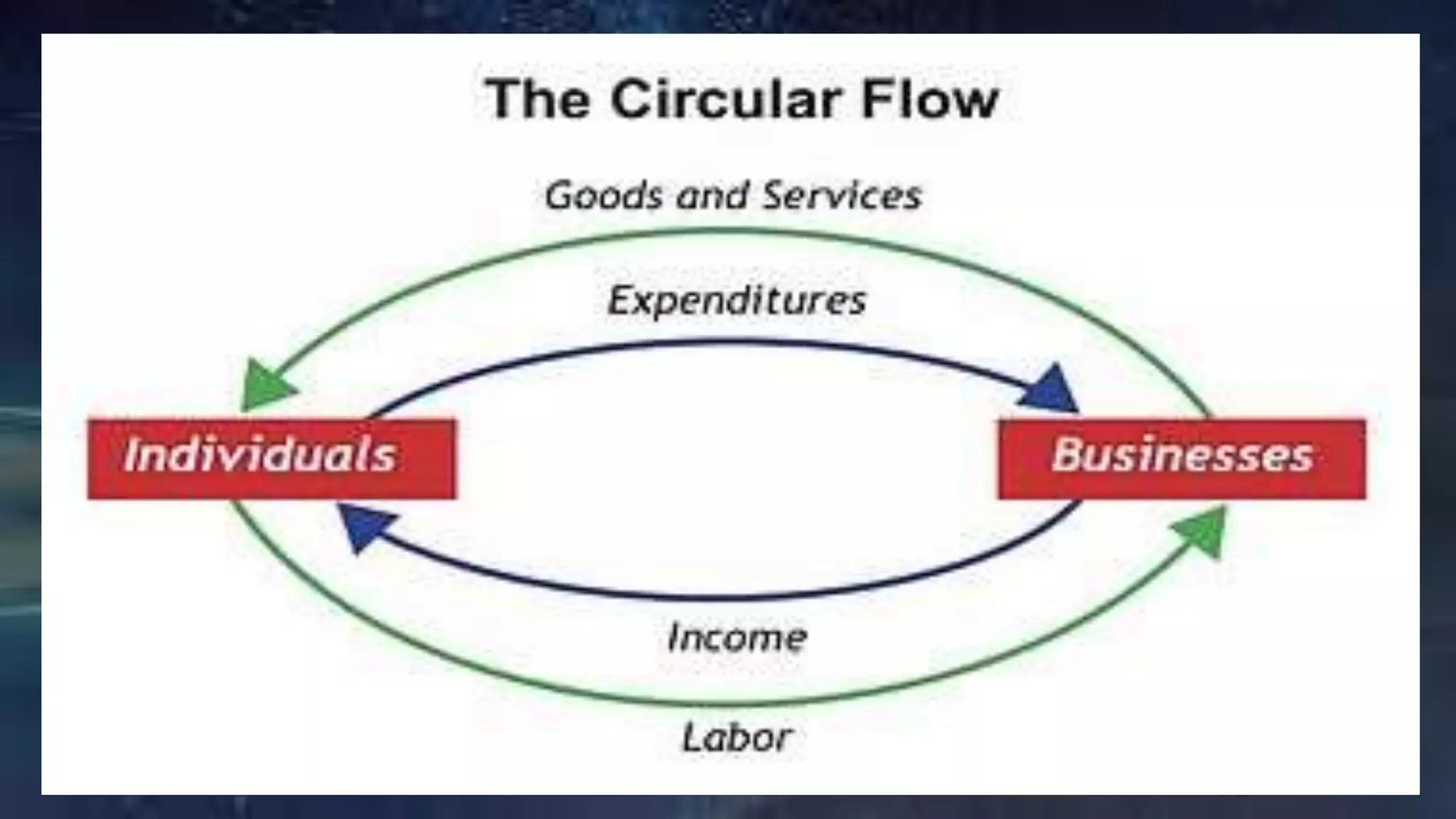
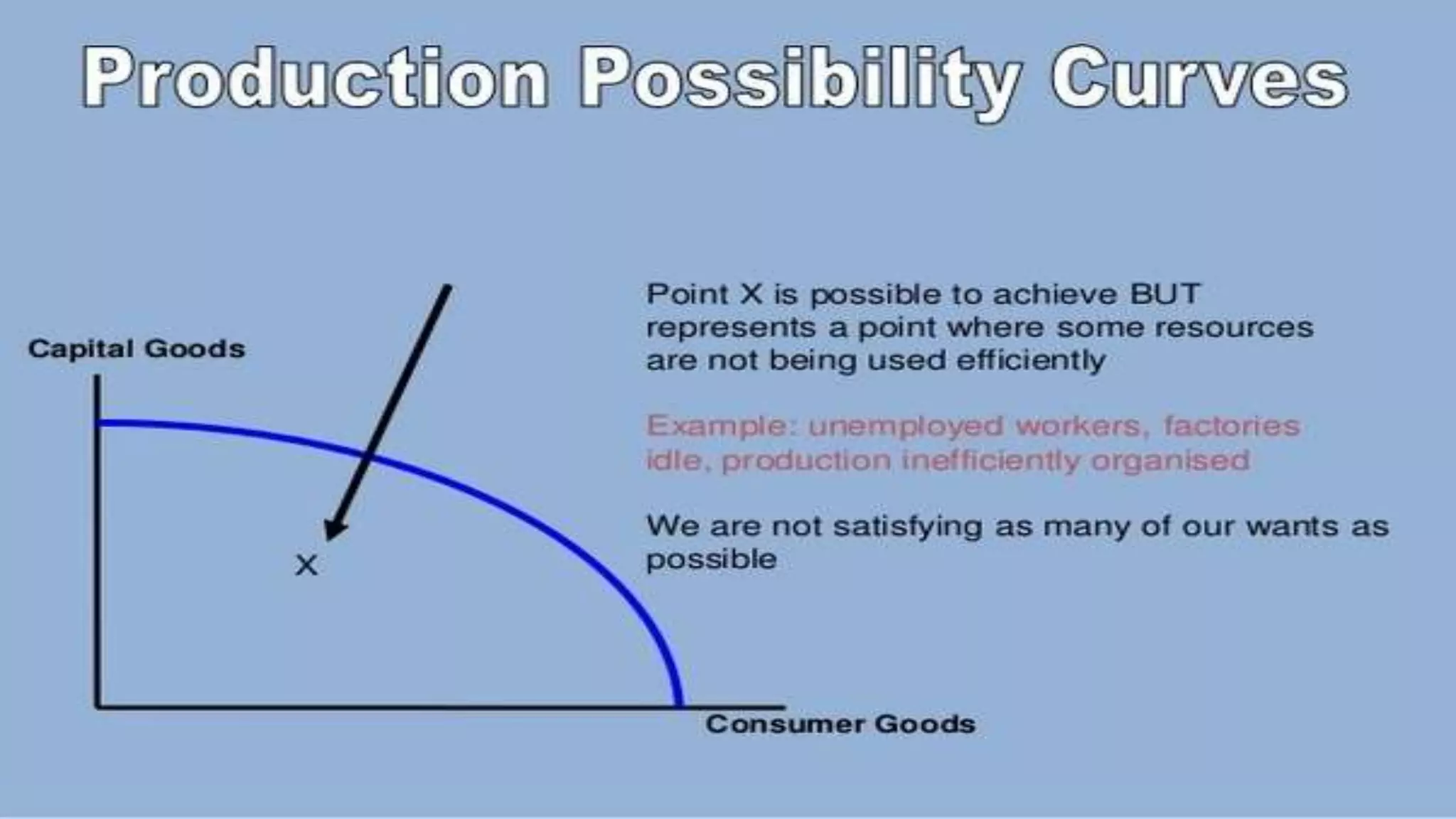
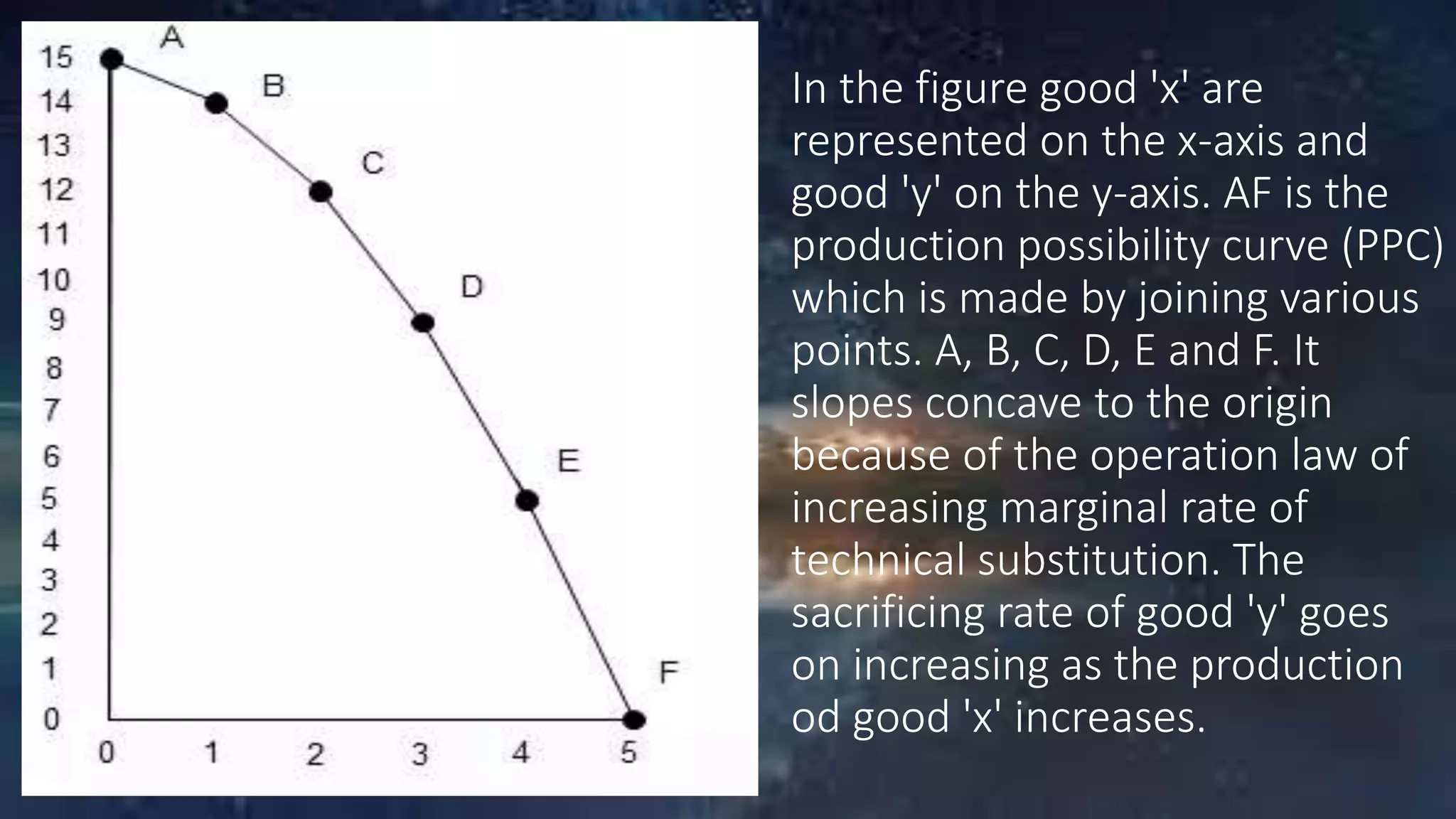
The circular flow model shows the basic economic relationships within a market economy. Money flows in one direction as consumers purchase goods and services from businesses, and goods and services flow in the opposite direction. Businesses use the money received to purchase resources from households. This continuous circular flow demonstrates how the economy functions as a whole.