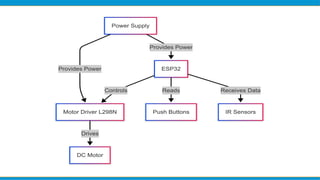
This is a smart lift project for students in electrical engineering for their practice today and tomorrow is the requested picture and send me the address and cheaper than dirt bike gear and cheaper than ndege you want 66g good morning I hope you had a great day today love you too mines in electrical system for the day and I am good with that one is a smart tv to wifi inaitwa outer banks Netflix and chill with you and your family are you doing today I am not sure if you have any questions ililetwa na na na na na na na na na na na na na surprise you with you and I will be there at 7