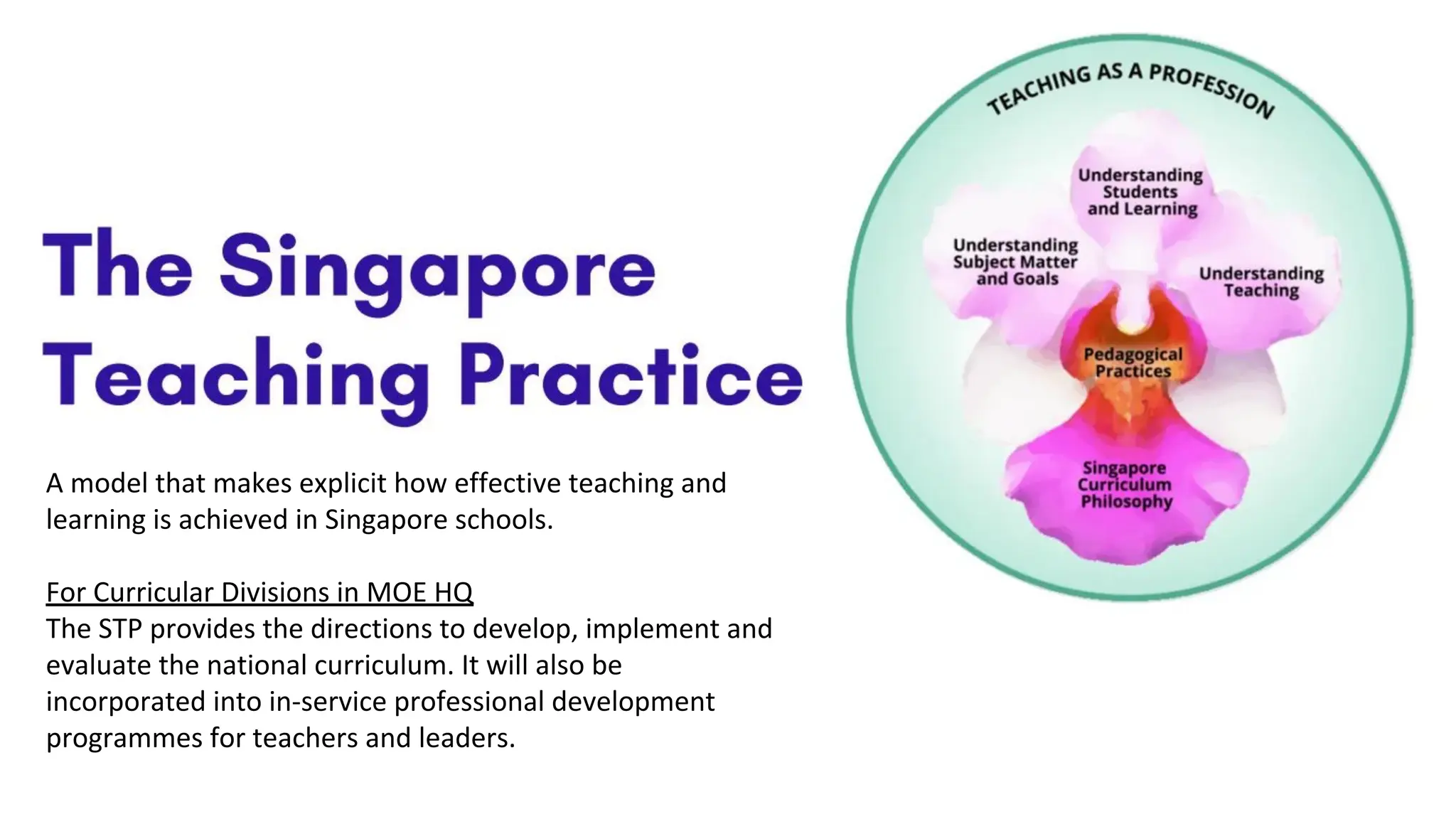
The STP provides directions for developing, implementing, and evaluating Singapore's national curriculum. It consists of 3 key components:
1) The Singapore Curriculum Philosophy which believes in holistic education centered on student well-being and character development.
2) Knowledge Bases which include understanding students, learning, teaching and subject matter to strengthen theory and practice.
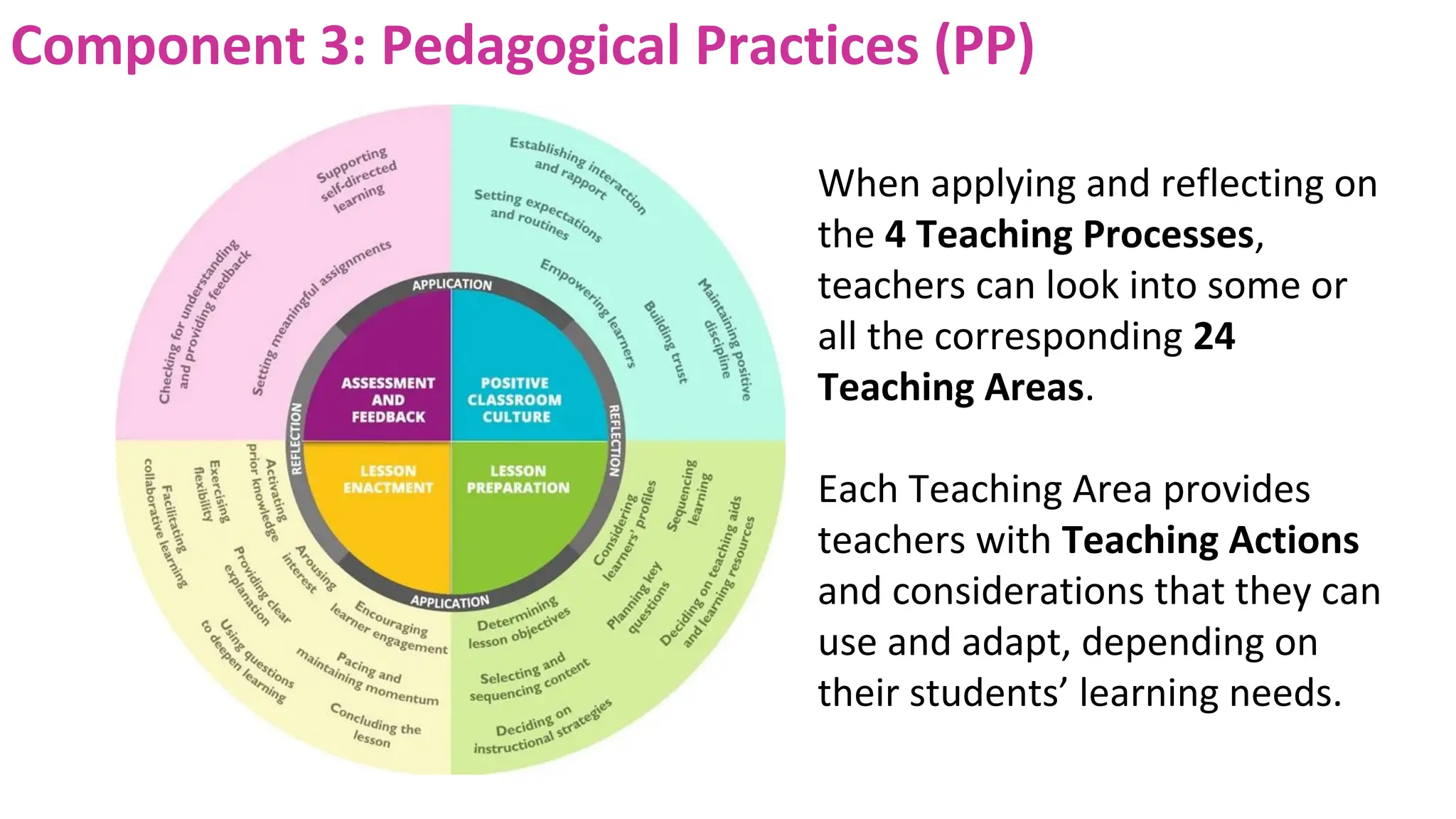
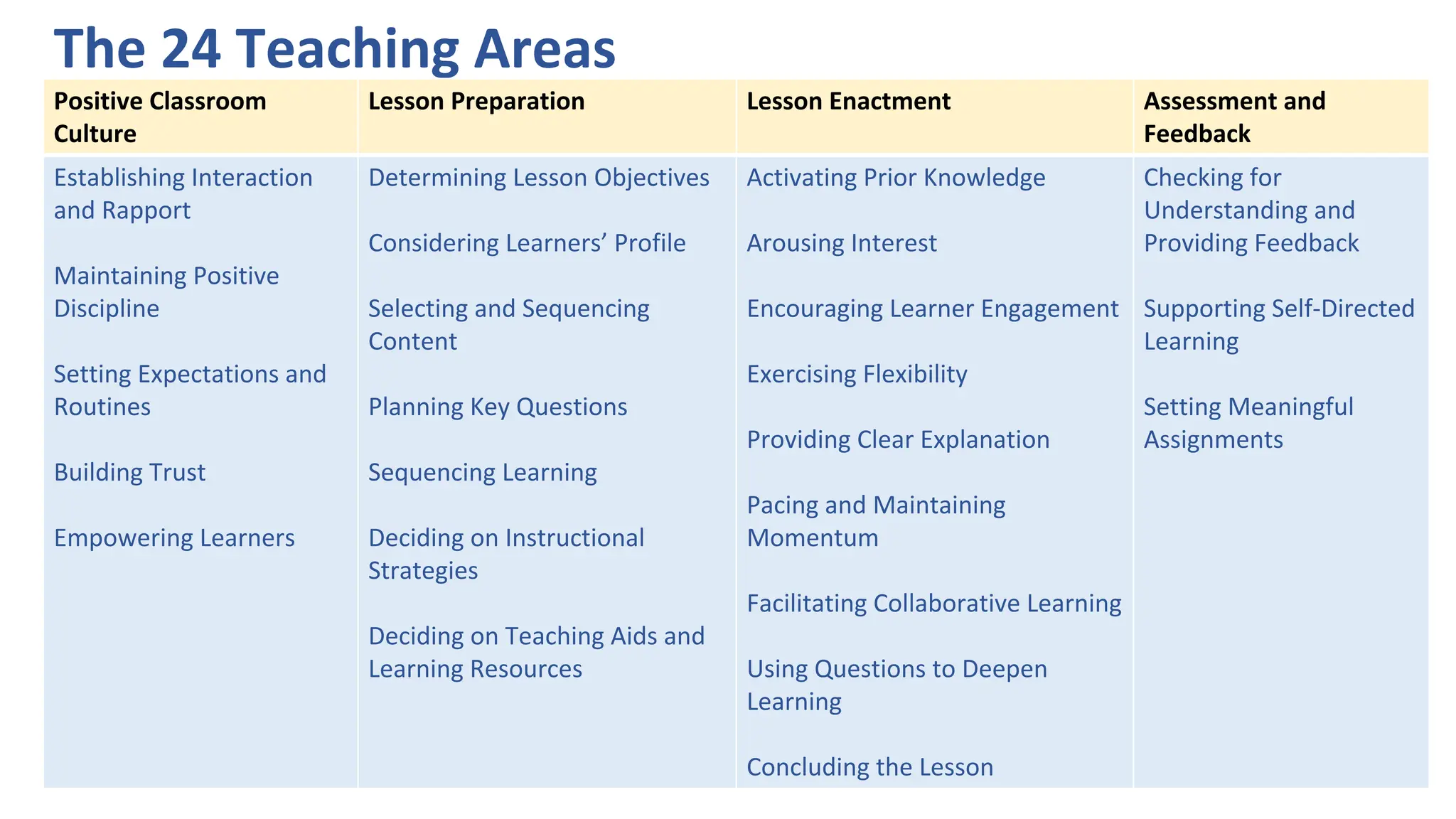
3) Pedagogical Practices which comprise 4 teaching processes: positive classroom culture, lesson preparation, lesson enactment, and assessment/feedback across 24 teaching areas to reflect on teaching.