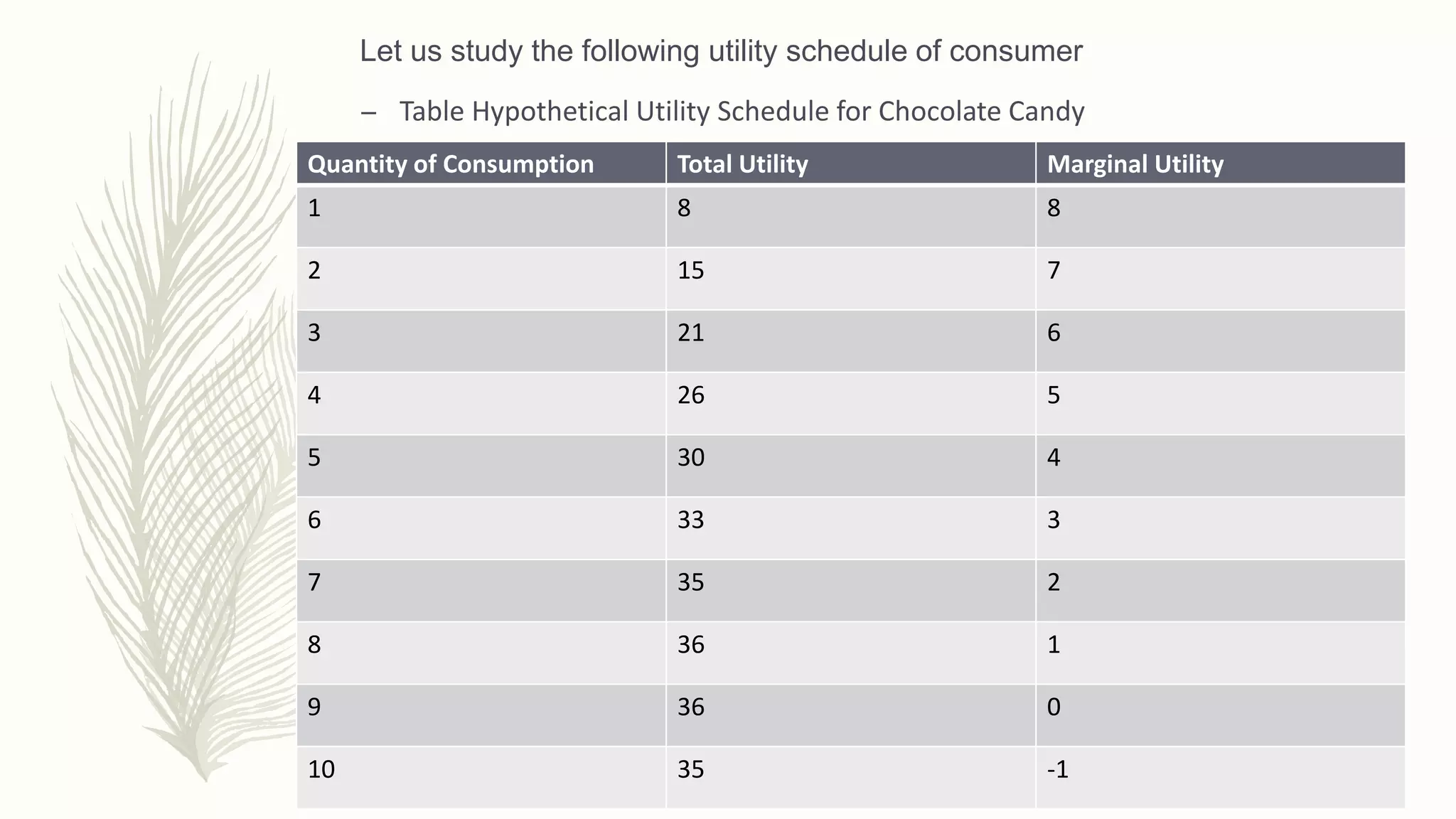
The document discusses the theory of consumer behavior and utility. It explains that utility is a measure of satisfaction derived from consuming goods and services. Total utility refers to the combined satisfaction from consuming units of a good, while marginal utility is the additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit. The document uses a hypothetical utility schedule for chocolate candy to illustrate how marginal utility diminishes as total consumption increases, eventually reaching zero additional satisfaction and then becoming negative. It also describes the law of diminishing marginal utility, which states that the satisfaction from each additional unit of a good consumed tends to decrease as a result of human wants becoming satisfied.