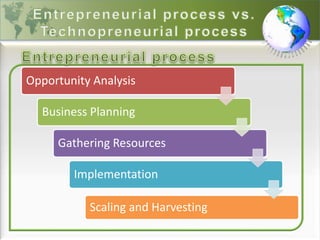
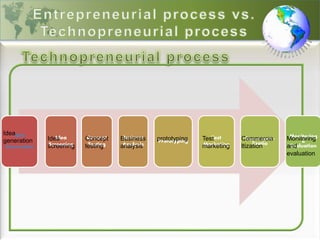
1) The document defines entrepreneurship, intrapreneurship, and technopreneurship. Technopreneurship refers to entrepreneurs who use technology as the driving factor in transforming resources into goods and services.
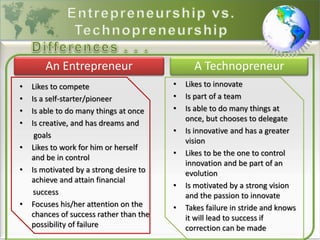
2) The differences between entrepreneurs and technopreneurs are discussed, with technopreneurs being more focused on innovation and technological changes.
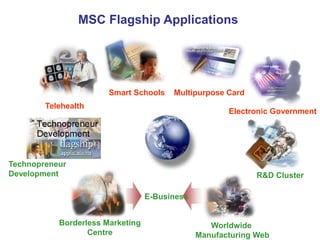
3) The development of technopreneurship in Malaysia is discussed, with initiatives by the Malaysian government starting in 1996 to support technology SMEs and launching programs to fund business plans and prototypes.