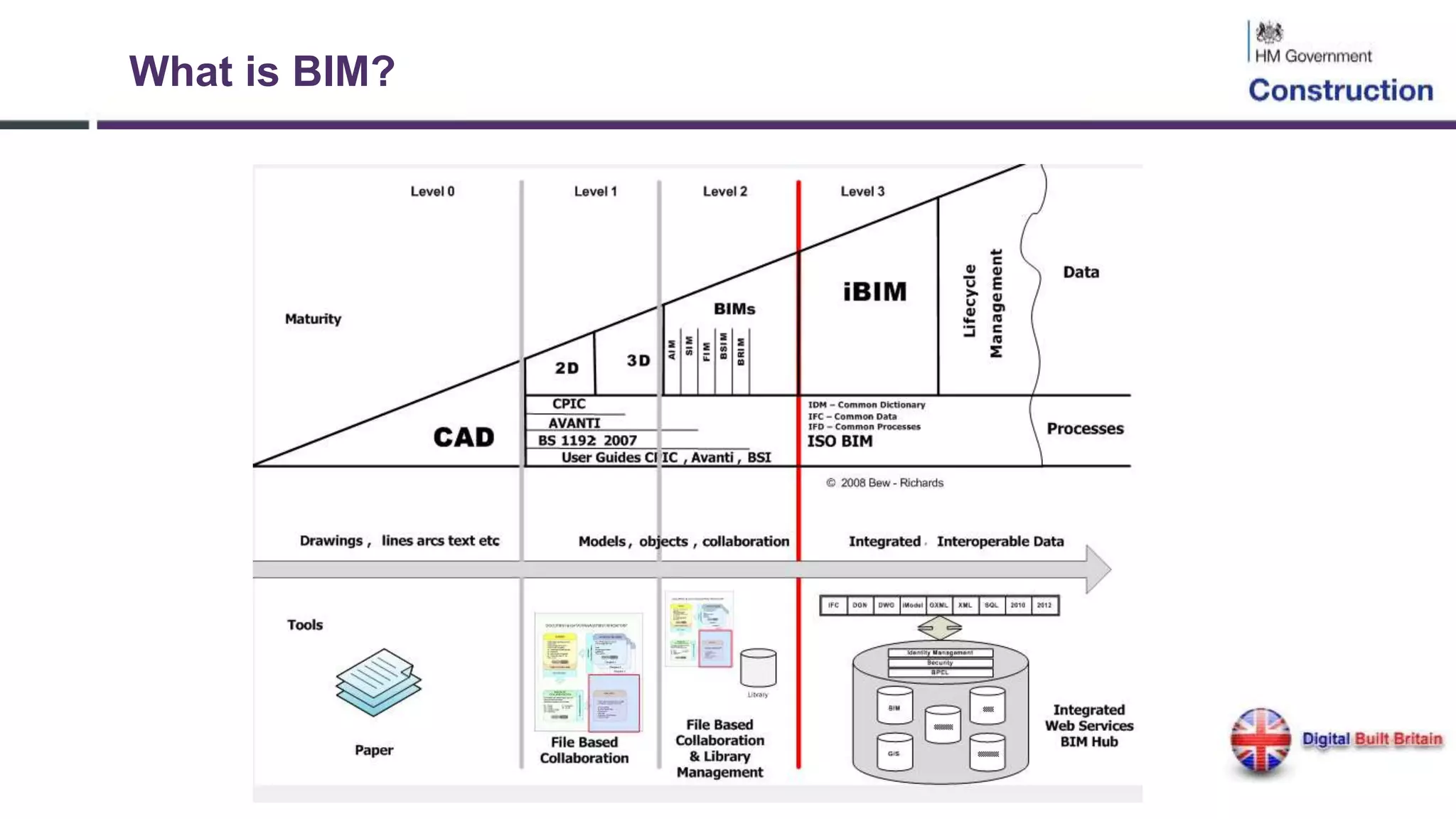
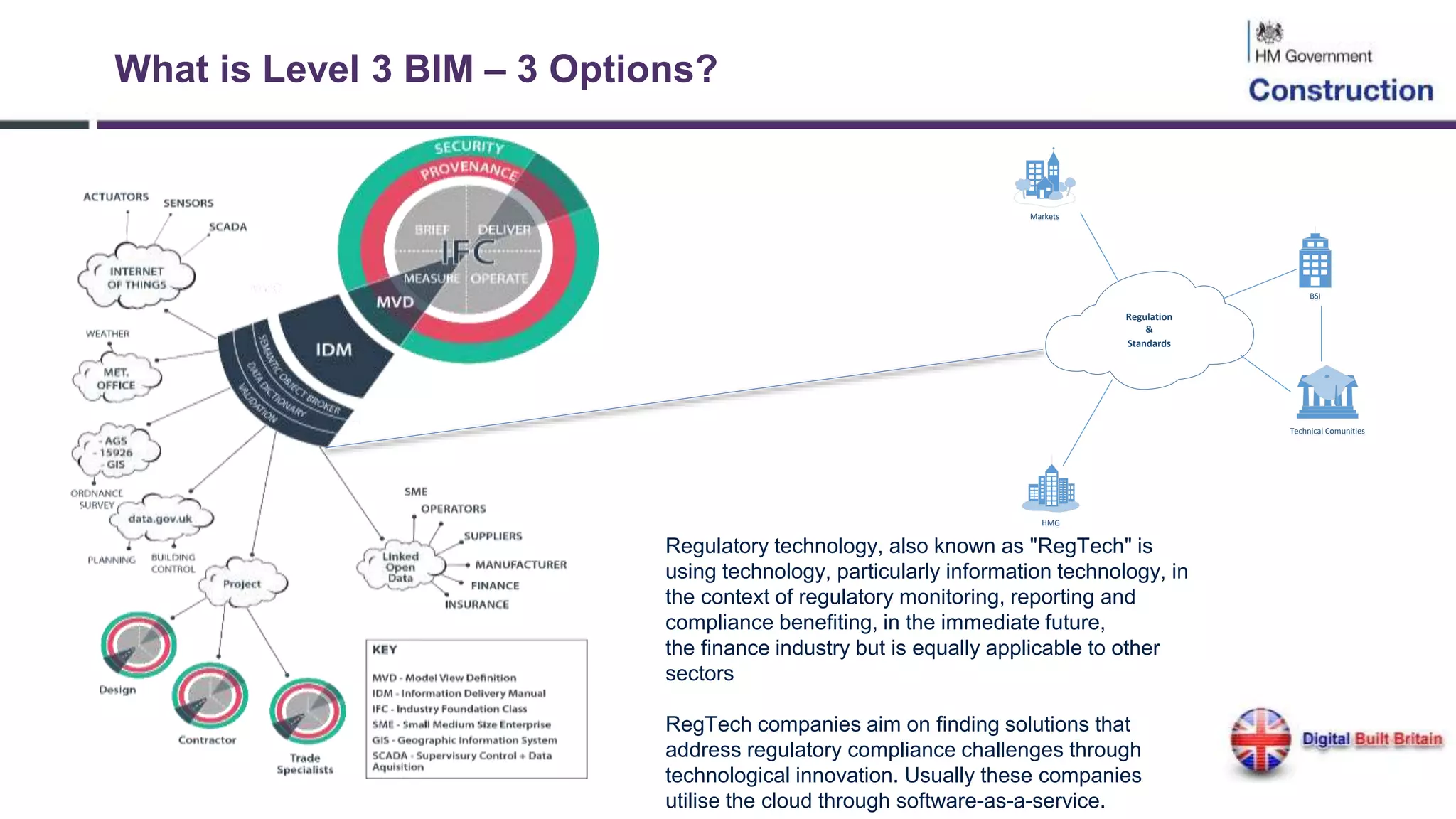
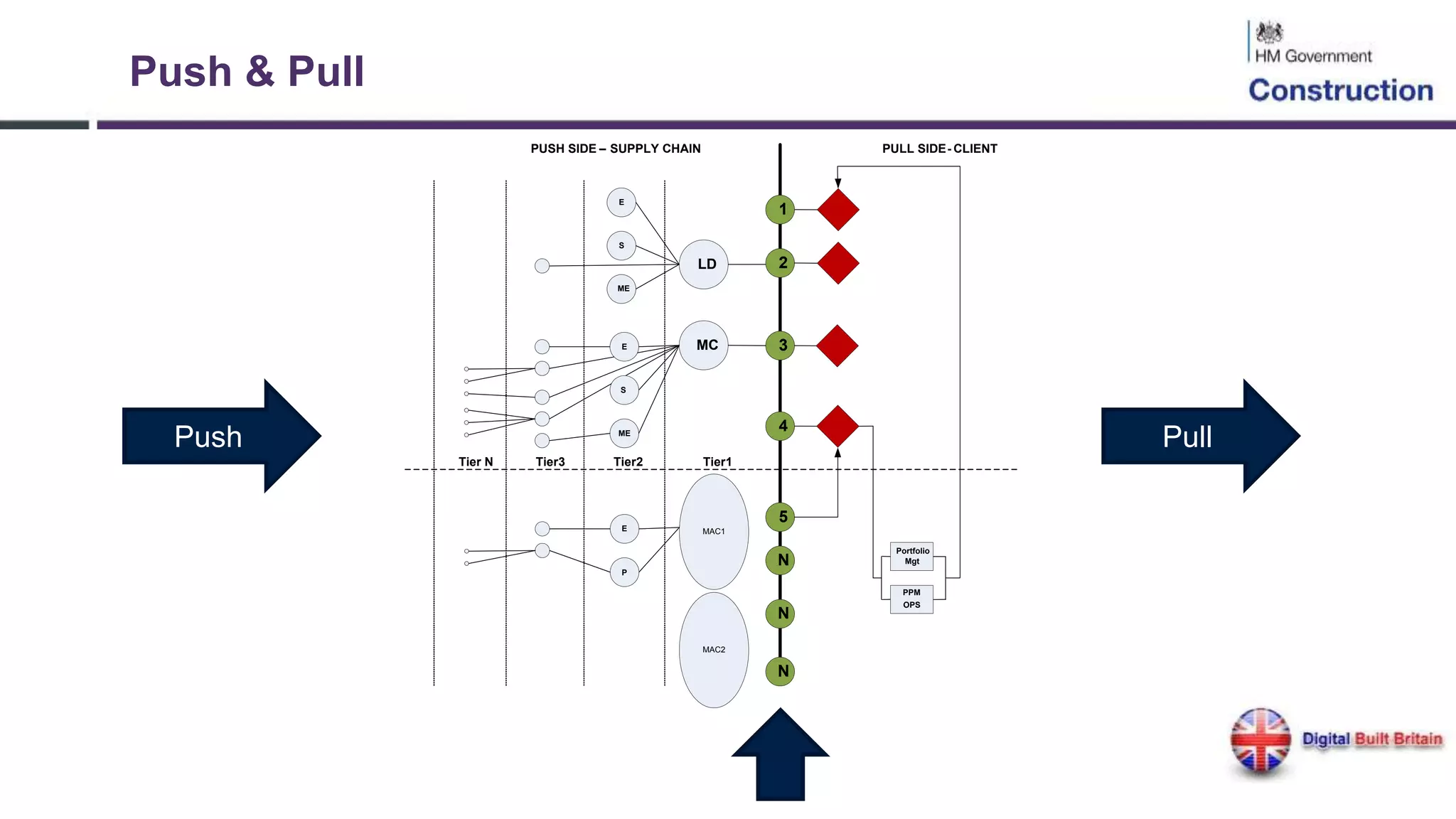
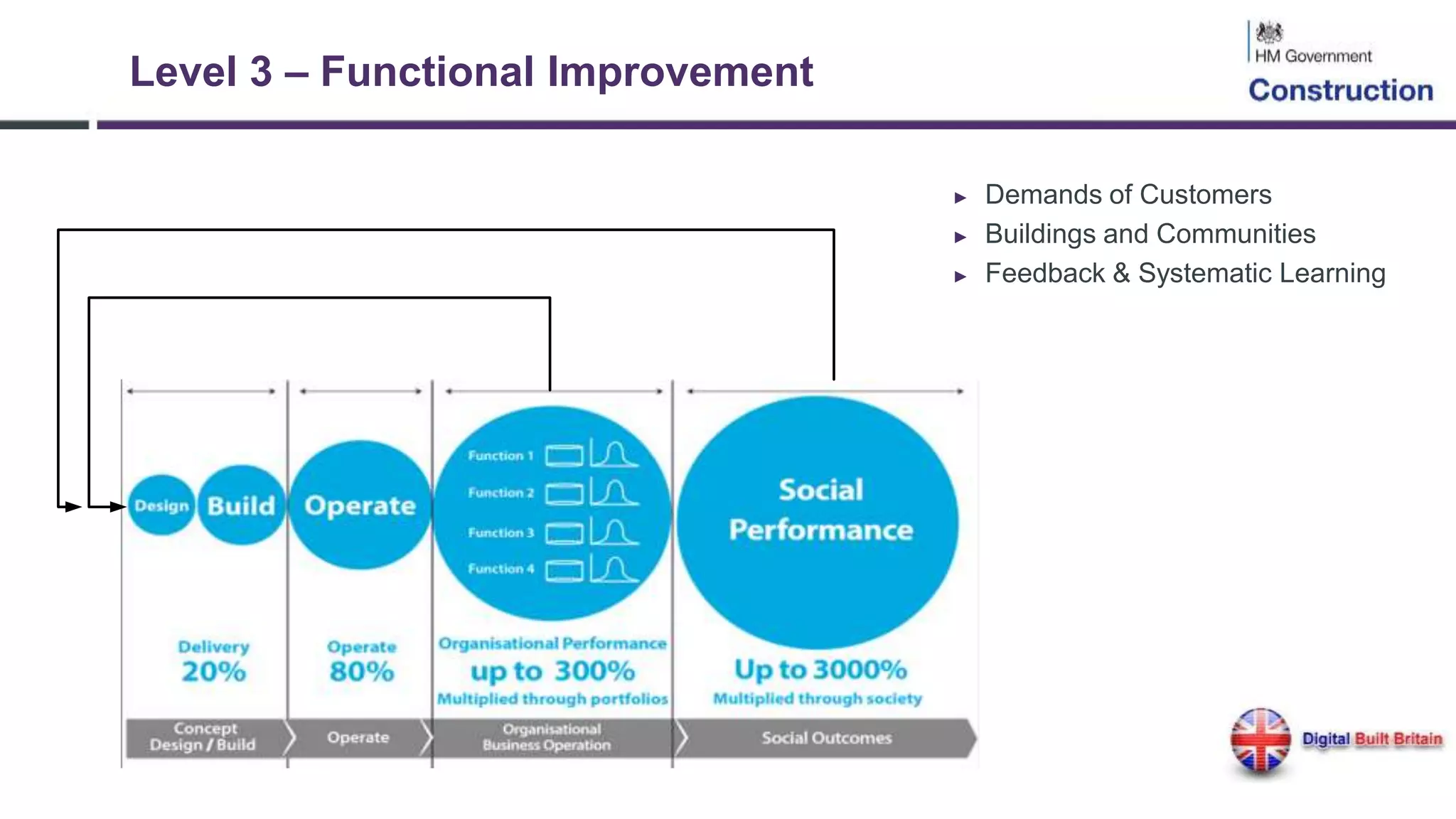
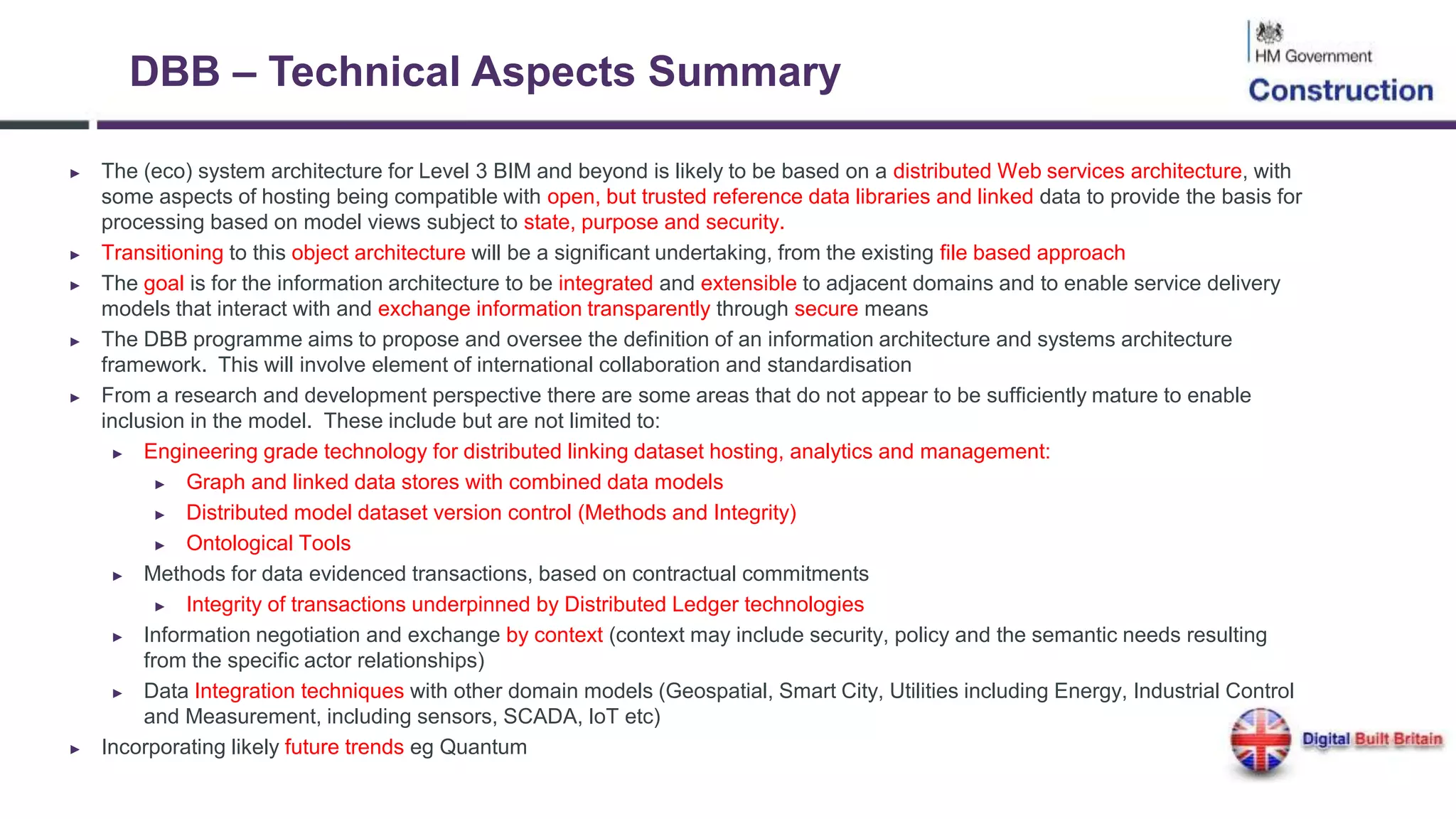
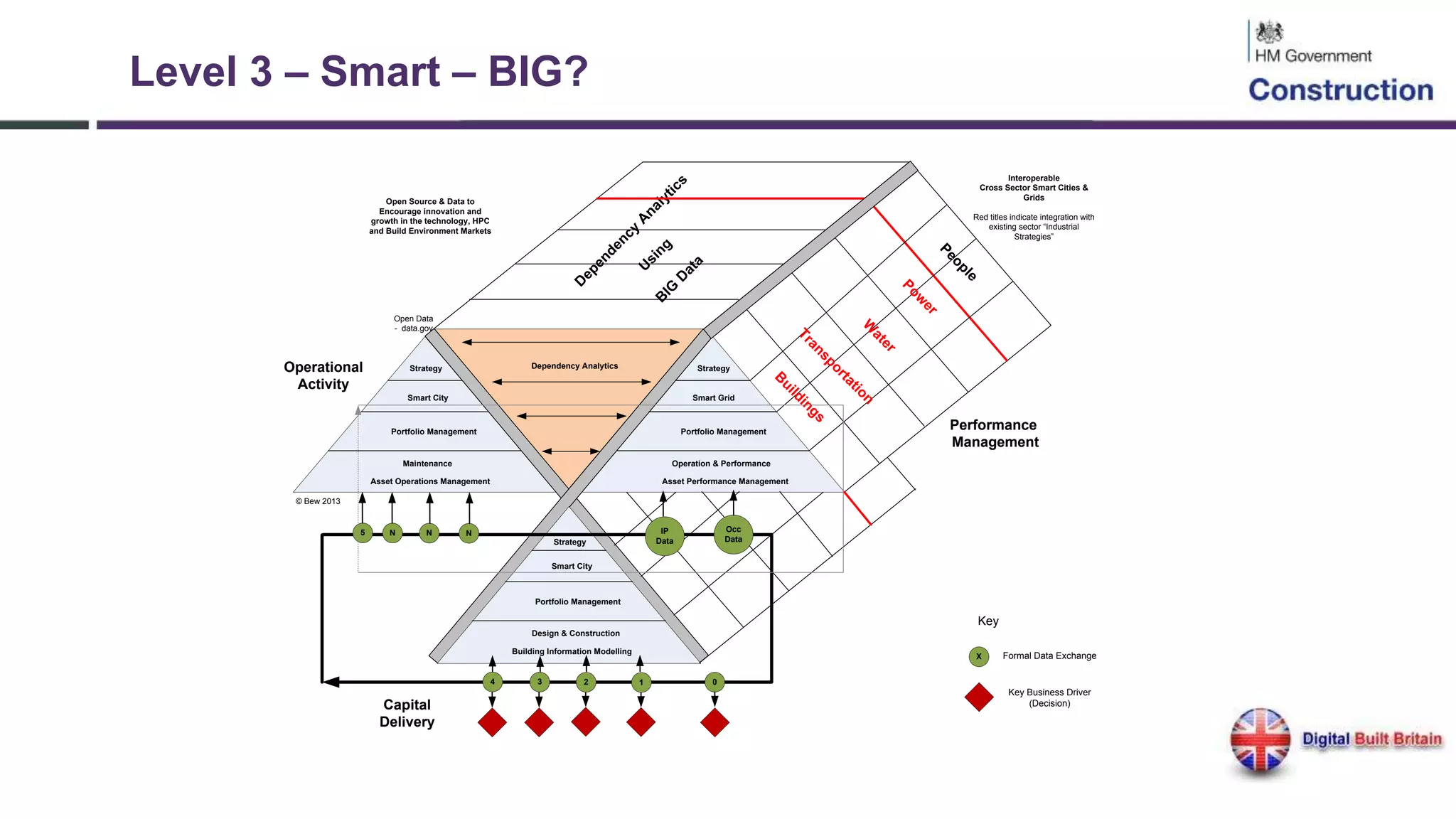
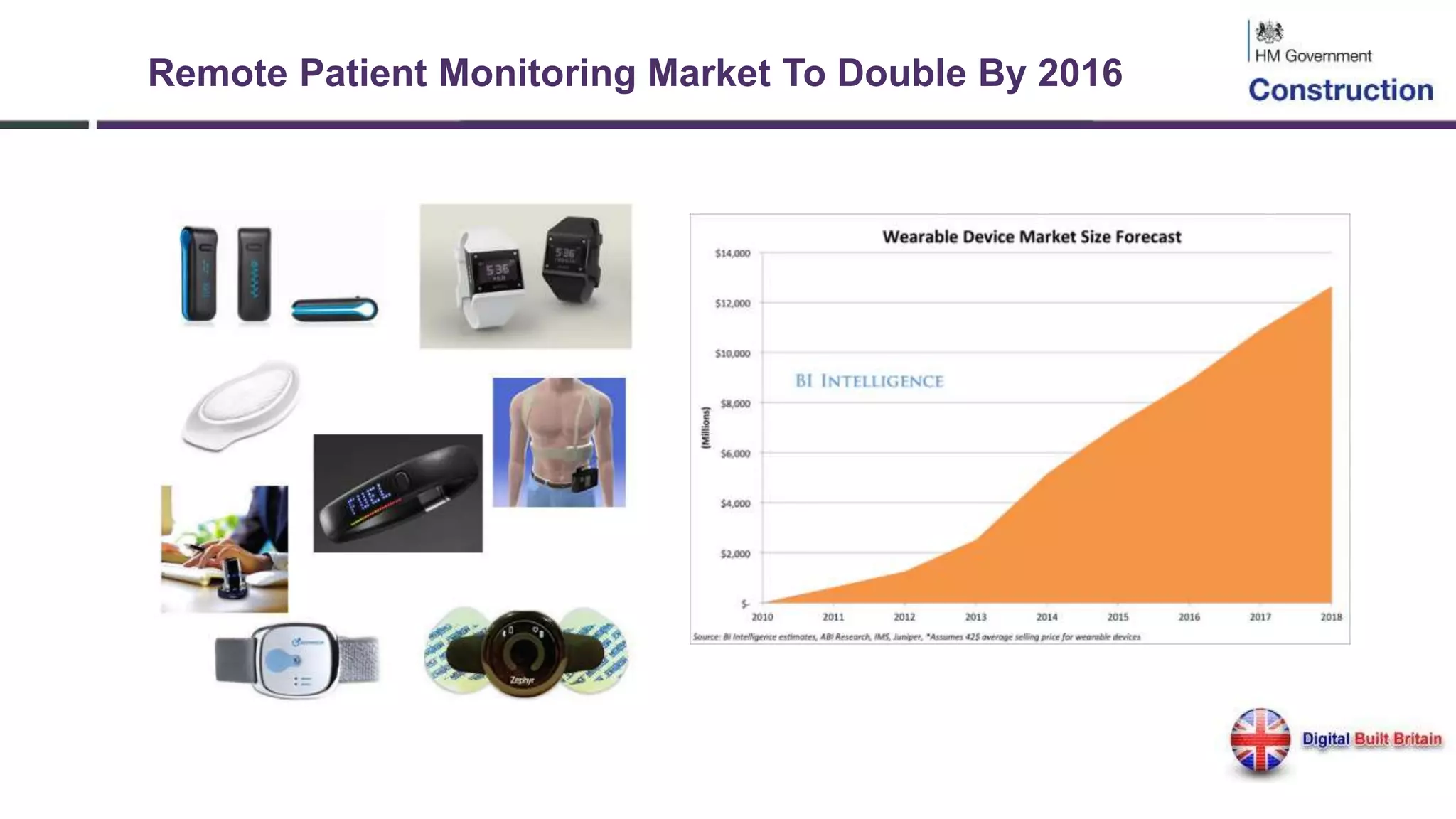
The document outlines the evolution and implementation of Building Information Modeling (BIM) in the UK, detailing various levels of BIM and related regulations such as PAS 1192 and the government's strategy towards improving construction efficiency. It also emphasizes the role of technology in regulatory compliance and the potential collaboration for international standards, focusing on the transition towards Level 3 BIM aimed at enhancing functional improvements and data management in smart cities. The document discusses the challenges and advancements in integrating BIM with modern technologies and data systems for improved service delivery.