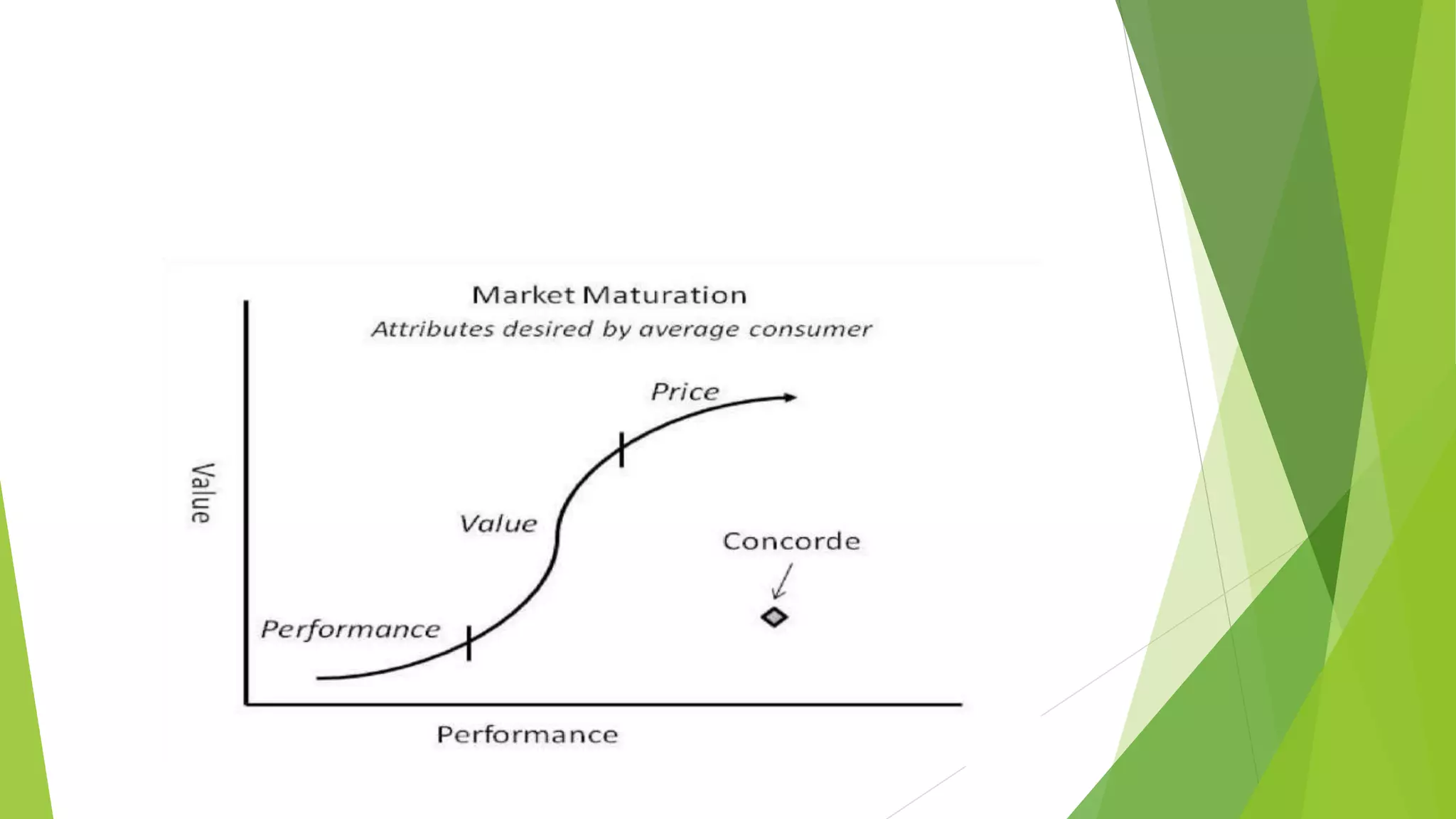
The Concorde project was a joint endeavor by France and Britain to create a supersonic aircraft, marked by engineering advances such as double delta wings and a cruising speed of Mach 2.04. Despite being a technical achievement, the project faced significant commercial challenges, including high costs, poor management, and limited market appeal, ultimately leading to financial difficulties over its 35-year operation. The experience highlights that advanced technology alone does not guarantee commercial success; thorough market research and financial planning are also crucial.