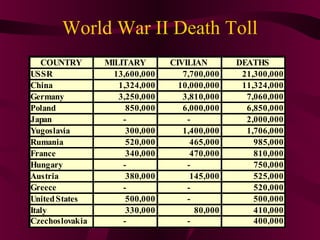
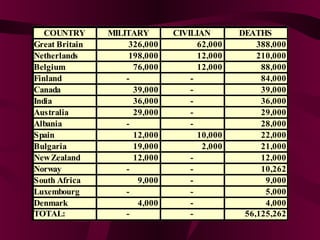
The document summarizes the rise of totalitarian regimes in the early 20th century and their impacts. It describes how the Great Depression led to the rise of dictators like Stalin, Mussolini, and Hitler who gained power by promising economic recovery and strong leadership. It then outlines some of the policies and impacts of these totalitarian regimes, including communism in the Soviet Union, fascism in Italy, and Nazism in Germany. Finally, it provides data on the enormous death toll from World War II, with over 50 million military and civilian deaths globally.