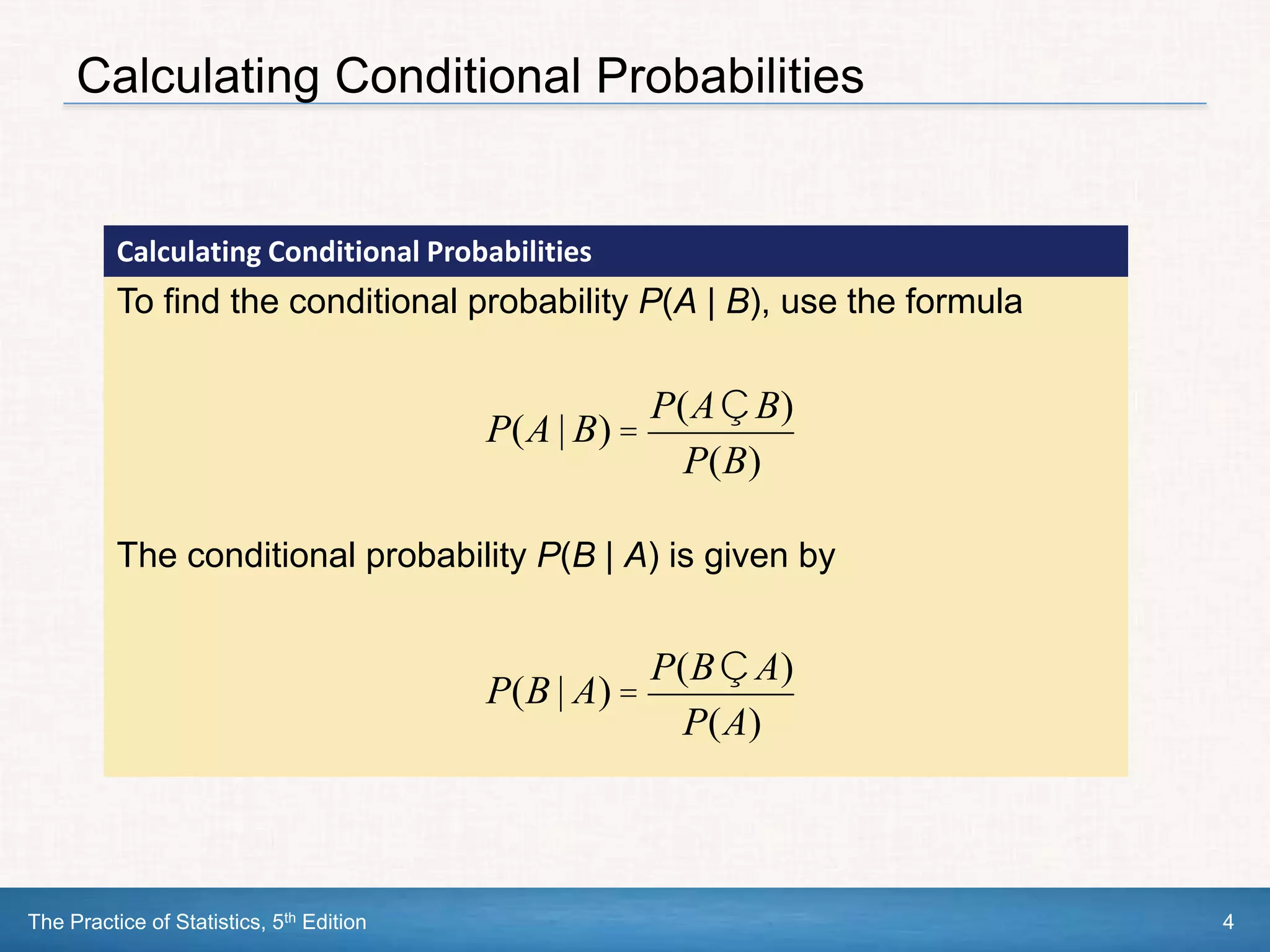
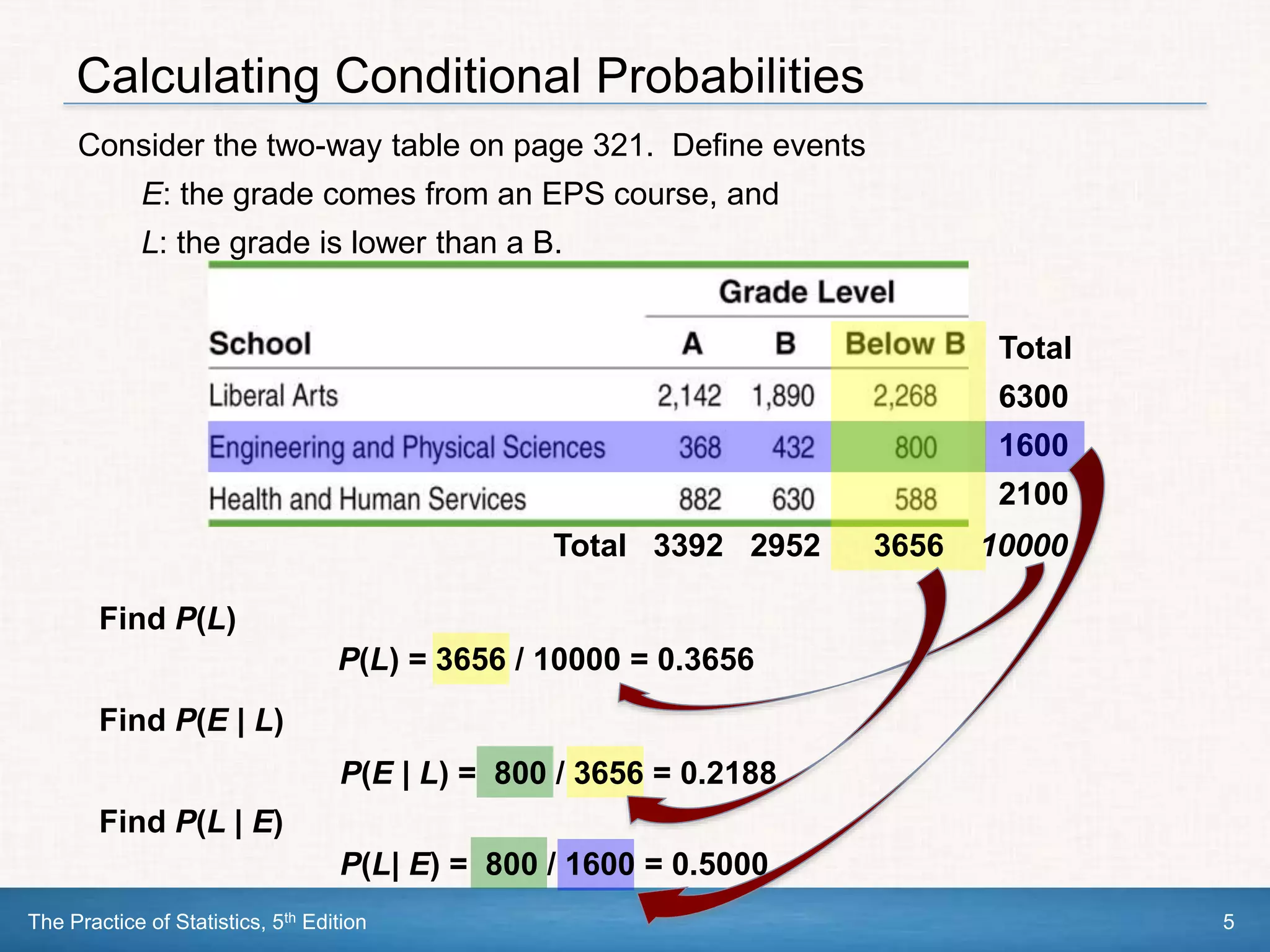
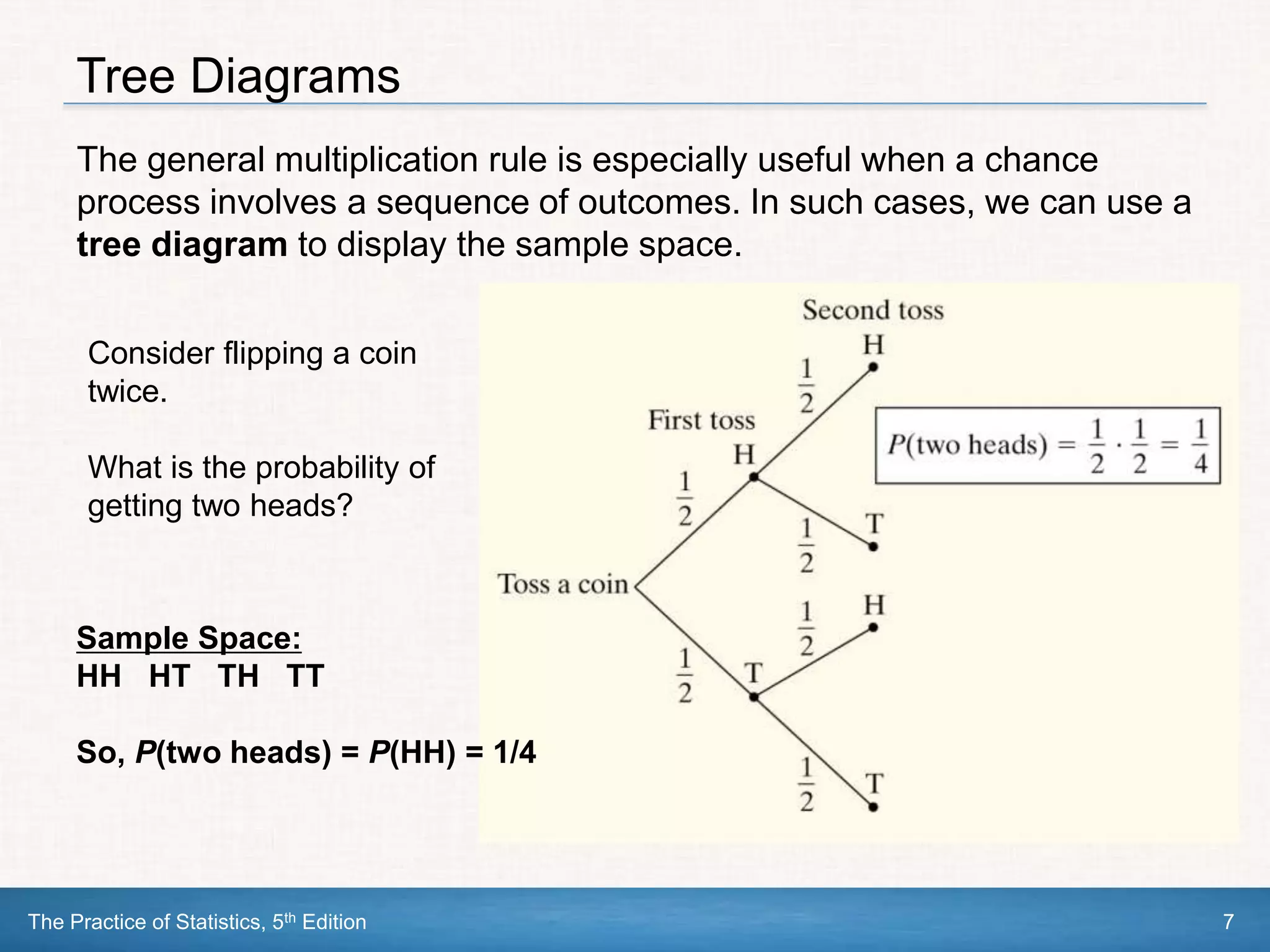
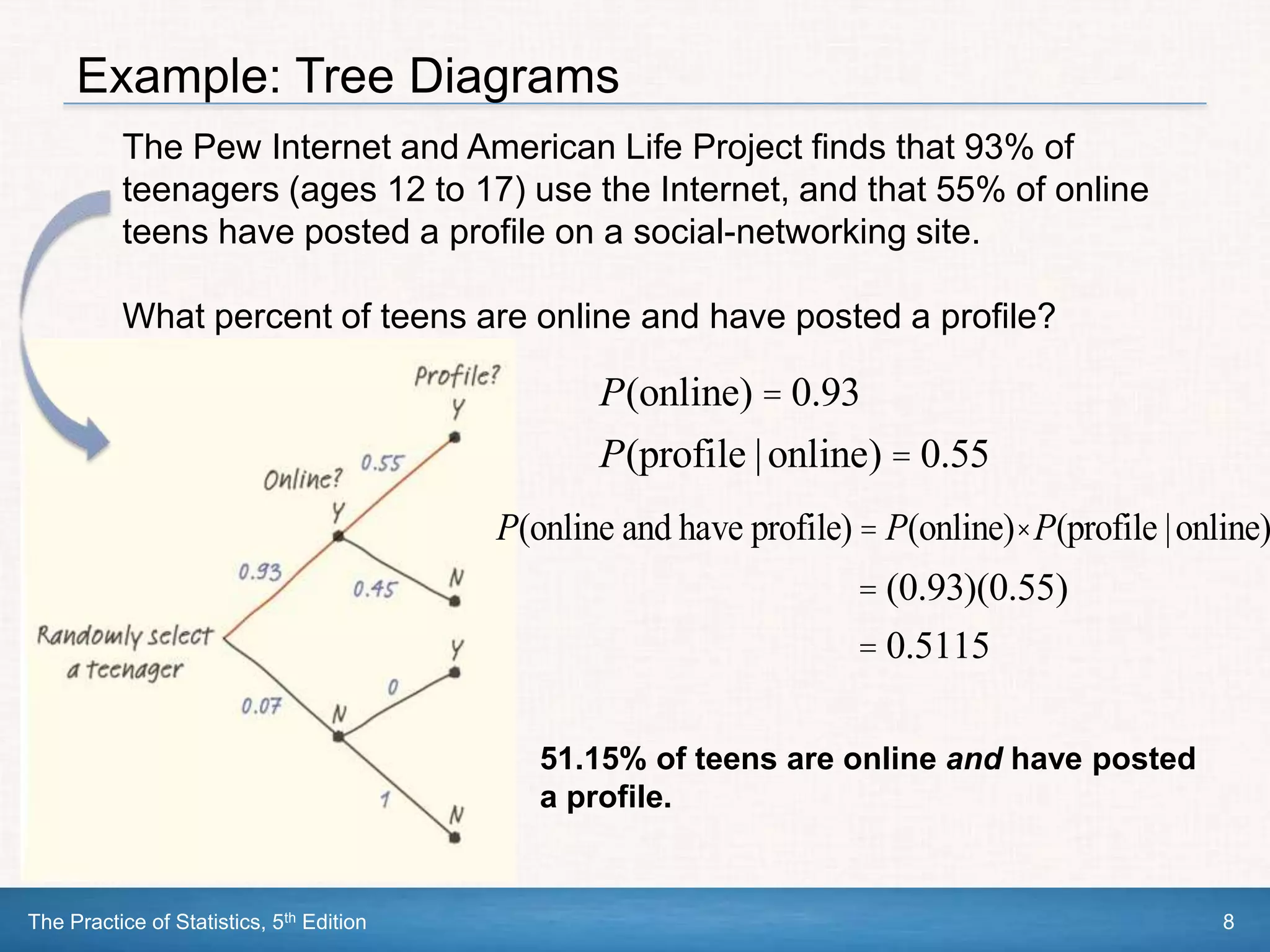
This document section discusses conditional probability and independence. It defines conditional probability as the probability of one event occurring given that another event is already known to have occurred. The general multiplication rule for calculating probabilities involving two or more events is introduced, as well as using tree diagrams to model chance processes. Events are defined as independent if knowing one event occurs does not impact the probability of the other occurring. The multiplication rule is simplified for independent events. Examples are provided to demonstrate these concepts.