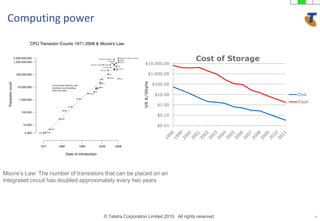
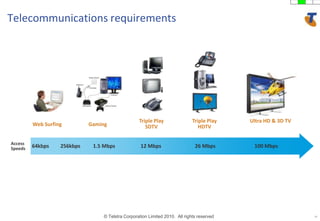
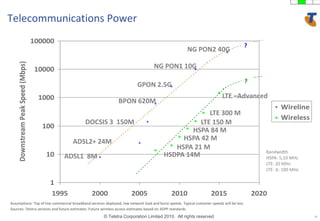
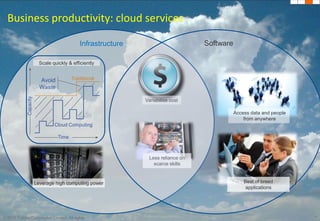
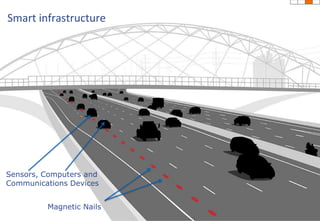
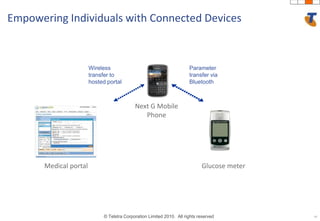
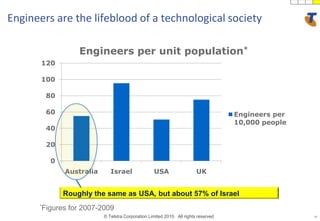
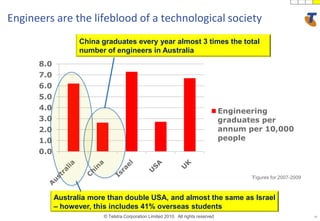
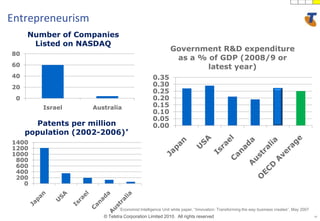
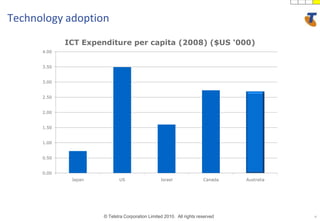
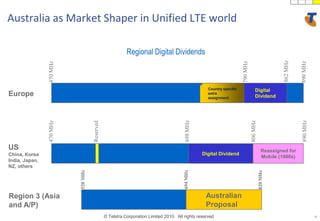
The document discusses how technology progress will impact society in the future. It will lead to ubiquitous sensing of the environment and individuals, ultra-broadband connectivity, smart infrastructure, transformed healthcare using wireless connected devices, and more efficient energy management. While Australia graduates more engineers than the US and is close to Israel, it lags far behind China. The document also addresses Australia's position in the global technology race and how it can help shape regional standards adoption.