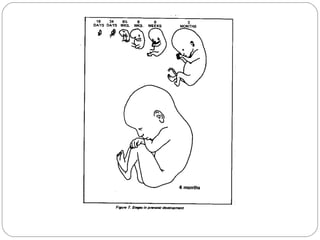
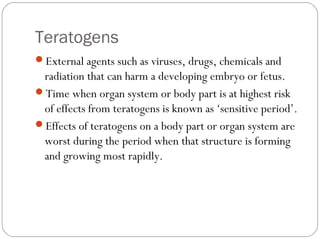
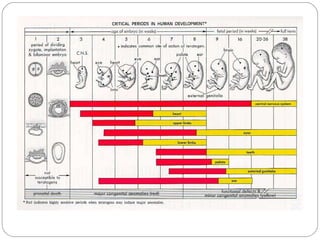
The document outlines the three trimesters of pregnancy, detailing key developmental stages of the fetus and the effects of teratogens on fetal development. It also discusses common conditions experienced by pregnant women, their causes, and recommended treatments, as well as the benefits of exercise during pregnancy. Additionally, it emphasizes the kinesiologist's role in assessing and supporting pregnant women to manage their health and well-being.