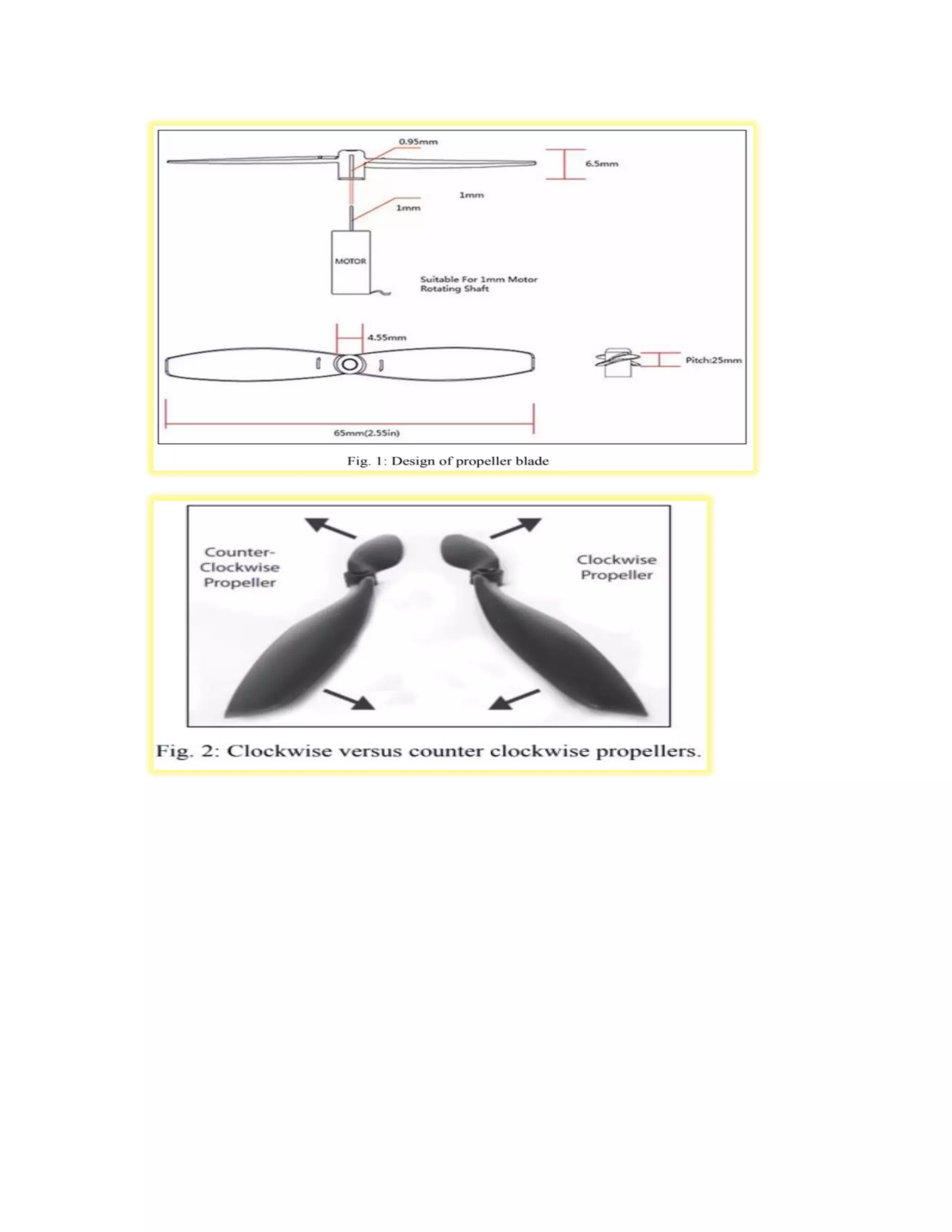
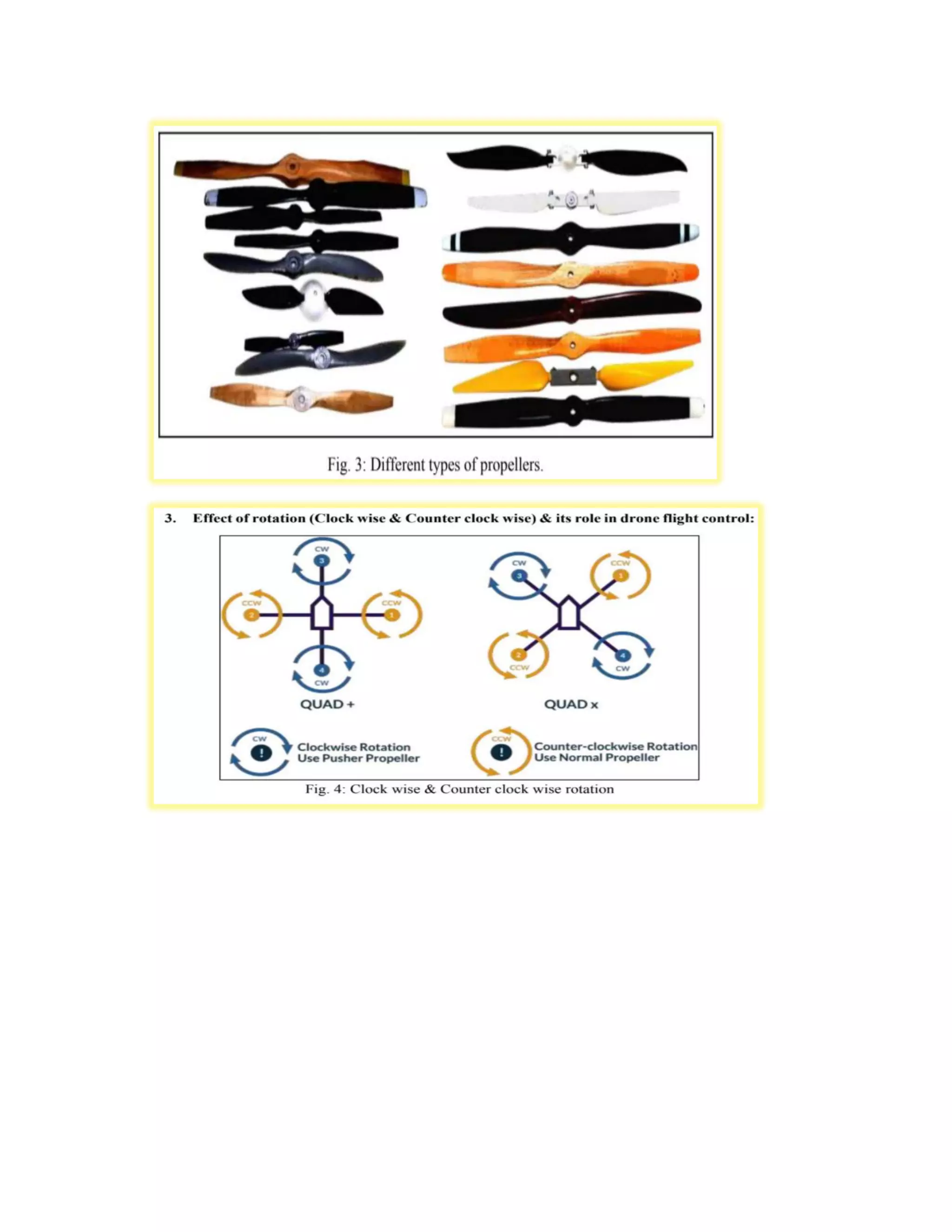
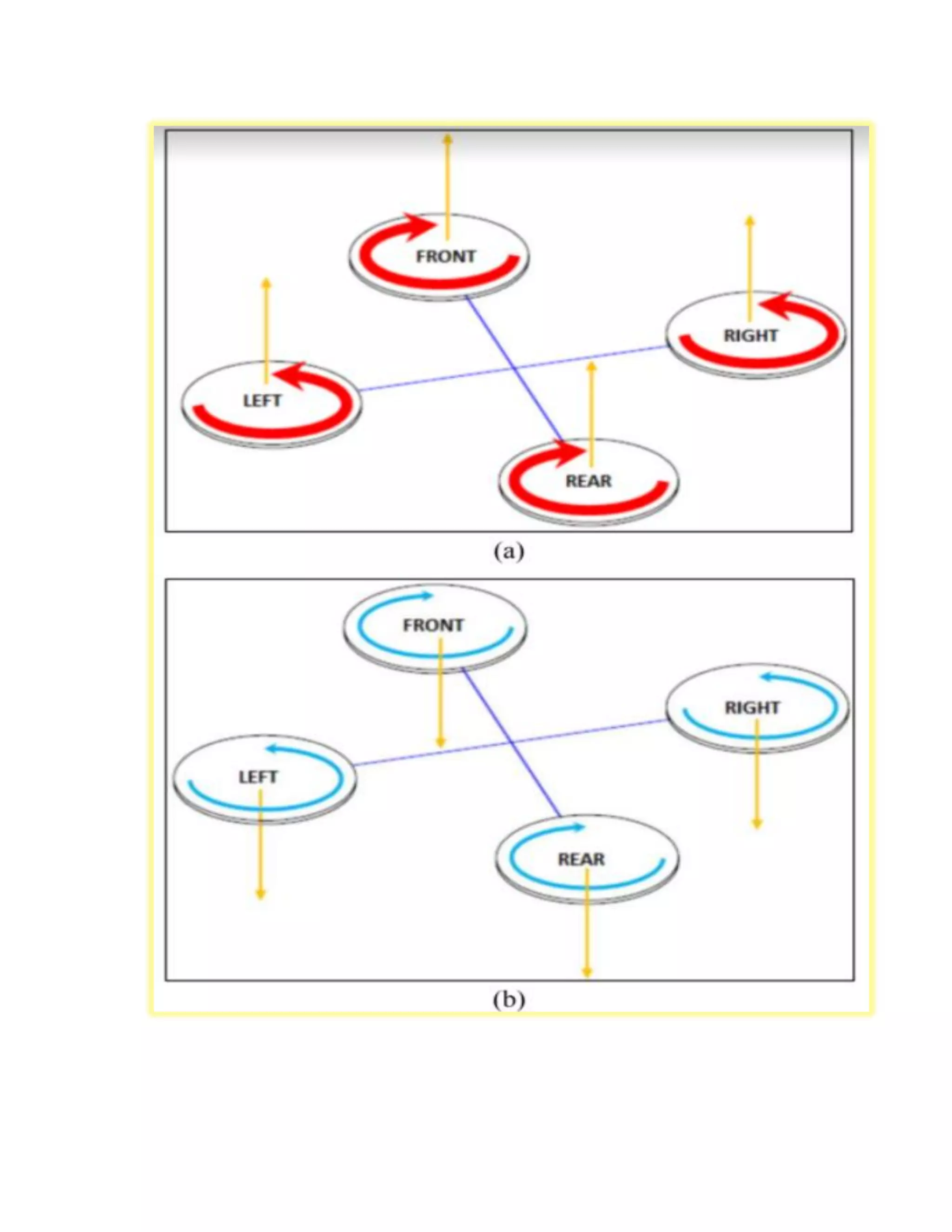
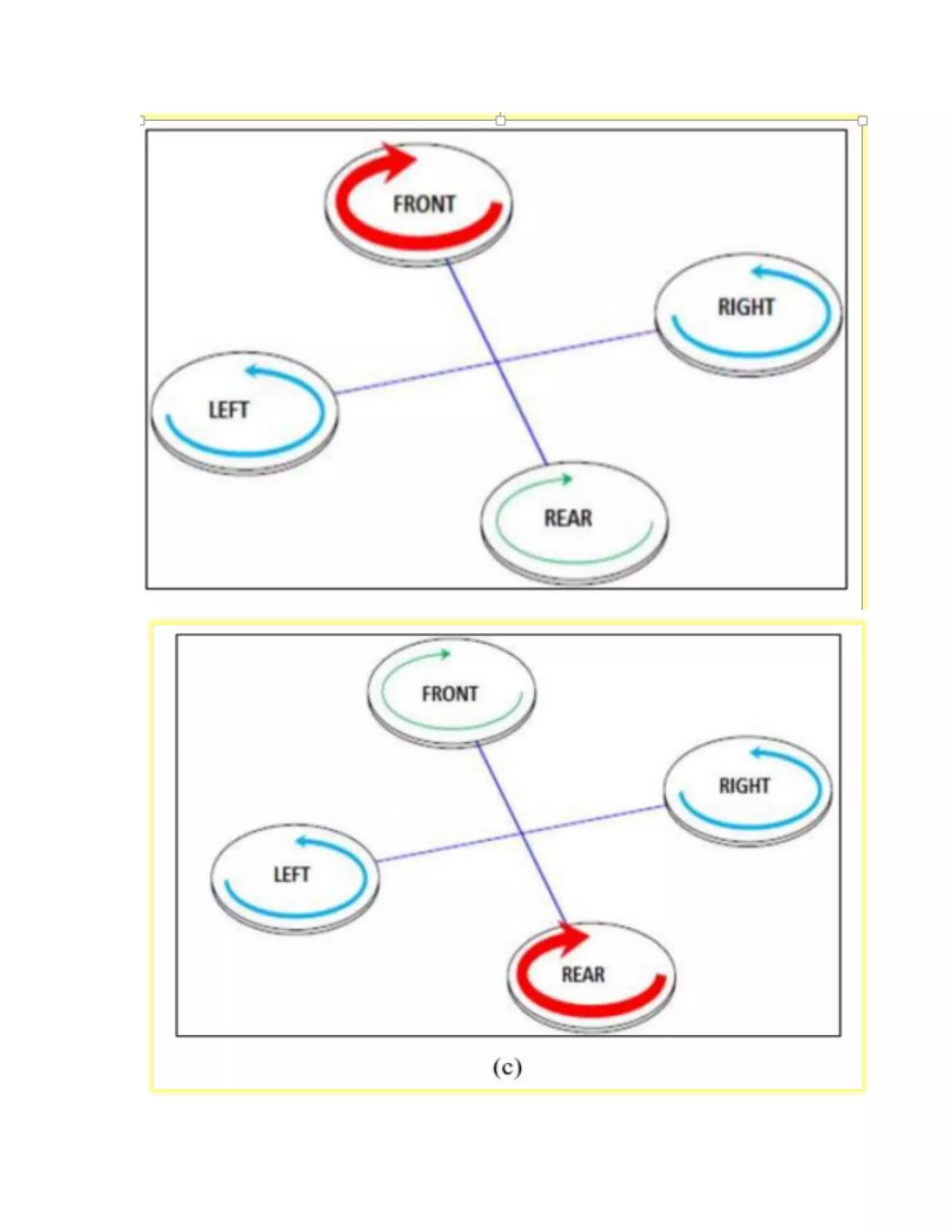
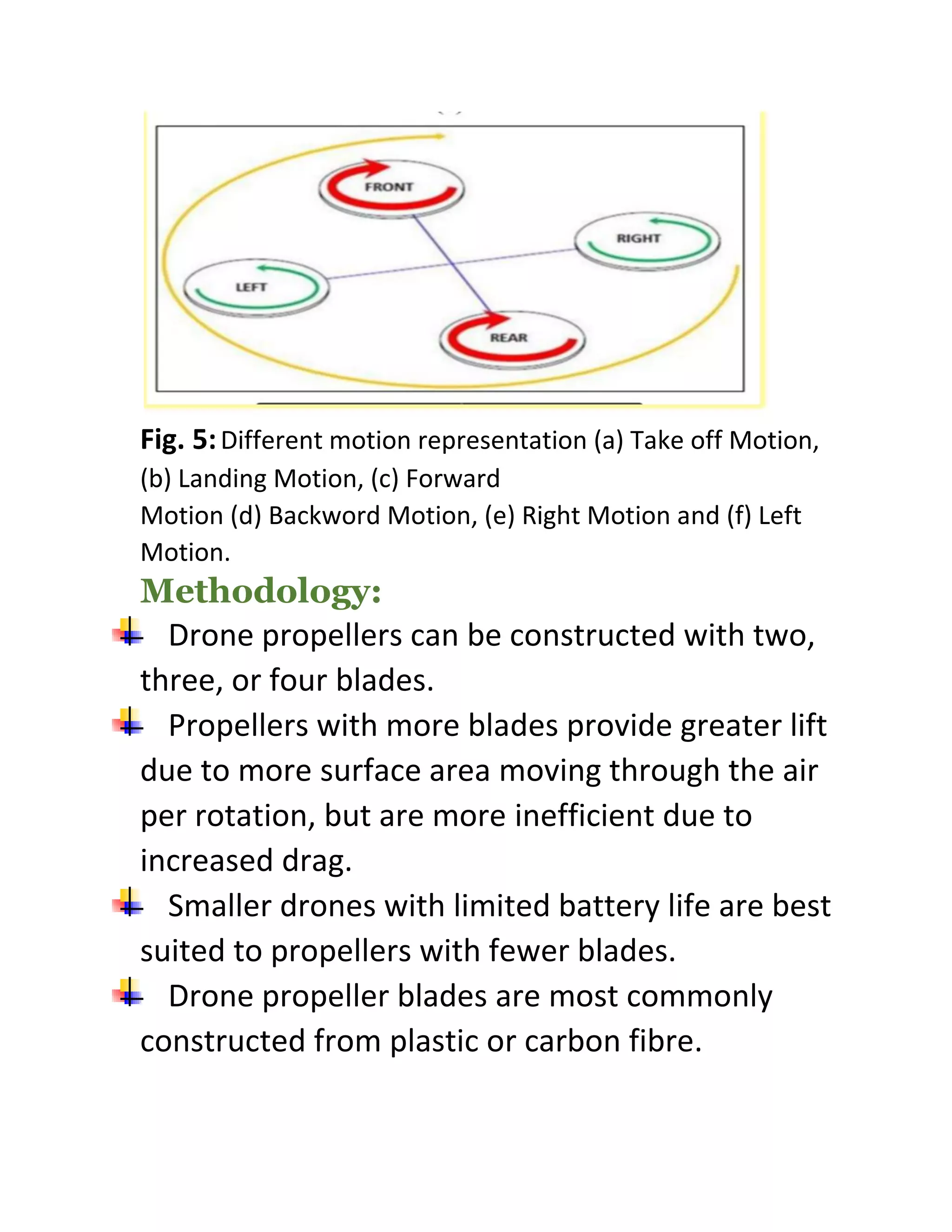
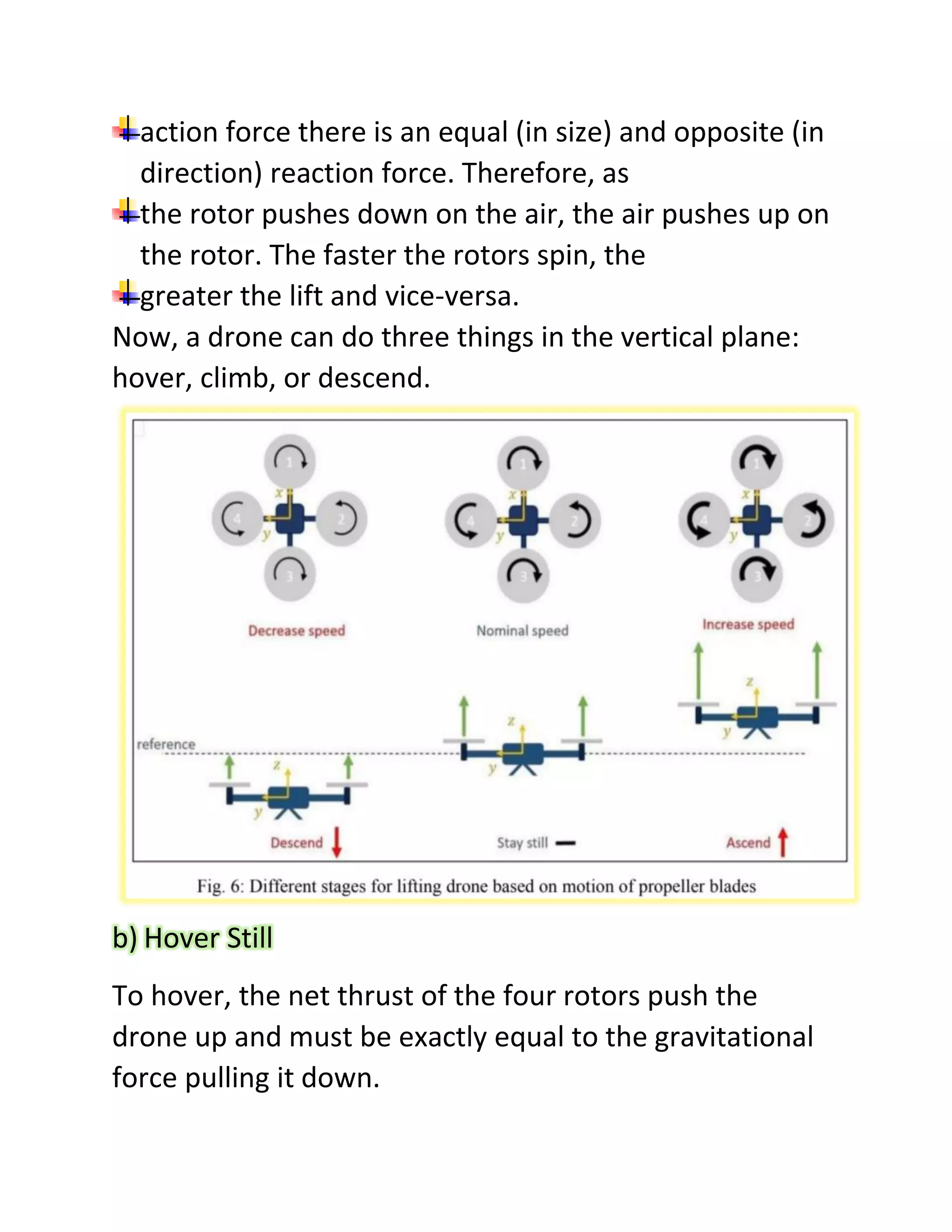
This experiment studied the role of propeller blade rotation in drone flight control. Specifically, it examined the effects of clockwise (CC) and counter-clockwise (CCL) rotation. The experiment tested how varying the speed of individual propeller motors allows drones to maneuver in different ways, such as taking off, landing, moving forward, backward, right, and left. It also explored how propeller blade shape, size, and construction materials like plastic or carbon fiber influence lift generation and flight performance. The results provide insight into how propeller rotation direction controls vertical and horizontal drone motion.