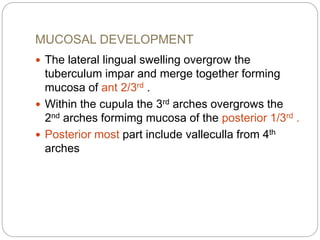
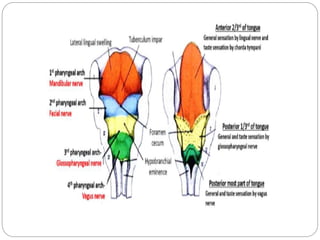
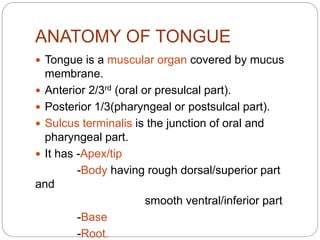
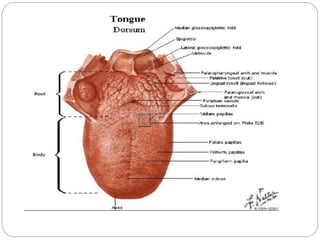
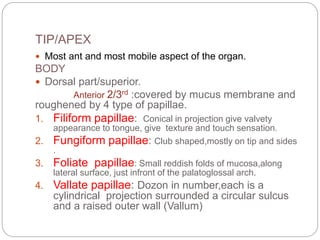
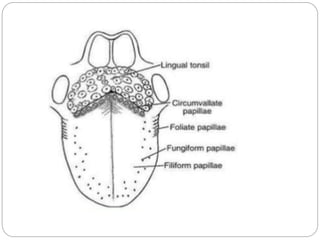
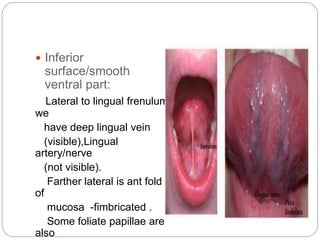
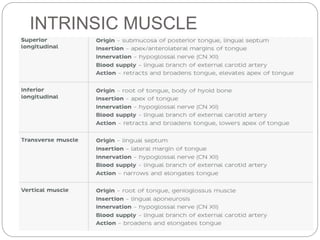
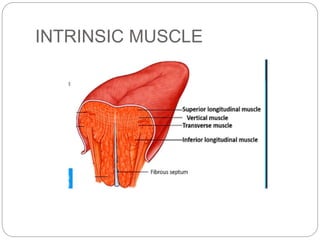
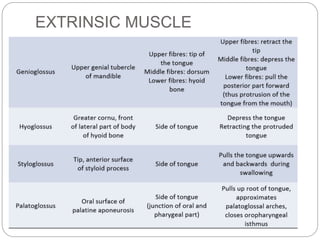
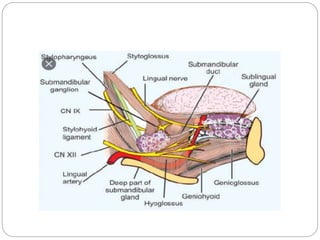
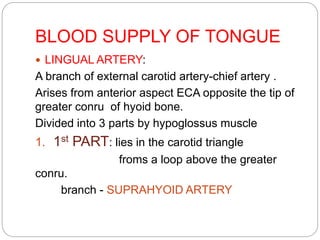
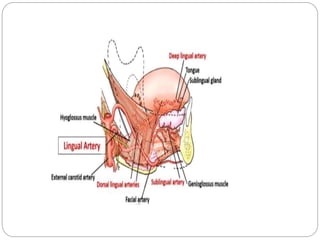
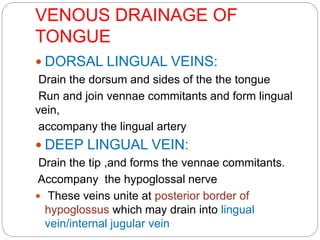
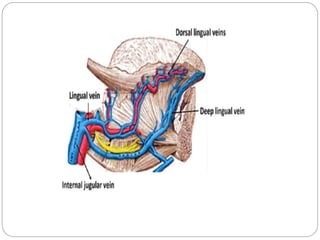
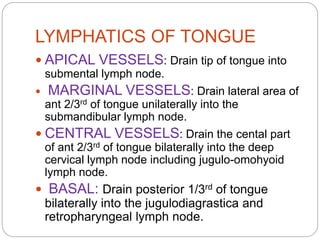
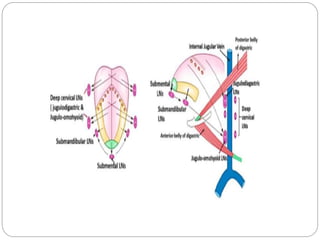
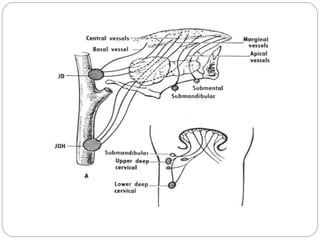
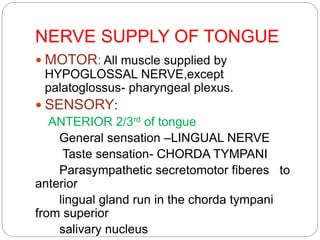
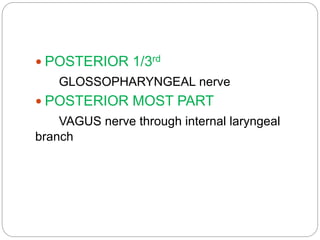
This document provides information on the anatomy of the tongue, including its development, structure, blood supply, lymphatics, innervation and applied anatomy. It describes how the tongue begins developing in the 4th week from the pharyngeal arches and somites. The tongue has intrinsic and extrinsic muscles that control its movement and texture. It discusses the major arteries, veins and nerves involved, and notes that tumors of the posterior 1/3 have a poorer prognosis.