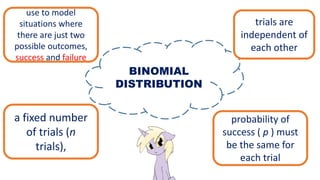
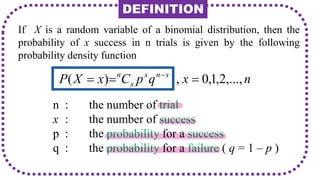
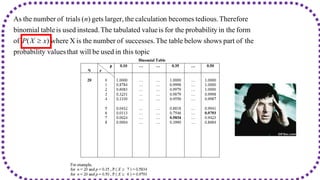
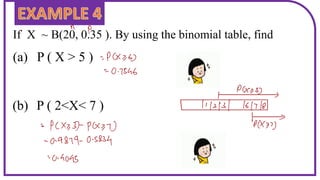
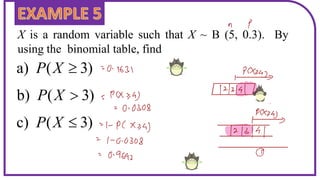
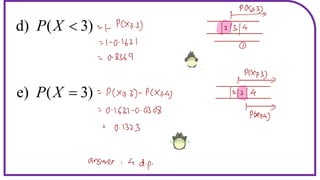
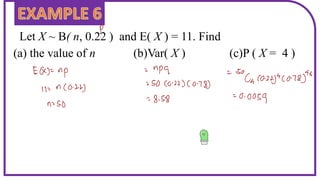
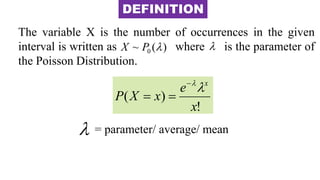
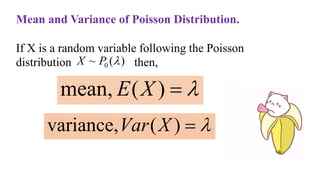
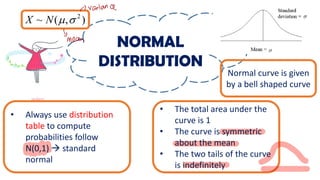
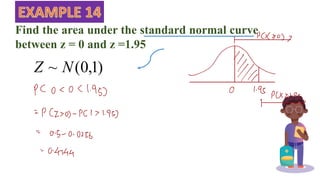
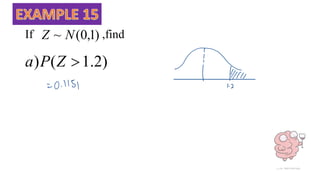
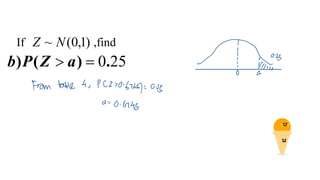
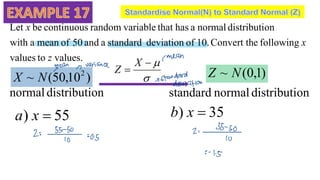
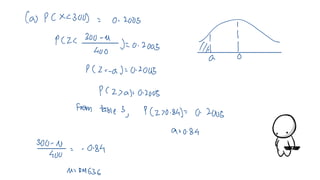
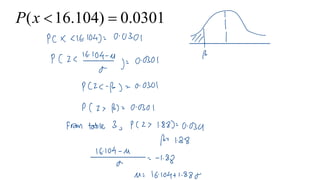
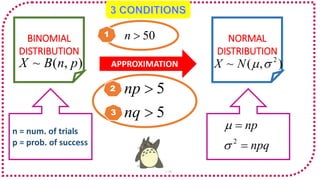
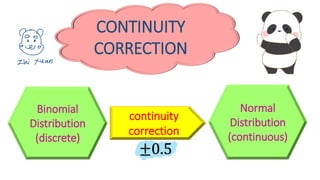
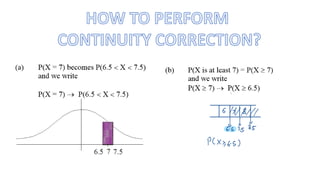
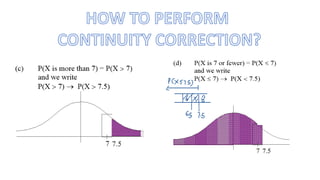
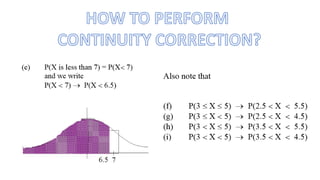
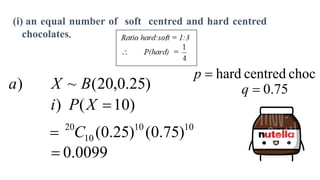
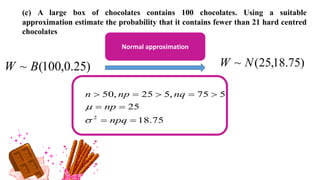
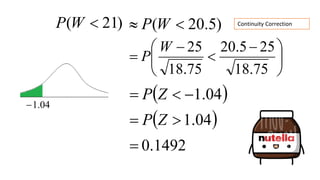
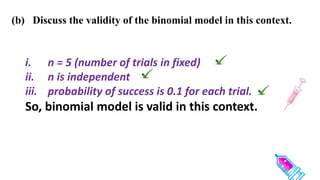
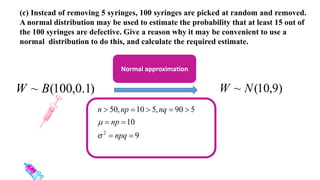
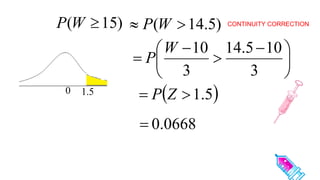
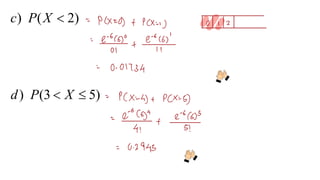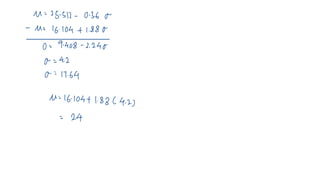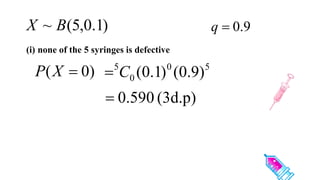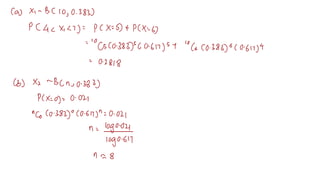This document discusses probability distributions including the binomial, Poisson, and normal distributions. It provides examples of how to identify each distribution and calculate probabilities using the appropriate formulas. For the binomial distribution, it explains how to find the mean and variance. For the Poisson distribution, it defines the parameter λ and gives the formulas for mean and variance. For the normal distribution, it introduces using the standard normal distribution and converting between z-scores and the original distribution parameters. The document also demonstrates solving several problems using the probability tables or formulas for each distribution type.