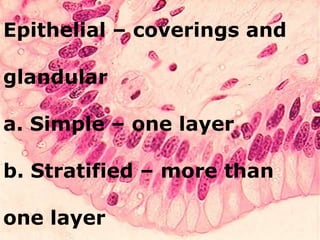
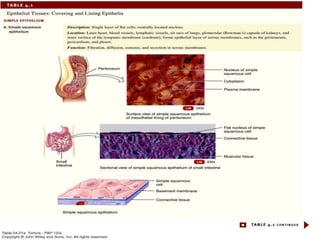
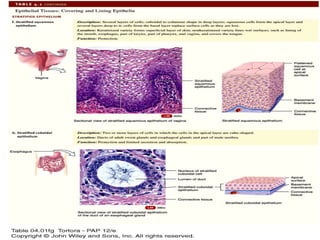
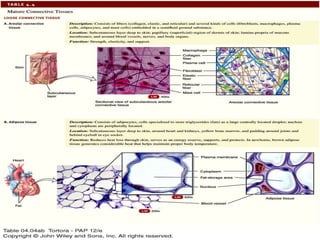
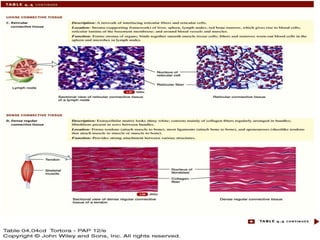
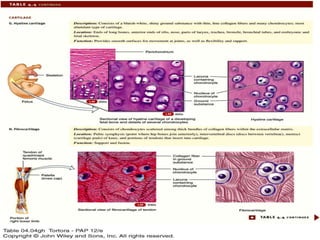
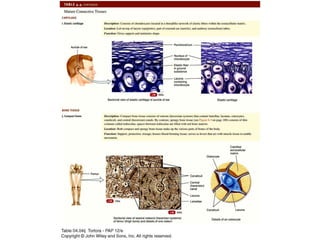
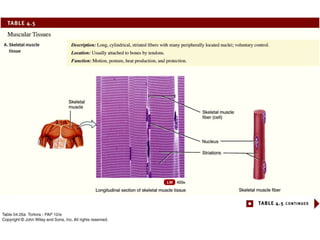
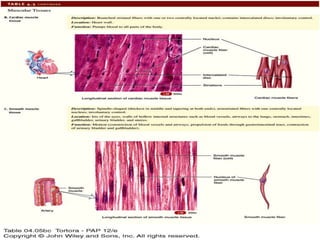
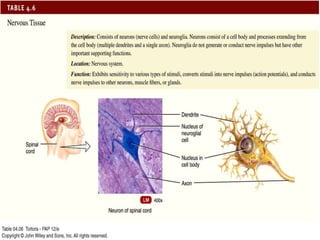
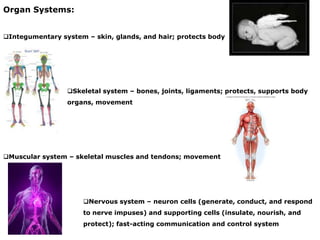
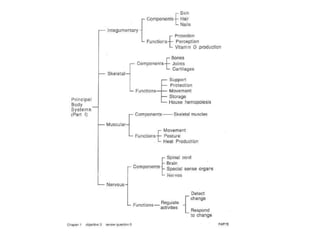
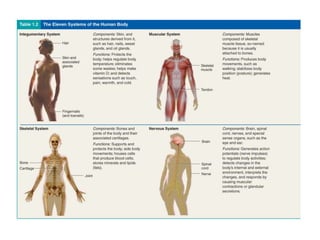
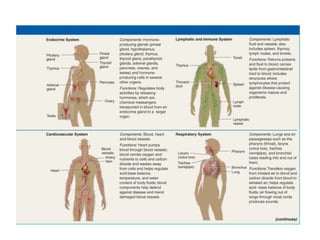
There are four main types of tissues in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue covers and lines body surfaces and forms glands. It can be simple with one cell layer or stratified with multiple cell layers. Connective tissue supports and binds other tissues. It includes connective tissue proper, bone, cartilage, and blood. Muscle tissue allows for movement and includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Nervous tissue facilitates communication in the body.