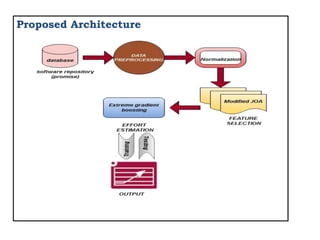
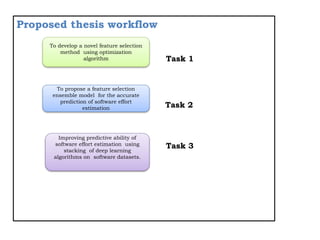
The document discusses using machine learning algorithms to accurately estimate software development effort (SDE). It proposes using a modified Jaya optimization algorithm to select important features which are then input to an extreme gradient boosting model for SDE estimation. The key objectives are to develop a novel feature selection method, propose an ensemble model for accurate prediction, and improve prediction ability using deep learning stacking. It reviews related work applying metaheuristic and machine learning techniques for SDE estimation and outlines the proposed approach of using modified Jaya optimization and extreme gradient boosting.

![Introduction
• Software effort estimation deals with estimating the
software effort, which is essential to build a software
project [1]
• It considers estimates of schedules, a probable sum of
cost and manpower essential in building a software
project
• The software effort estimation approach will foretell the
practical quantity of effort required to maintain and
develop the software from undetermined, insufficient,
noisy, and inconsistent data input [2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-3-320.jpg)
![Motivation
• Over the past few decades, the much-needed response
to the question of how accurately, the cost of the
project can be measured or forecasted at the start and
construction phase of the project is very important.
• If the project is not estimated at the early stage then
the probability of project failure is higher.
• According to latest surveys, the key explanation for the
failure of the project is accuracy in estimating prices, in
the starting phases. Both underestimation and
overestimation of the projects can cause severe
problems in software development. [3]
• It is the explanation for enhancing the planning to
estimate the best exact value for the project's
performance at optimized cost and effort.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-4-320.jpg)

![Optimizations Algorithms
• In the Artificial Intelligence, the search for the optimal
solution in the search space is one of the common issues
in almost all sub-fields such as machine learning, deep
learning[4].
• The traditional search techniques depend on the
heuristic concepts which are problem-dependent trying
to search for approximate solutions often with less focus
on the quality[5].
• Meta heuristic-based algorithms attract the attentions of
artificial intelligence research communities due to its
impressive capability in manipulating the search space of
optimization problems [6]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-6-320.jpg)
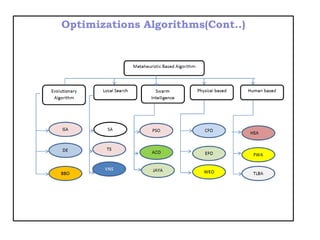
![Optimizations Algorithms(Cont..)
• Meta heuristic-based algorithms are conventionally
categorized in several ways [7]:
– Nature-inspired vs. non-nature inspired
– population-based vs. single point search,
– dynamic vs. static objective function,
– single vs. various neighborhood structures,
– memory usage vs. memory-less.
• Recently, the research community combined these
algorithms in categories based on the natural inspirations
of the Metaheuristic algorithm such as evolutionary
algorithms (EAs), Local Search (LSA), Swarm intelligence,
physical based, chemical-based, human-based[8]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-7-320.jpg)
![Machine learning Techniques
• The following machine learning techniques are applied over
the various datasets considered to calculate the effort of a
software product.
• The decision about choosing a machine learning technique
for implementation purpose in the proposed research is
performed based on the past research study done in the
literature survey[9].
• Some of the machine learning techniques are decision tree,
SVR, Random forest, SGB, XGB, ANN etc .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-9-320.jpg)
![Related work(cont..)
• Rankovic et al [1] proposed a new approach to software
effort estimation using different artificial neural network
architectures and Taguchi orthogonal arrays.
• Minku, L. L [2] proposed a novel online supervised hyper
parameter tuning procedure applied to cross-company
software effort estimation.
• Ezghari, S., & Zahi, A. [3] proposed software effort
estimation using a consistent fuzzy analogy-based method.
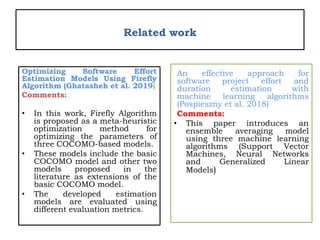
• Ghatasheh, N., Faris, et al[4] proposed Optimizing technique
in software effort estimation models using the firefly
algorithm.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-12-320.jpg)
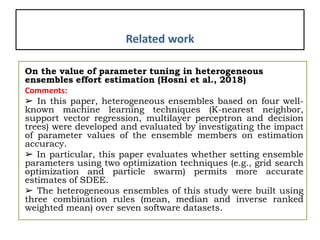
![Related work(cont..)
• Fávero, E. M. D. B., et al[5] proposed A model for software
effort estimation using pre-trained embedding models
• Sehra, S. K. et al [6]. proposed Software effort estimation
using FAHP and weighted kernel LSSVM machine.
• Xia, T., Krishna, et al[7] proposed a Hyper-parameter
optimization for effort estimation.
• Kaushik, A., & Singal, N. [8] proposed A hybrid model of
wavelet neural network and metaheuristic algorithm for
software development effort estimation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-13-320.jpg)
![Major Findings From The Literature Survey Based On The
Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) and Swarm Optimization
Algorithms:
• Hyper parameters tuning is crucial as they control the
overall behavior of a machine learning model. Every
machine learning models will have different hyper parameters
that can be set.
• A hyper parameter is a parameter whose value is set before
the learning process begins.
• But all EA’s and PSO algorithms depends on parameter
tuning.
• For this reason, evolutionary algorithms are best employed on
problems where it is difficult or impossible to test for
optimality.
• This also means that an evolutionary algorithm never knows
for certain when to stop, aside from the length of time, or the
number of iterations or candidate solutions, that you wish to
allow it to explore [10-15].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-14-320.jpg)
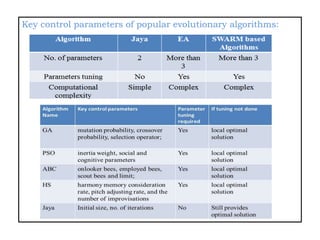
![Major Findings From The Literature Survey Based On The
Evolutionary Algorithms And Swarm Optimization
Algorithms[16-21]:
• All the evolutionary and swarm intelligence based
algorithms are probabilistic algorithms and require
common controlling parameters like population size,
number of generations, elite size, etc.
• Besides the common control parameters, different
algorithms require their own algorithm-specific control
parameters.
• The improper tuning of algorithm-specific parameters
either increases the computational effort or yields the local
optimal solution.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-15-320.jpg)
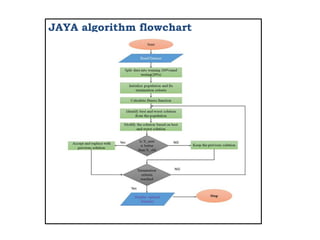
![Jaya Algorithm
• It can be used for maximization or minimization of a
function
• It is a population based method which repeatedly modifies a
population of individual solutions
• To reduce the search space and gives optimal solutions
• Formulated for solving constrained and unconstrained
optimization problem
• Based on the concept that the solution obtained for a given
problem should move towards the best solution and should
avoid the worst solution[22]
Common control parameters
Population size
No of generations(iterations)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-19-320.jpg)






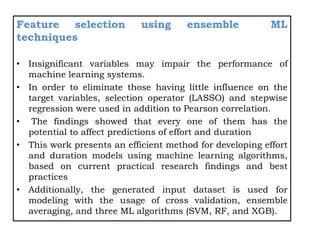
![Stacking of deep learning (DL)algorithms
• Deep Learning, a subfield of Machine Learning, was
pioneered by Hinton, LeCun, Bengio and Andrew Ng, and
gained popularity from around 2010, with their high
potential being established with the availability of large-
scale data and high-speed computing devices[23]
• This works presents an efficient method for developing
effort and duration models using deep learning algorithms,
based on current practical research findings and best
practices.
• The DL algorithms include CNN and LSTM models, and
stacking of DL algorithms based on optimal features
selected from optimization algorithm applied.
• The stacking of these model is theoretically expected to
give a better performance than individual regressors. These
models are being experimented upon and the parameters
adjusted according to performance.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-28-320.jpg)

![References
[1] Rankovic, N., Rankovic, D., Ivanovic, M., & Lazic, L. (2021). A new
approach to software effort estimation using different artificial neural network
architectures and Taguchi orthogonal arrays. IEEE Access, 9, 26926-26936.
[2] Minku, L. L. (2019). A novel online supervised hyperparameter tuning
procedure applied to cross-company software effort estimation. Empirical
Software Engineering, 24(5), 3153-3204.
[3]Ezghari, S., & Zahi, A. (2018). Uncertainty management in software effort
estimation using a consistent fuzzy analogy-based method. Applied Soft
Computing, 67, 540-557.
[4] Ghatasheh, N., Faris, H., Aljarah, I., & Al-Sayyed, R. M. (2019). Optimizing
software effort estimation models using the firefly algorithm. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1903.02079.
[5] Fávero, E. M. D. B., Casanova, D., & Pimentel, A. R. (2022). SE3M: A
model for software effort estimation using pre-trained embedding models.
Information and Software Technology, 147, 106886.
[6]Sehra, S. K., Brar, Y. S., Kaur, N., & Sehra, S. S. (2019). Software effort
estimation using FAHP and weighted kernel LSSVM machine. Soft Computing,
23(21), 10881-10900.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-38-320.jpg)
![References
[7]. Xia, T., Krishna, R., Chen, J., Mathew, G., Shen, X., & Menzies, T.
(2018). Hyperparameter optimization for effort estimation. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1805.00336.
[8]. Kaushik, A., & Singal, N. (2019). A hybrid model of wavelet neural
network and metaheuristic algorithm for software development effort
estimation. International Journal of Information Technology, 1-10.
[9]. Phan, H., & Jannesari, A. (2022). Heterogeneous Graph Neural
Networks for Software Effort Estimation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.11023.
[10]. Rhmann, W. (2021). An ensemble of Hybrid Search-Based algorithms
for Software effort prediction. International Journal of Software Science and
Computational Intelligence (IJSSCI), 13(3), 28-37.
[11]. Alhammad, N. K. L., Alzaghoul, E., Alzaghoul, F. A., & Akour, M.
(2020). Evolutionary neural network classifiers for software effort estimation.
International Journal of Computer Aided Engineering and Technology, 12(4),
495-512.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-39-320.jpg)
![References
[12] De Carvalho, H. D. P., Fagundes, R., & Santos, W. (2021). Extreme
Learning Machine Applied to Software Development Effort Estimation. IEEE
Access, 9, 92676-92687.
[13] Padmaja, M., & Haritha, D. (2018). Software effort estimation using grey
relational analysis with K-Means clustering. In Information Systems Design
and Intelligent Applications (pp. 924-933). Springer, Singapore.
[14]Predescu, E. F., Tefan, A., & Zaharia, A. V. (2019). Software effort
estimation using multilayer perceptron and long short term memory.
Informatica Economica, 23(2), 76-87.
[15] Puspaningrum, A., Muhammad, F. P. B., & Mulyani, E. (2021). Flower
Pollination Algorithm for Software Effort Coefficients Optimization to Improve
Effort Estimation Accuracy. JUITA: Jurnal Informatika, 9(2), 139-144.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-40-320.jpg)
![References
[16] Idri, A., Abnane, I., & Abran, A. (2018). Evaluating Pred (p) and
standardized accuracy criteria in software development effort
estimation. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, 30(4), e1925.
[17] Shahpar, Z., Khatibi, V., & Khatibi Bardsiri, A. (2021). Hybrid PSO-
SA approach for feature weighting in analogy-based software project
effort estimation. Journal of AI and Data Mining, 9(3), 329-340.
[18] Benala, T. R., & Mall, R. (2018). DABE: differential evolution in
analogy-based software development effort estimation. Swarm and
Evolutionary Computation, 38, 158-172.
[19] Zakrani, A., Hain, M., & Idri, A. (2019). Improving software
development effort estimating using support vector regression and
feature selection. IAES International Journal of Artificial Intelligence,
8(4), 399.
[20] Jørgensen, M., & Halkjelsvik, T. (2020). Sequence effects in the
estimation of software development effort. Journal of Systems and
Software, 159, 110448.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-41-320.jpg)
![References
[21] Shah, M. A., Jawawi, D. N. A., Isa, M. A., Younas, M., Abdelmaboud, A.,
& Sholichin, F. (2020). Ensembling artificial bee colony with analogy-based
estimation to improve software development effort prediction. IEEE Access, 8,
58402-58415.
[22] Rao RV, More KC (2017) Design optimization and analysis of selected
thermal devices using self-adaptive jaya algorithm.Energy Convers Manag
140:24–35
[23] LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. Deep learning. 436-44.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/registrationppt-copy-240325072439-7bd6eb7d/85/the-application-of-machine-lerning-algorithm-for-SEE-42-320.jpg)
