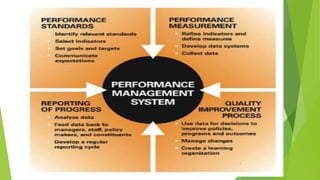
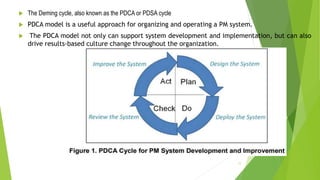
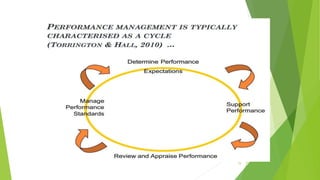
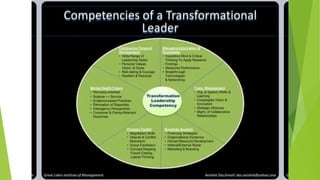
The document outlines the components and functions of a performance management system (PMS), emphasizing a continuous cycle of planning, performance, reviewing, and development. It discusses the importance of feedback, employee engagement, and setting clear performance standards, with various models such as Deming's cycle and the Torrington & Hall model highlighting effective practices. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of transformational leadership and 360-degree feedback in improving organizational performance and fostering employee growth.