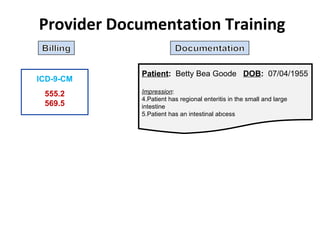
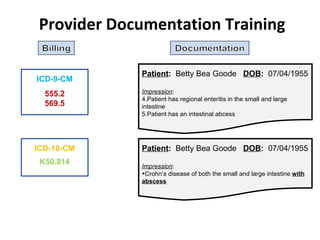
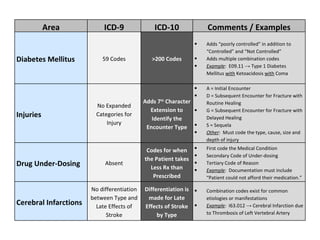
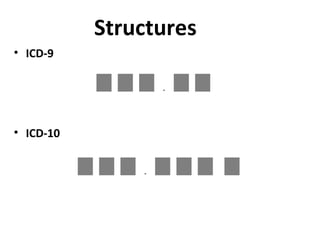
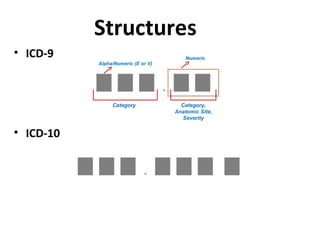
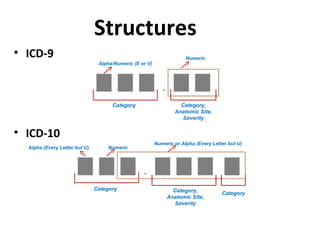
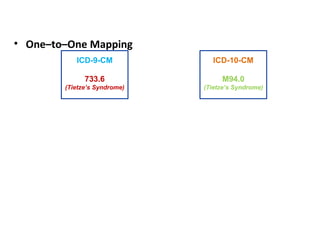
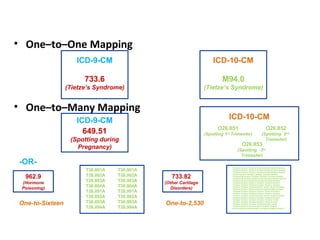
The document outlines the transition to ICD-10, emphasizing its broader scope compared to ICD-9, with potential coding errors increasing by 10-25% in the first year. It highlights the necessity of training for coders, billers, and physicians, focusing on accurate documentation and detailed coding requirements as critical for compliance. Implementation of ICD-10 is effective October 1, 2013, requiring all providers and payers to prepare for both ICD-9 and ICD-10 systems.