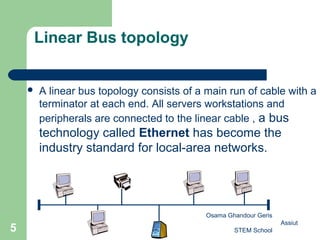
This document outlines an agenda for a class on network topologies and access methods. The class will include demonstrations by the teacher on different network topologies like bus, star, ring and tree. Students will participate in activities where they research and present information on various topologies. The teacher will also demonstrate network operating systems and different access methods like CSMA/CD, token passing and demand priority. Students will watch videos and ask questions about these topics. They will be assigned homework to summarize and compare peer-to-peer and client-server networks.