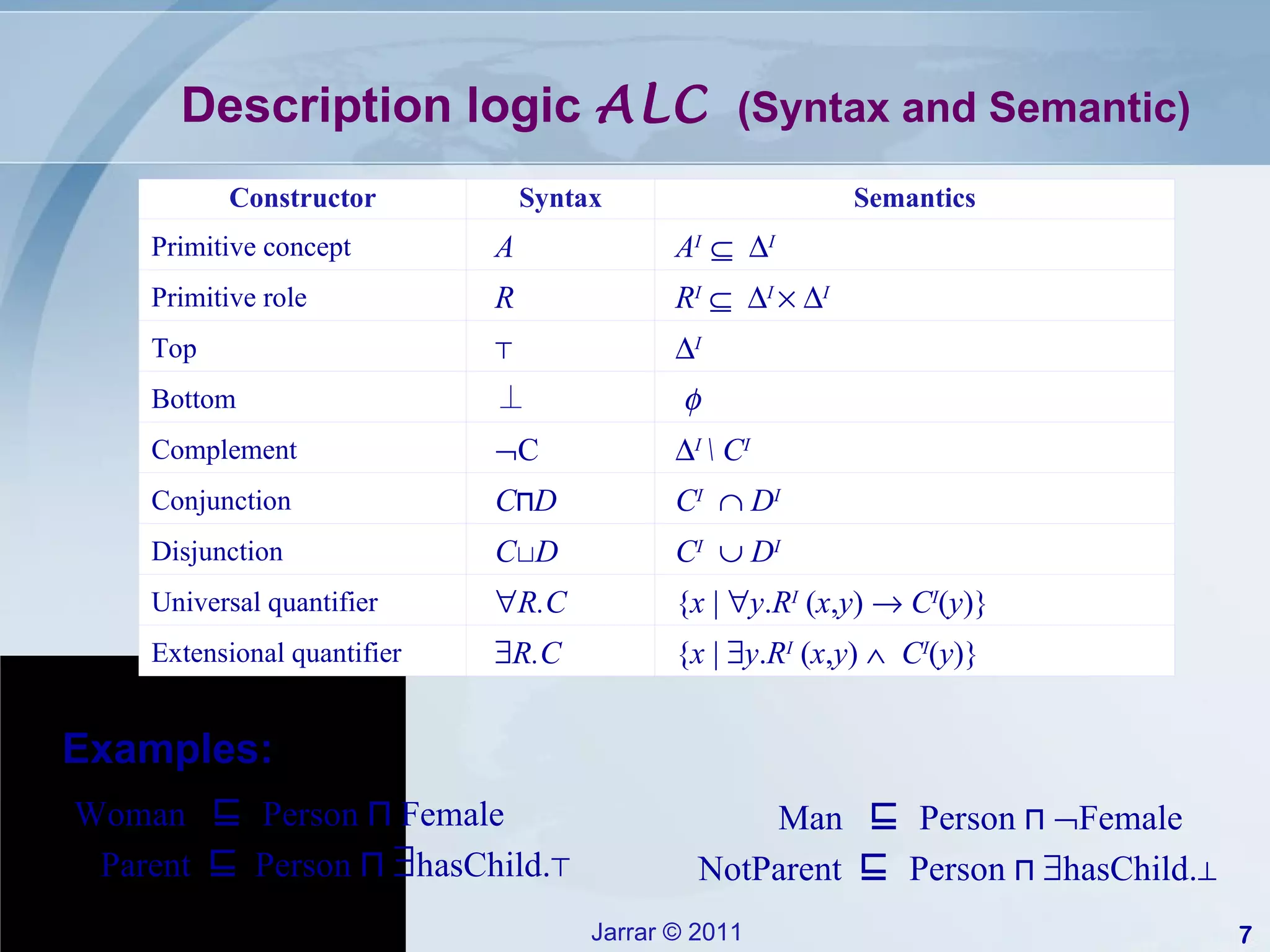
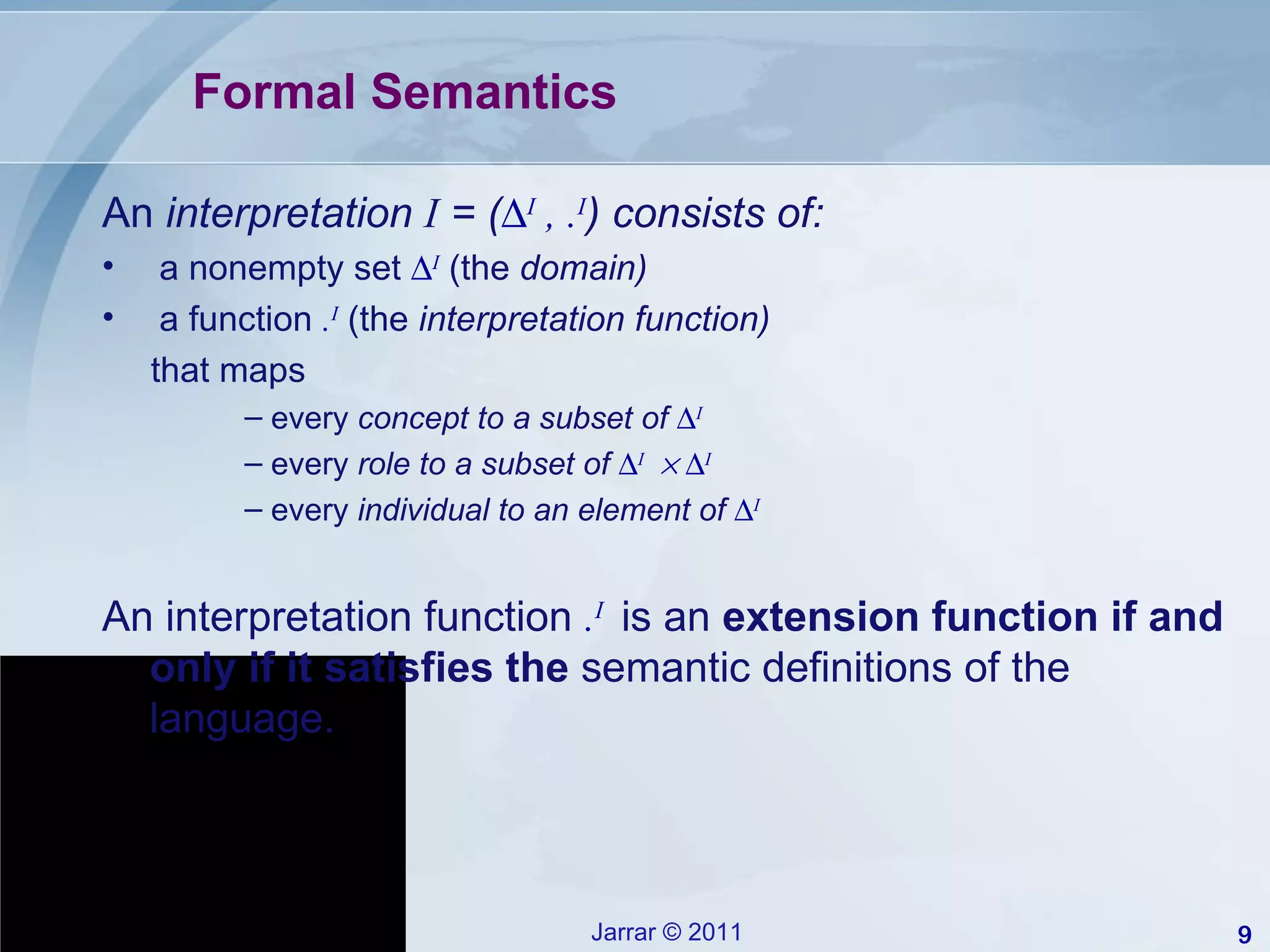
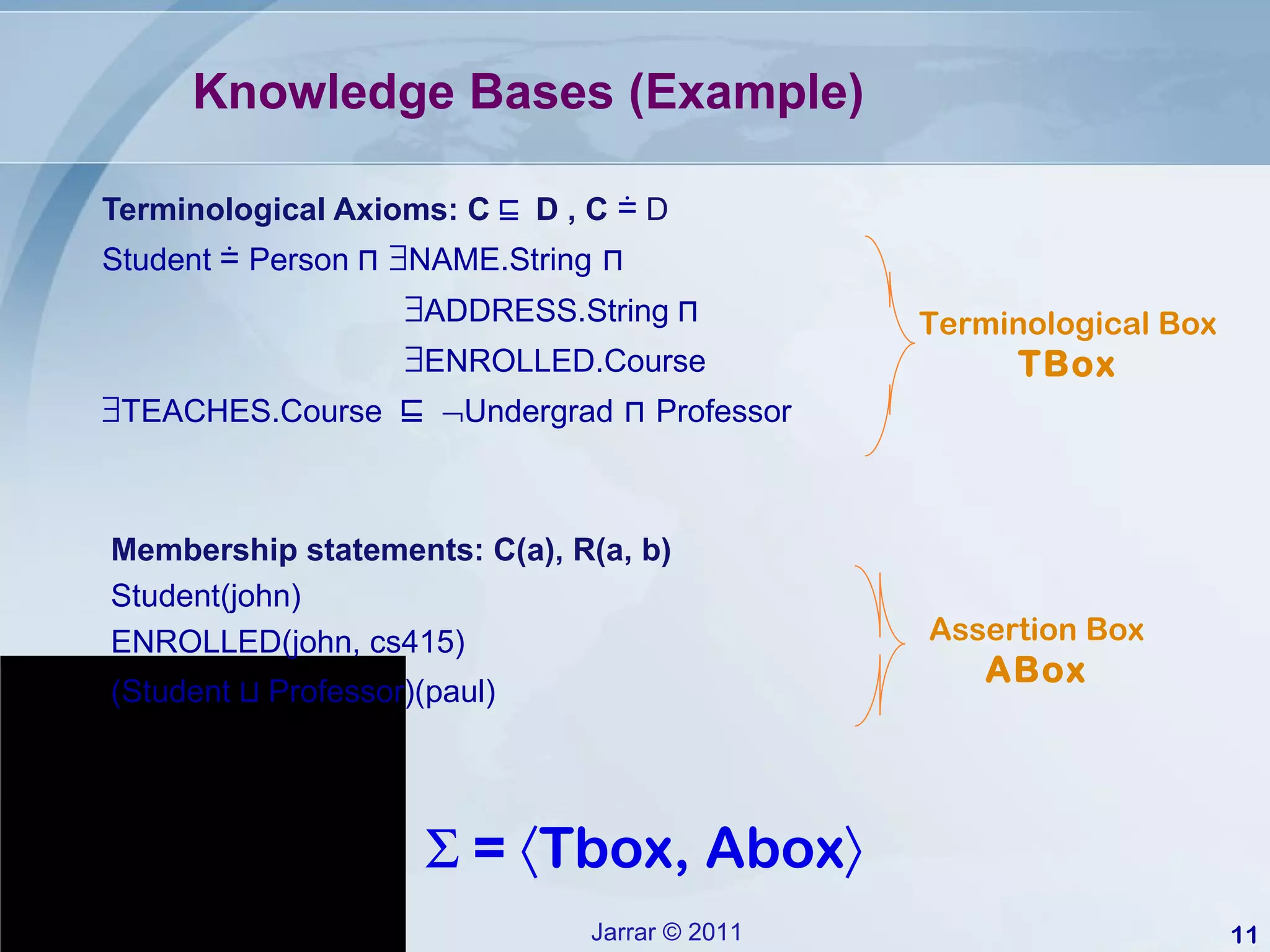
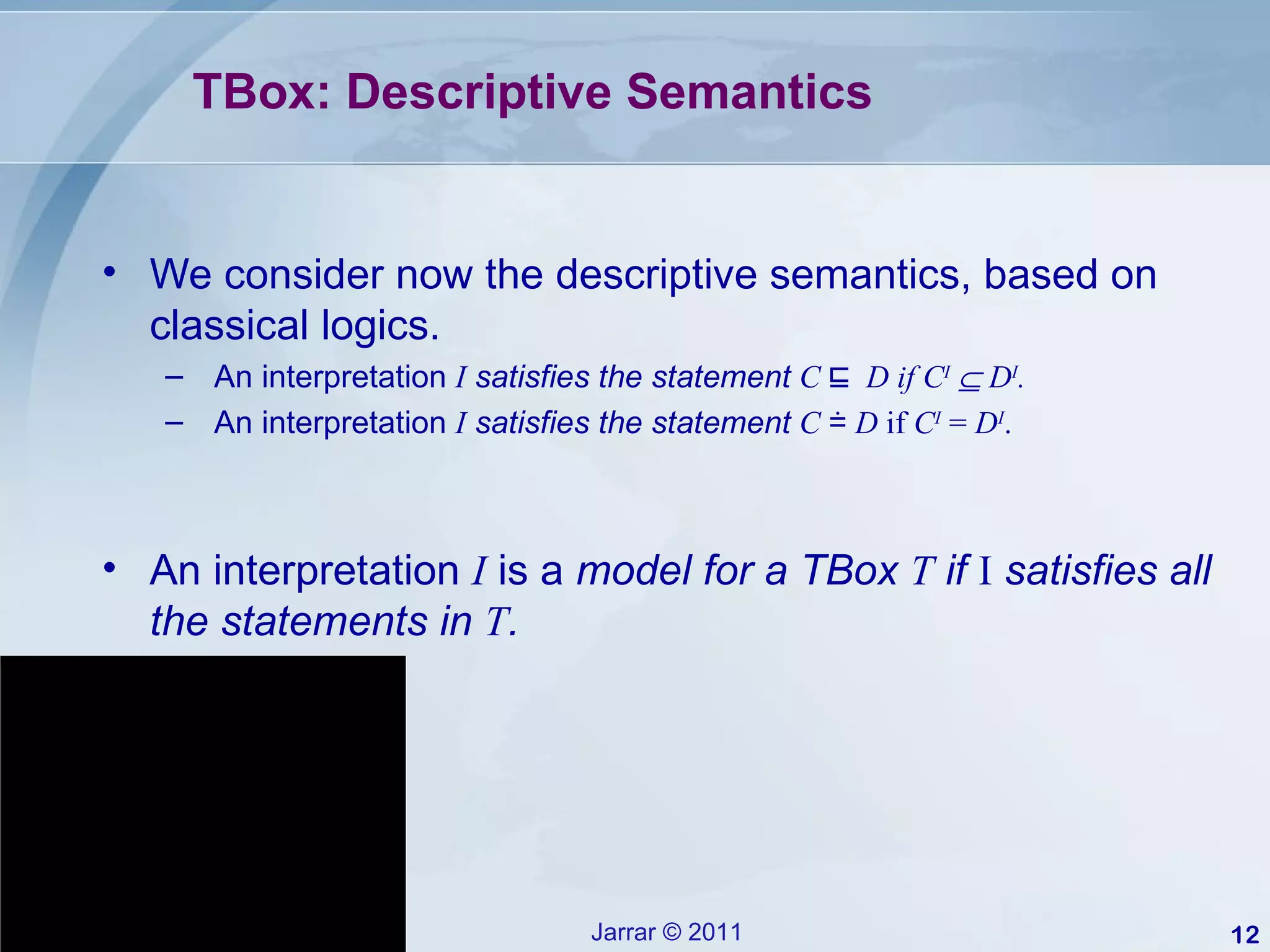
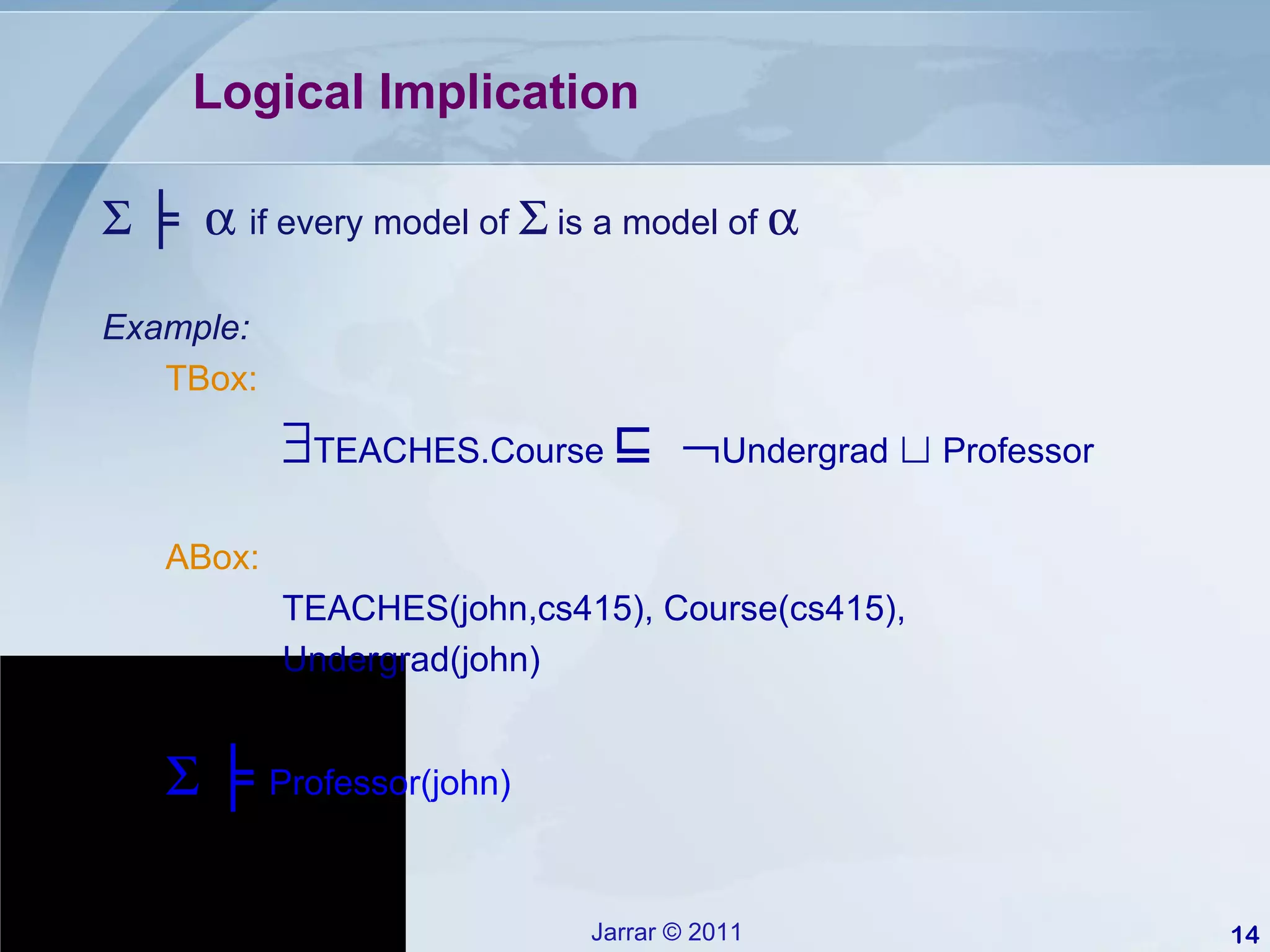
This document provides an introduction to description logics, which are a family of logics concerned with knowledge representation. Description logics allow structuring knowledge through concepts, relationships, and axioms. They provide a decidable fragment of first-order logic with automated reasoning procedures. The document discusses key description logics like ALC, constructors, formal semantics, terminological and assertion boxes, logical implication, and reasoning services like concept satisfiability, subsumption, and instance checking. It also covers extensions like cardinality restrictions and individuals.
![Dr. Mustafa Jarrar [email_address] www.jarrar.info University of Birzeit Description Logic (and business rules) Advanced Artificial Intelligence (SCOM7341) Lecture Notes, Advanced Artificial Intelligence (SCOM7341) University of Birzeit 2 nd Semester, 2011](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jarrar-lecturenotes-aai-2011s-descriptionlogic-110917072150-phpapp02/75/Jarrar-lecture-notes-aai-2011s-descriptionlogic-1-2048.jpg)


















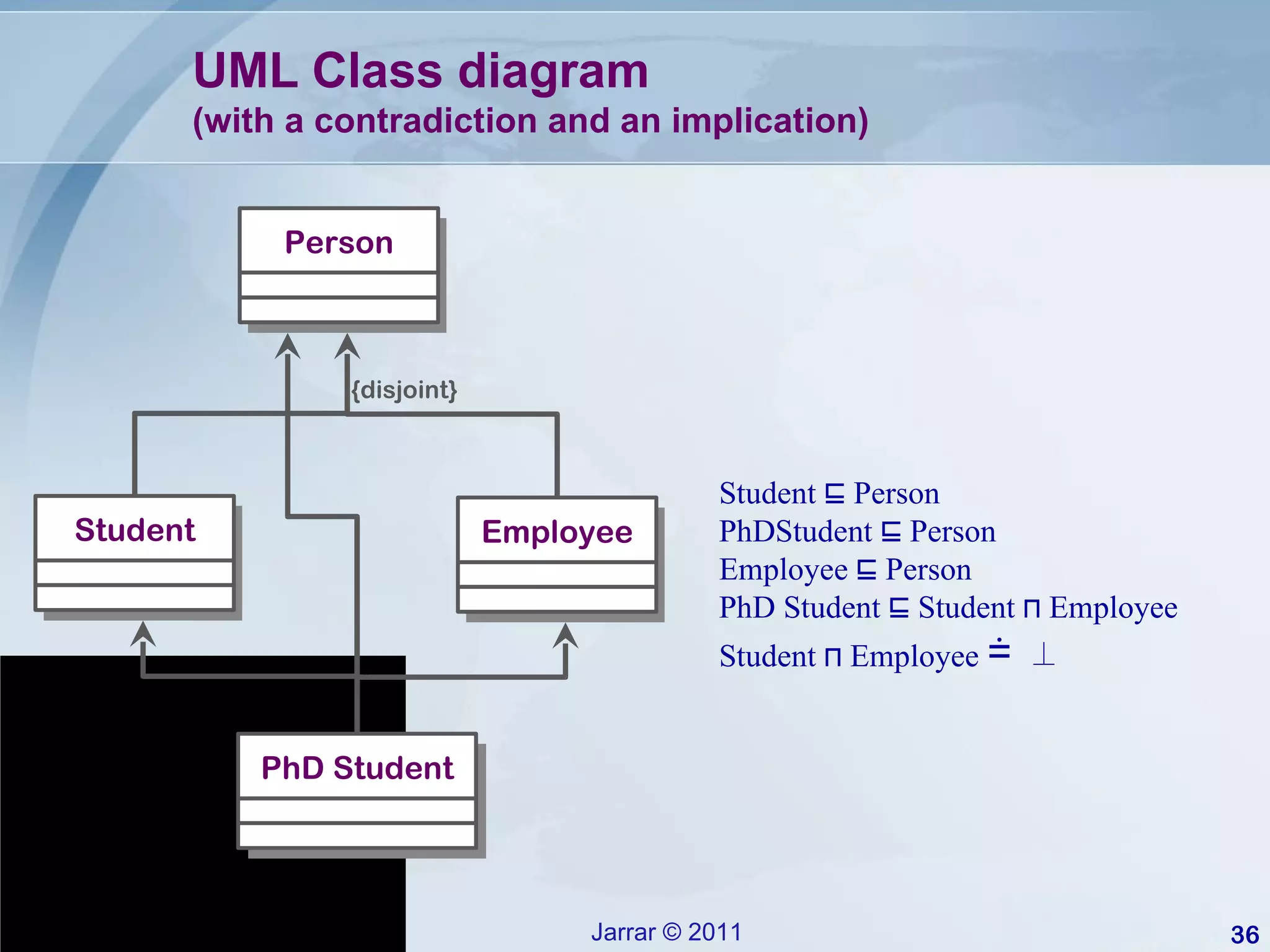
![Infinite Domain: the democratic company [Franconi 2007] Supervisor ⊑ =2 Supervises.Employee Employee ⊑ Supervisor Supervises 2..2 0..1 implies “ the classes Employee and Supervisor necessarily contain an infinite number of instances”. Since legal world descriptions are finite possible worlds satisfying the constraints imposed by the conceptual schema, the schema is inconsistent . Supervisor Employee](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jarrar-lecturenotes-aai-2011s-descriptionlogic-110917072150-phpapp02/75/Jarrar-lecture-notes-aai-2011s-descriptionlogic-37-2048.jpg)