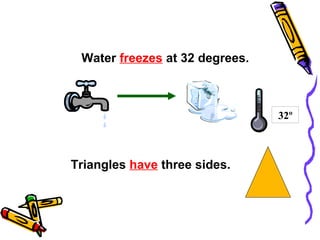
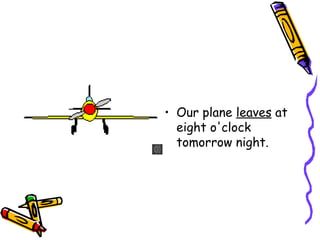
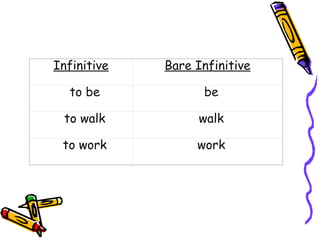
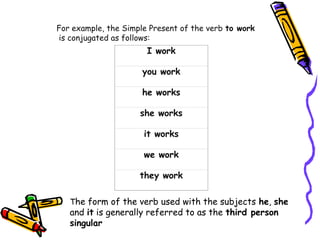
The document discusses the uses of the simple present tense in English. It is used to describe actions that occur regularly or habits. It can also be used to state general truths and describe future events. The simple present is formed by using the bare infinitive of the verb. Auxiliary verbs like do and does are used to form interrogative and negative sentences. The formation of the third person singular is also explained, along with examples of affirmative, interrogative, and negative sentences in the simple present tense.