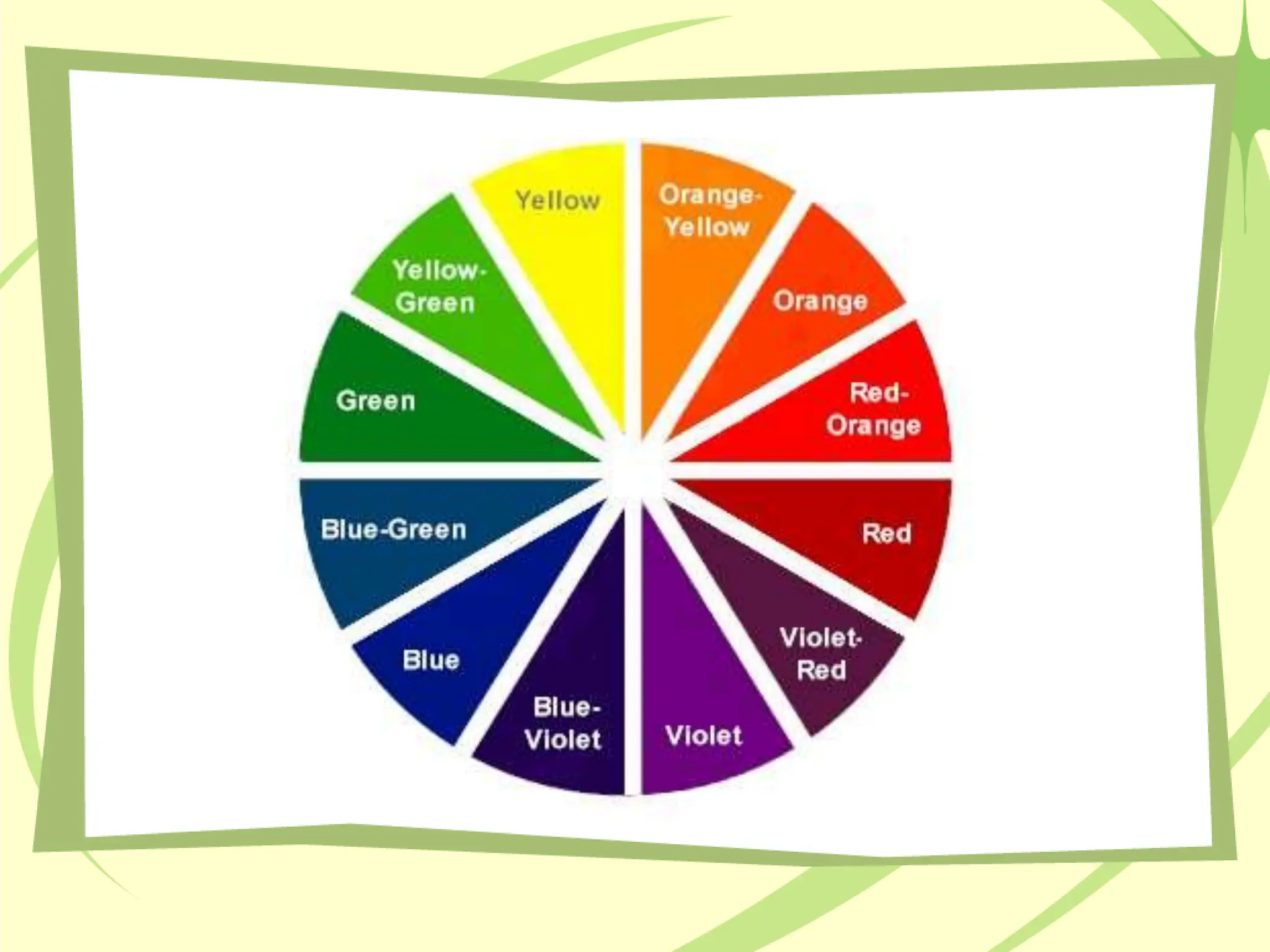
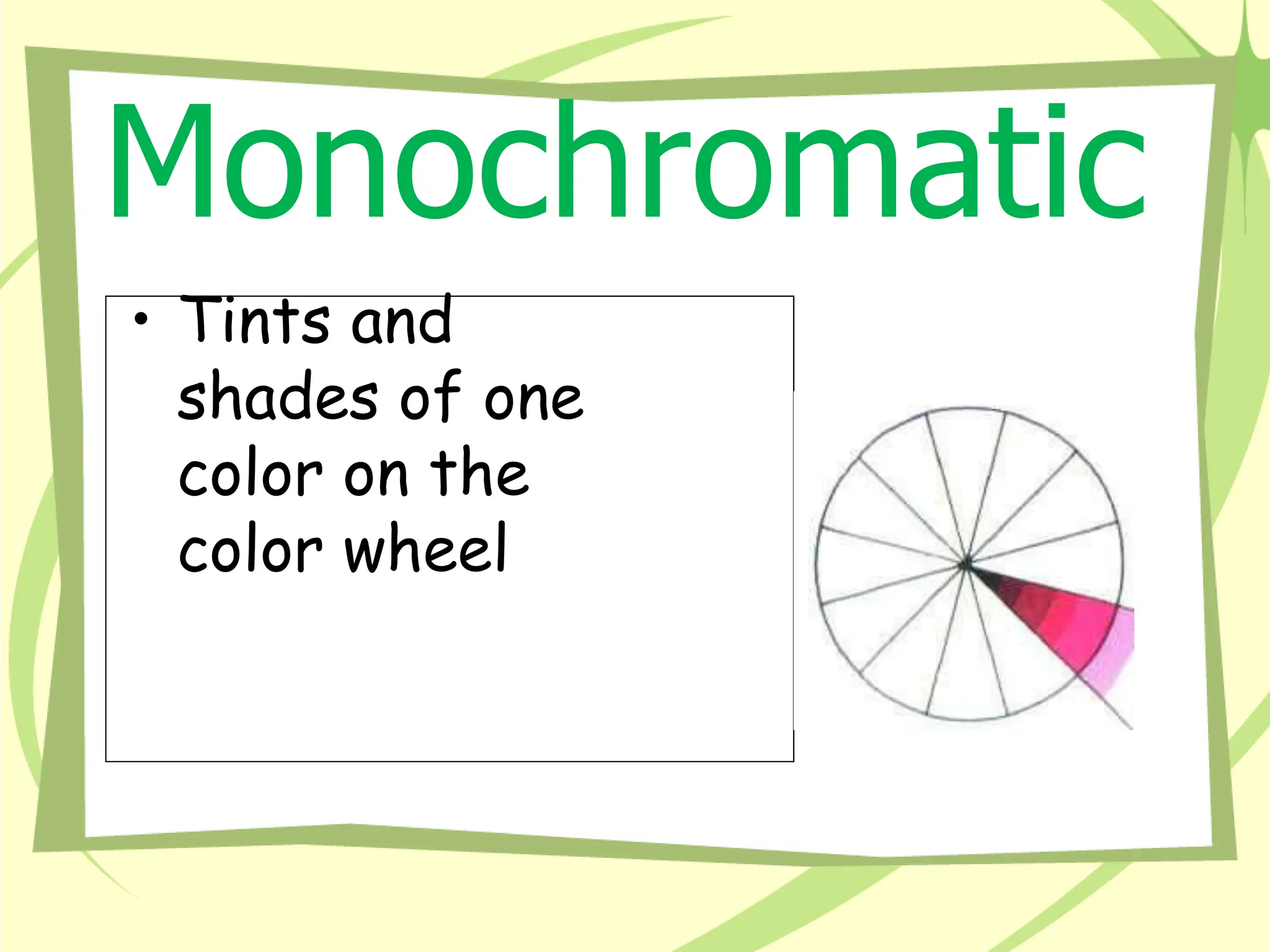
The document discusses the impact of warm and cool colors in design, highlighting their emotional and spatial effects. It outlines various aspects of color, such as hue, intensity, and value, as well as different color schemes like monochromatic, complementary, and triadic. Understanding these principles can enhance room design by creating desired moods and perceptions of space.