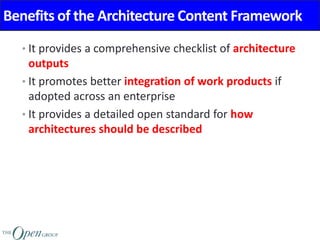
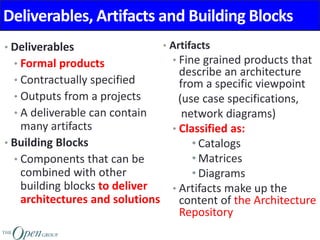
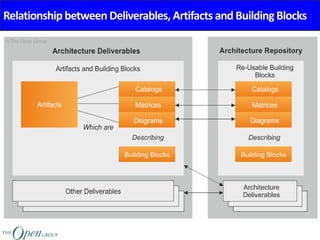
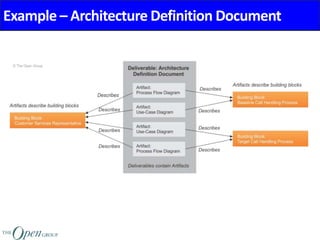
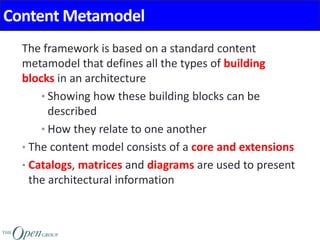
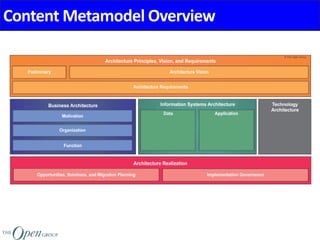
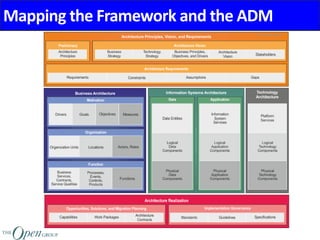
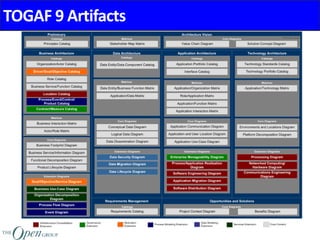
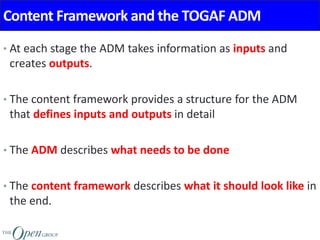
The Architecture Content Framework provides a standardized way to organize and classify architectural outputs. It defines three main categories for work products - deliverables, artifacts, and building blocks. Deliverables are formal project outputs that can contain many artifacts. Artifacts describe architecture from specific viewpoints, and building blocks are reusable components. The framework establishes a consistent structure for architectural work in TOGAF using a content metamodel and mapping to the ADM.