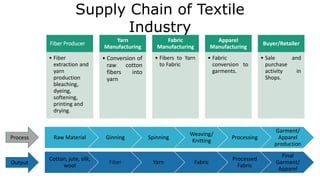
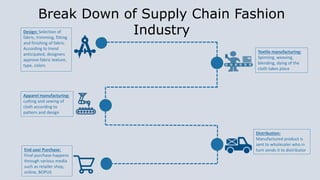
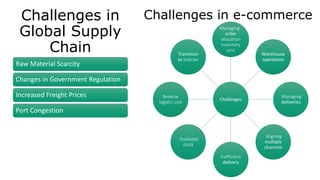
The document summarizes the supply chain of the textile industry. It begins with the raw materials of cotton, jute, silk and wool which are produced by fiber producers. These raw materials then go through various stages of production including yarning, fabric manufacturing, apparel manufacturing and distribution before reaching the end consumer. It outlines the various players involved at each stage and describes the process flow. It also discusses characteristics of the textile supply chain such as the use of push and pull systems, centralized buying, overseas sourcing and short product life cycles. Finally, it outlines challenges faced in inventory management, collaboration and achieving sustainability across the complex global textile supply chain.