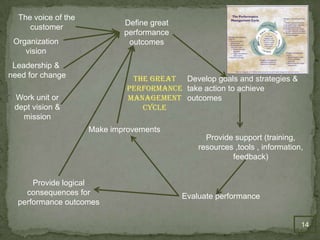
The document discusses a nine vector view of human performance management. It outlines nine primary disciplines that are important for effective change management: stakeholder relationship management, leading change, change strategy, communication, human capital management, learning and training, process and infrastructure, project management, and performance management. It then provides more details about each discipline and explains that a holistic approach considering all nine vectors is needed for transformational change efforts.