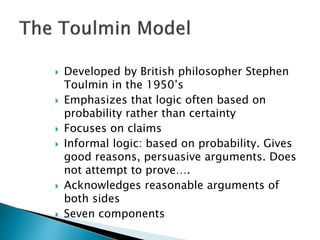
This document discusses Stephen Toulmin's modern argument model from the 1950s. [1] It focuses on informal logic and probability rather than certainty. [2] The model has seven components: claim, data, warrant, backing, rebuttal, qualifier, and grounds. [3] The enthymeme outlines the core components of claim (main point), data (evidence/reasons), and warrant (unstated assumption connecting data and claim).