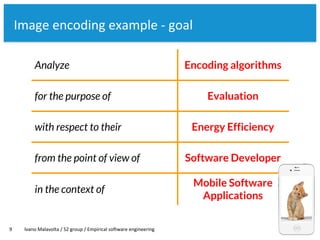
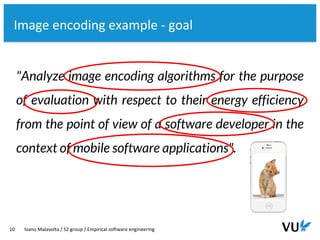
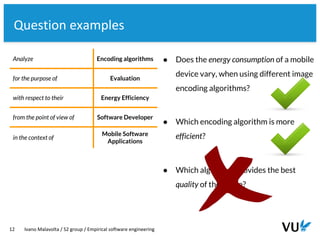
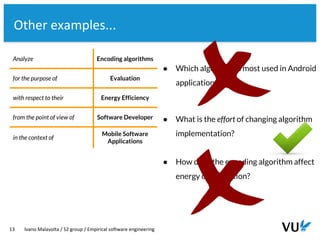
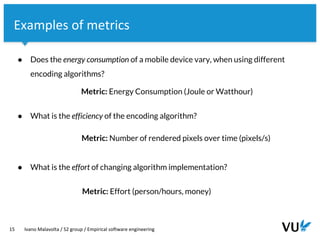
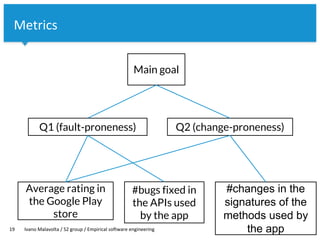
The document discusses the goal-question-metric (GQM) approach for defining research goals in software engineering experiments, emphasizing the importance of scoping and quantifying goals effectively. It provides a framework to analyze goals through questions and metrics, illustrated by examples related to image encoding algorithms and Android app success. The lecture concludes with guidelines for defining experiment goals and preparing for assignments.


![Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam
3 Ivano Malavolta / S2 group / Empirical software engineering
Experiment scoping
[1] V.R. Basili, "Software Modeling and Measurement: The Goal Question Metric Paradigm," Computer
Science Technical Report Series, CS-TR-2956 (UMIACS-TR-92-96), University of Maryland, College Park,
MD, September 1992.
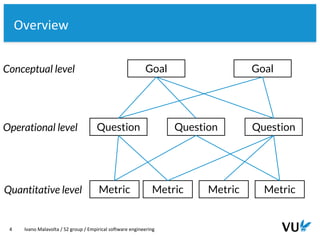
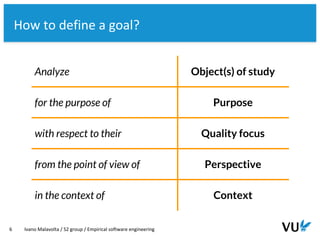
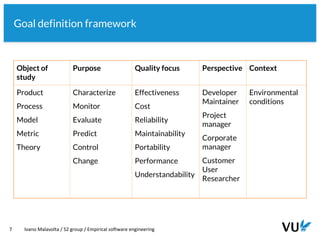
● Research approach: Goal-Question-Metric [1]
● Define the goal of the study](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02-bexperimentscoping-161108211733/85/The-Green-Lab-02-B-Experiment-scoping-3-320.jpg)