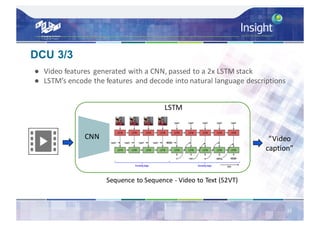
This document summarizes work on automatic video captioning as part of the TRECVid video-to-text task. It discusses the motivation for automatic video captioning due to the exponential growth of multimedia content. It describes the video dataset used, which consisted of over 50k Vine videos that were manually captioned. It then discusses several approaches that participants used for generating captions, including keyframe extraction and spatial cropping. Evaluation metrics included BLEU, METEOR, CIDEr and semantic textual similarity. Results showed that while performance is good, human captions are still superior. Future work may incorporate audio and generate descriptions that consider temporal context.




















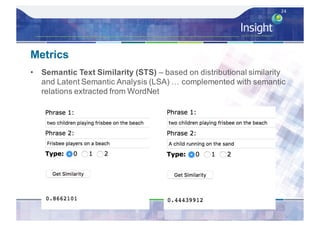
![Direct Assessment (DCU)
• Brings human (AMT) into the evaluation by
crowdsourcing how well a caption describes a video …
rate a caption [0..100]
• Automatically degrade the quality of some manual captions
to rate the quality of the assessors – distinguish genuine
from those gaming the system
• A variation on what is used in the main benchmark in MT,
the Workshop on Statistical Machine Translation (WMT)
• Re-ran this on VTT 2016 submissions, twice, with 0.99
correlation on scores and rankings, showing consistency
25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eccv2018vtt-180917204213/85/The-Video-to-Text-task-evaluation-at-TRECVID-25-320.jpg)









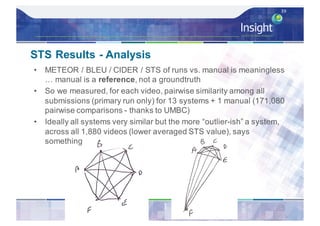
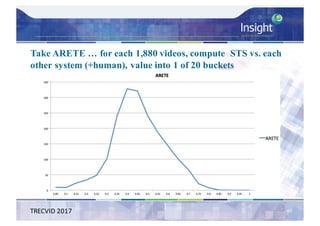
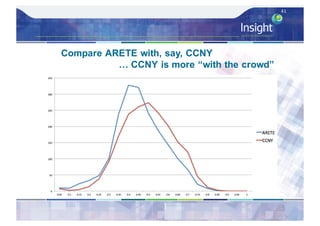
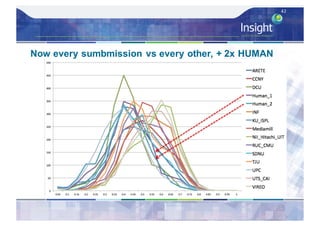
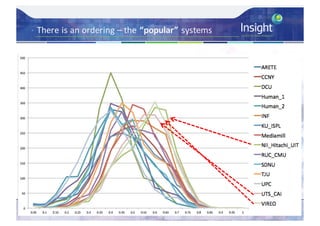
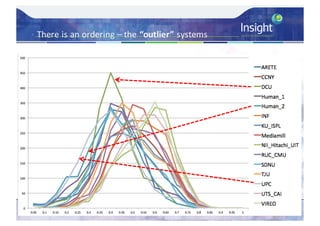
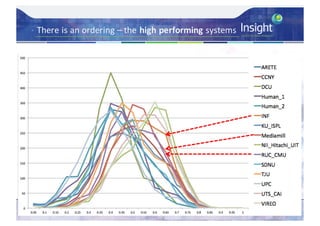

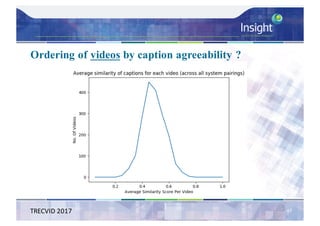

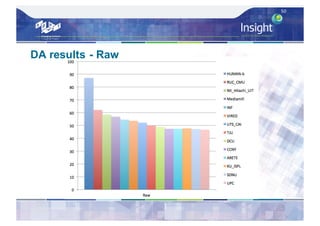
![Direct Assessment Results - Analysis
– Average Direct Assessment score [0..100] for each
system – micro-averaged per caption then overall
average
– Also did average Direct Assessment score per system
after standardisation per individual AMT worker’s mean
and std. deviation score, ordering unchanged
49](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eccv2018vtt-180917204213/85/The-Video-to-Text-task-evaluation-at-TRECVID-49-320.jpg)