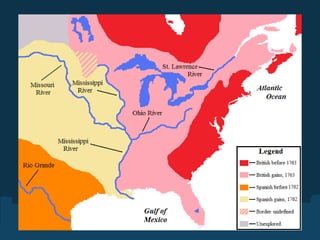
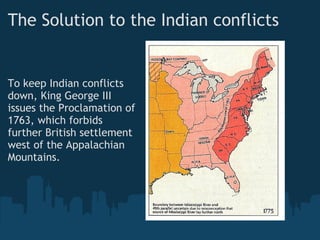
The French and Indian War began as a series of conflicts between England, France, and Spain from 1689 to 1754 over territorial claims in North America. England and France both claimed the Ohio River Valley, leading George Washington to fire on French soldiers in 1754, sparking open war. The British captured the key French forts of Duquesne and Montreal by 1760, gaining control of most of North America east of the Mississippi River but also accumulating massive war debts. To help pay these debts and maintain control, Parliament began taxing the American colonies through acts like the Sugar Act, Quartering Act, and Stamp Act in 1764-1765, fueling colonial opposition and resentment.