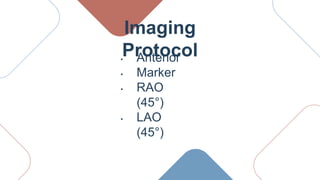
The document provides an overview of thyroid scans, detailing how radiopharmaceuticals like iodine and technetium are used to assess thyroid function and structure. It outlines patient preparation requirements, imaging protocols, and interpretation of uptake patterns to indicate conditions such as hyperthyroidism or potential malignancies. Additionally, it covers the evaluation of thyroid nodules and monitoring procedures after thyroid surgery.