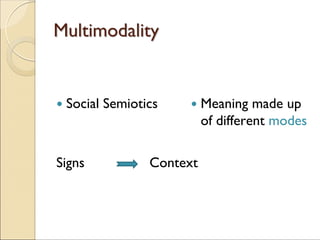
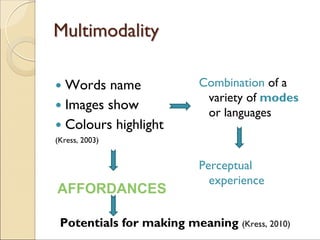
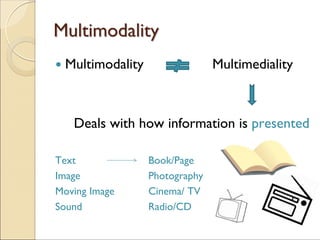
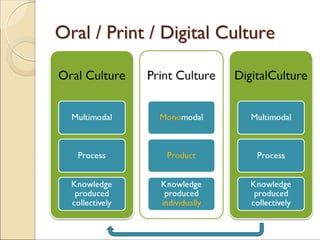
The document discusses the concept of multimodality and its impact on reading, writing, and thinking in the context of technological convergence and digital culture. It emphasizes that communication has always been multimodal, incorporating various modes such as text, image, and sound, and highlights the necessity for multiliteracies in education to accommodate diverse forms of communication. Additionally, it examines the political implications of a multimodal approach that challenges traditional literacy models.