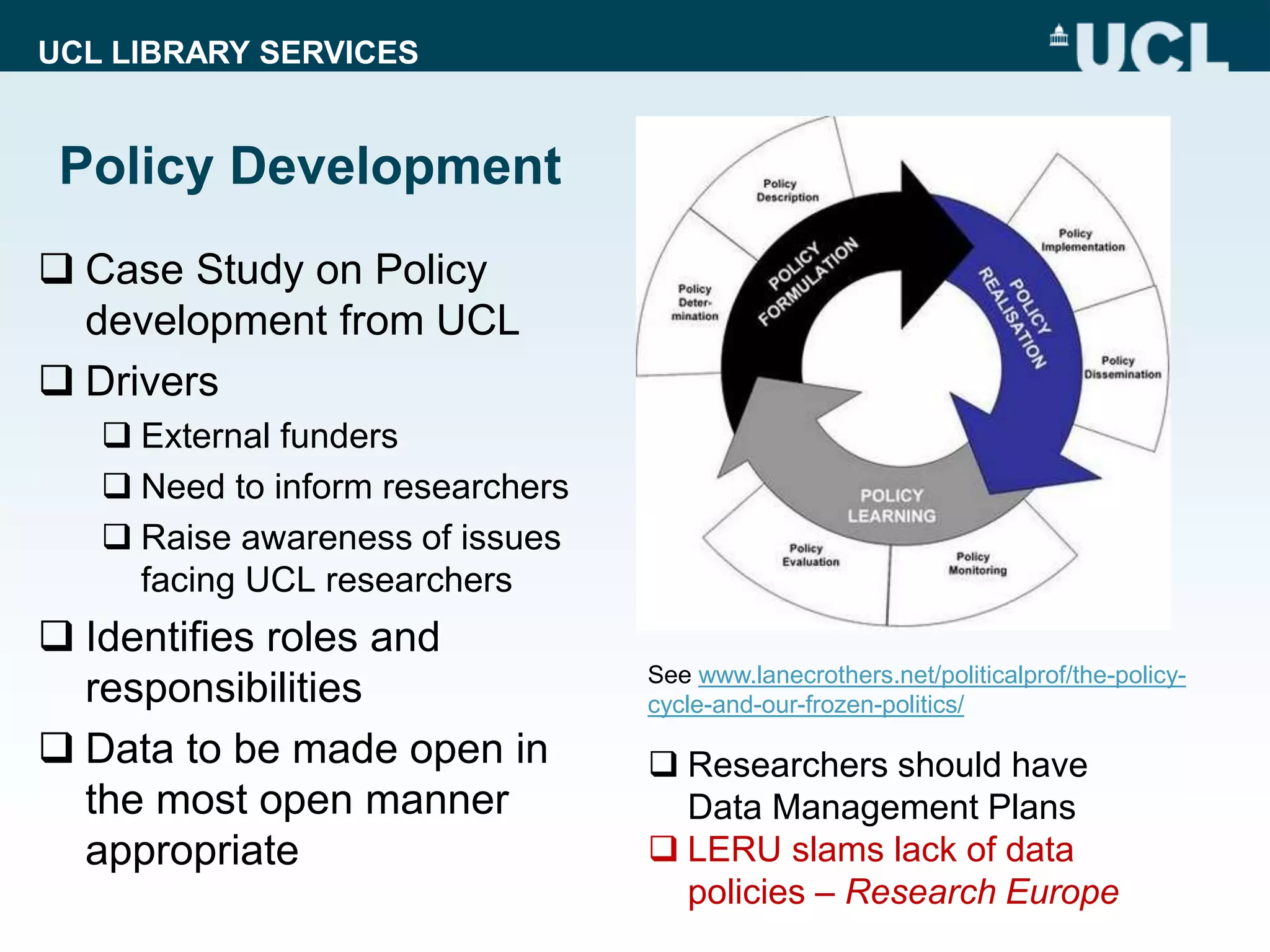
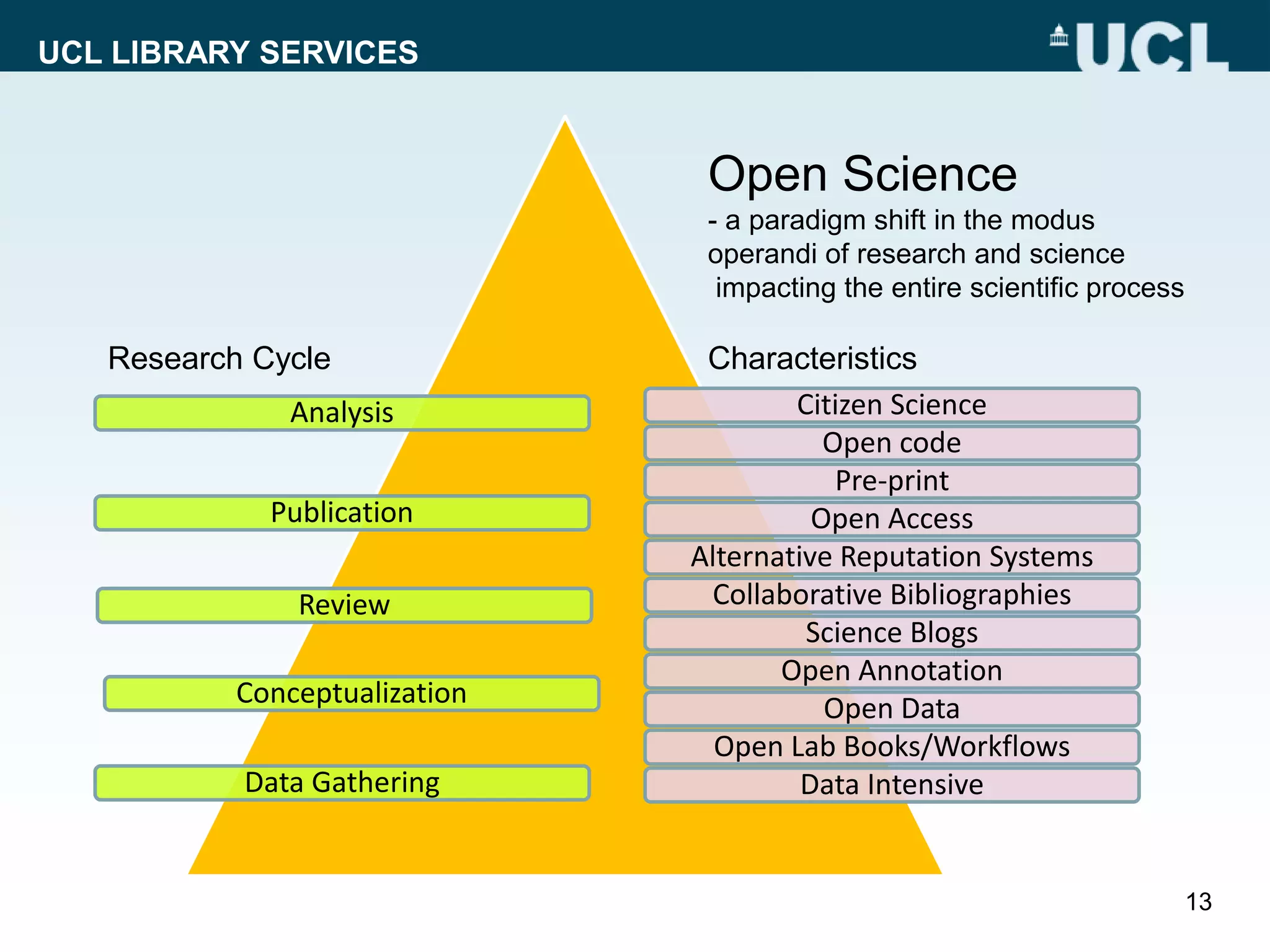
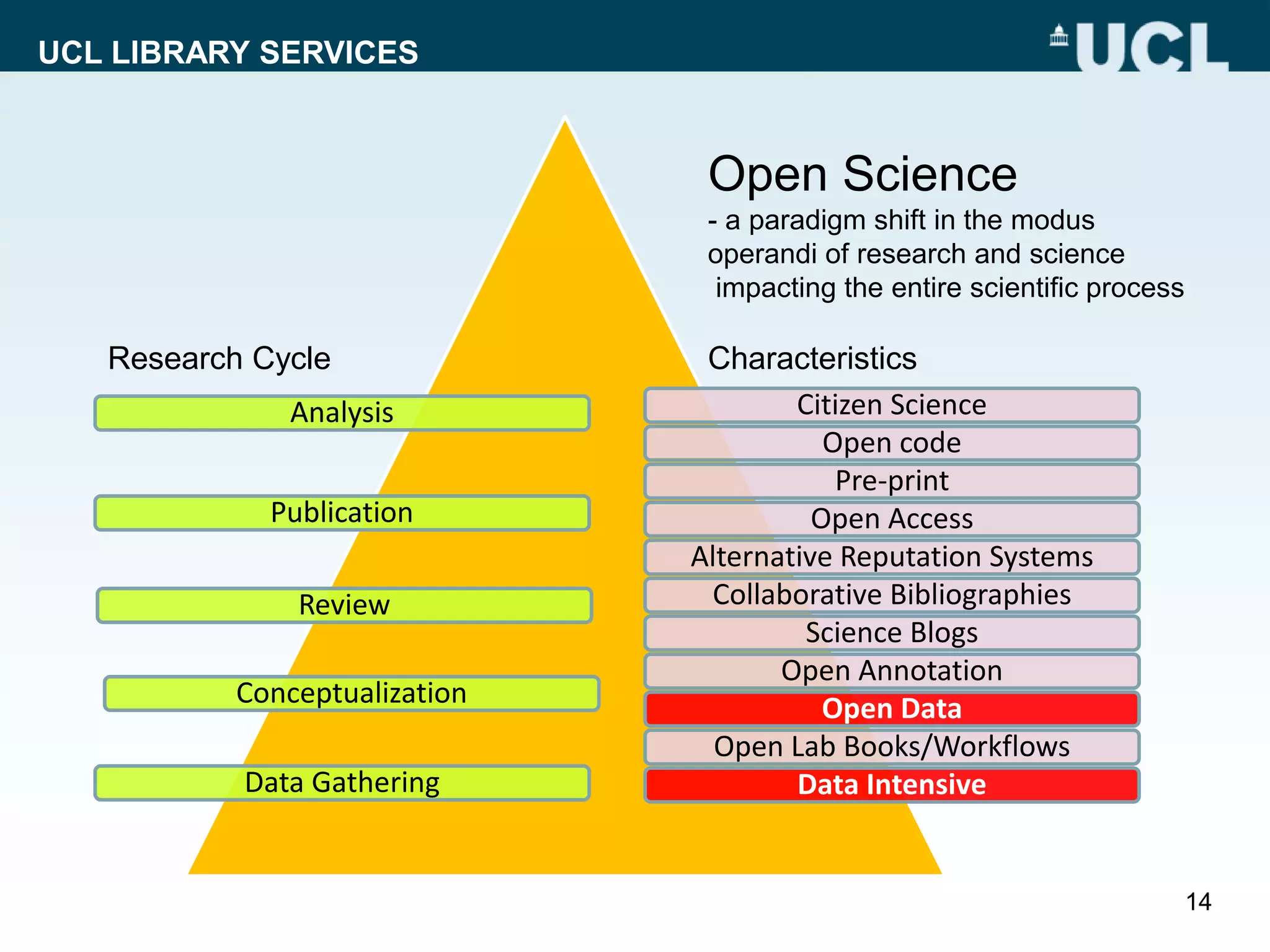
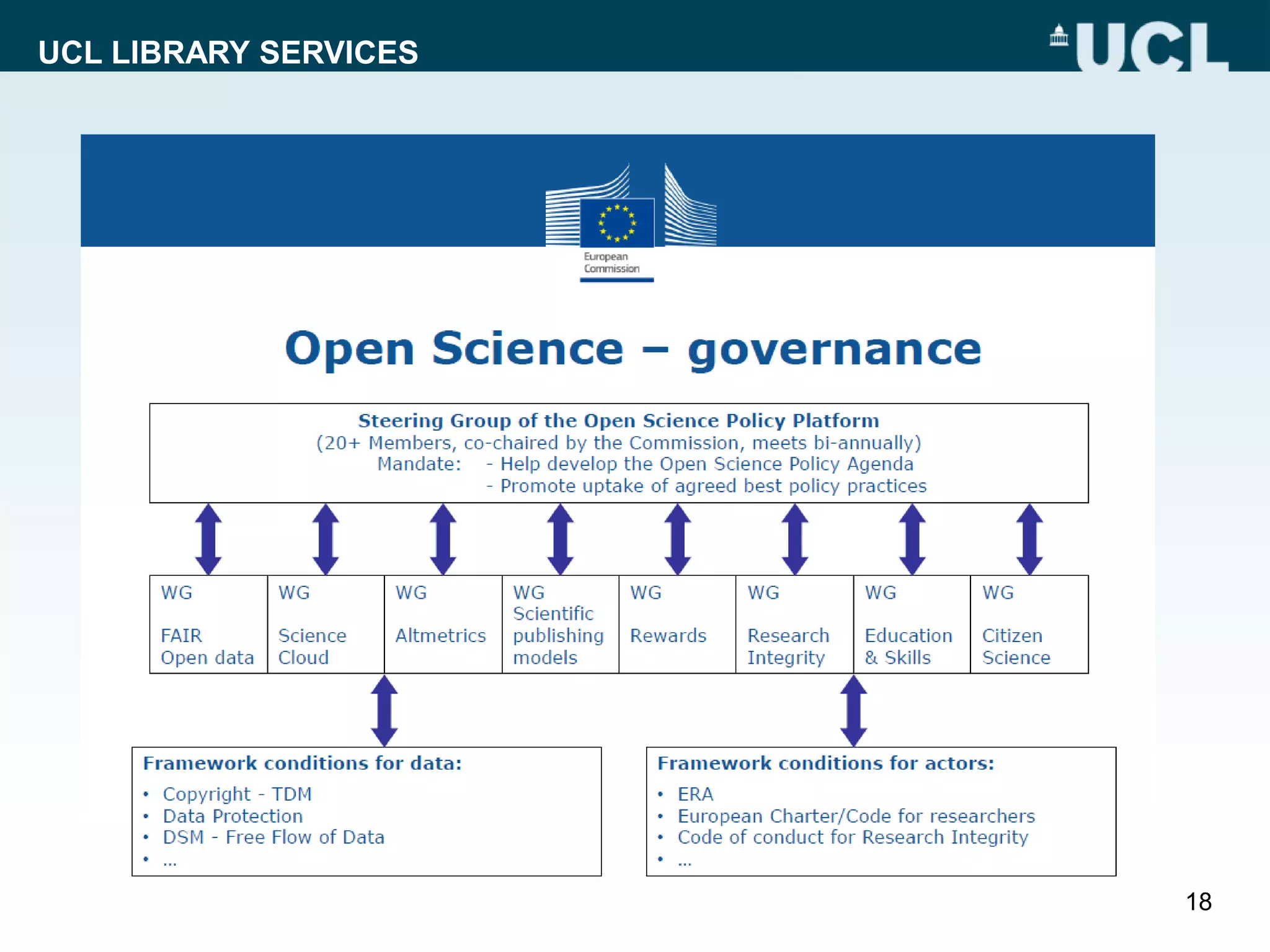
The document discusses UCL Library Services' role in research data management (RDM) within the context of the LERU roadmap and the European Open Science Cloud. It emphasizes the importance of establishing RDM strategies, supporting open data, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders to improve research transparency and efficiency. Key initiatives include the development of model RDM policies and toolkits, and advocating for the re-use of research data.