Embed presentation
Downloaded 13 times


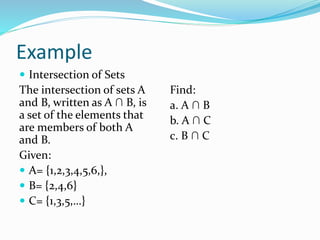



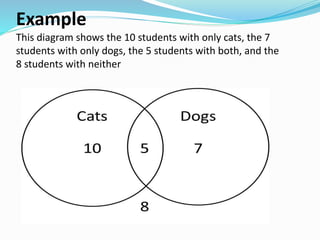

The document discusses objectives for learners across three domains: cognitive, affective, and psychomotor. In the cognitive domain, learners will illustrate set operations like union, intersection, and difference through examples with sets A, B, and C. In the affective domain, learners will discuss real-life applications of well-defined sets and their properties. In the psychomotor domain, learners will create Venn diagrams to represent sets, subsets, and set operations like those showing students with cats and/or dogs.






