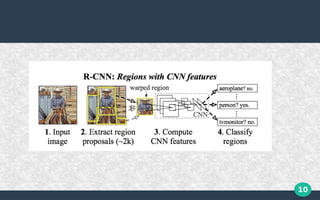
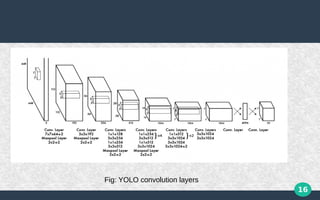
This document discusses object detection using deep neural networks. It describes different types of neural networks including convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which are well-suited for object detection tasks. CNNs use techniques like parameter sharing and sparse connections to recognize visual patterns. Popular object detection algorithms that use CNNs are R-CNN, which proposes regions and classifies them, and YOLO (You Only Look Once), which frames detection as a single regression problem from image to bounding boxes. While very fast, YOLO struggles with small or grouped objects and unusual aspect ratios.