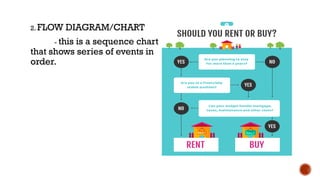
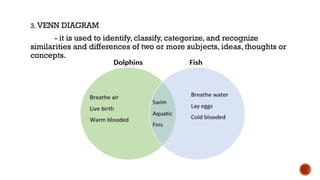
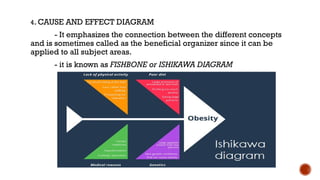
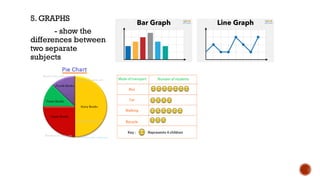
The document outlines the objectives for a lesson on understanding and converting linear and non-linear texts. It defines linear texts as traditional texts read sequentially, while non-linear texts allow for non-sequential reading, highlighting various textual aids such as concept maps, flow diagrams, and Venn diagrams. The document also provides steps for transcoding information between these two types of texts.