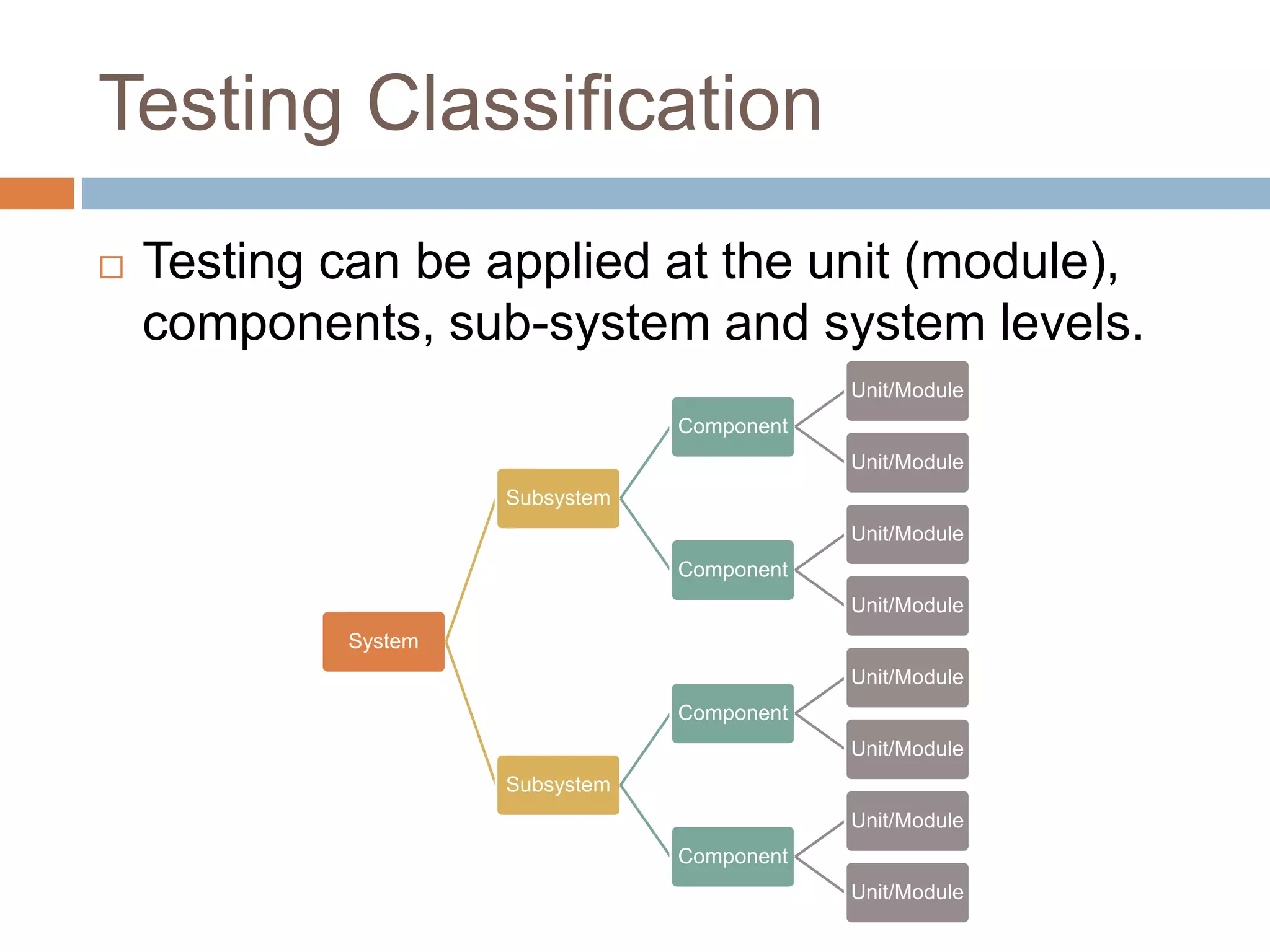
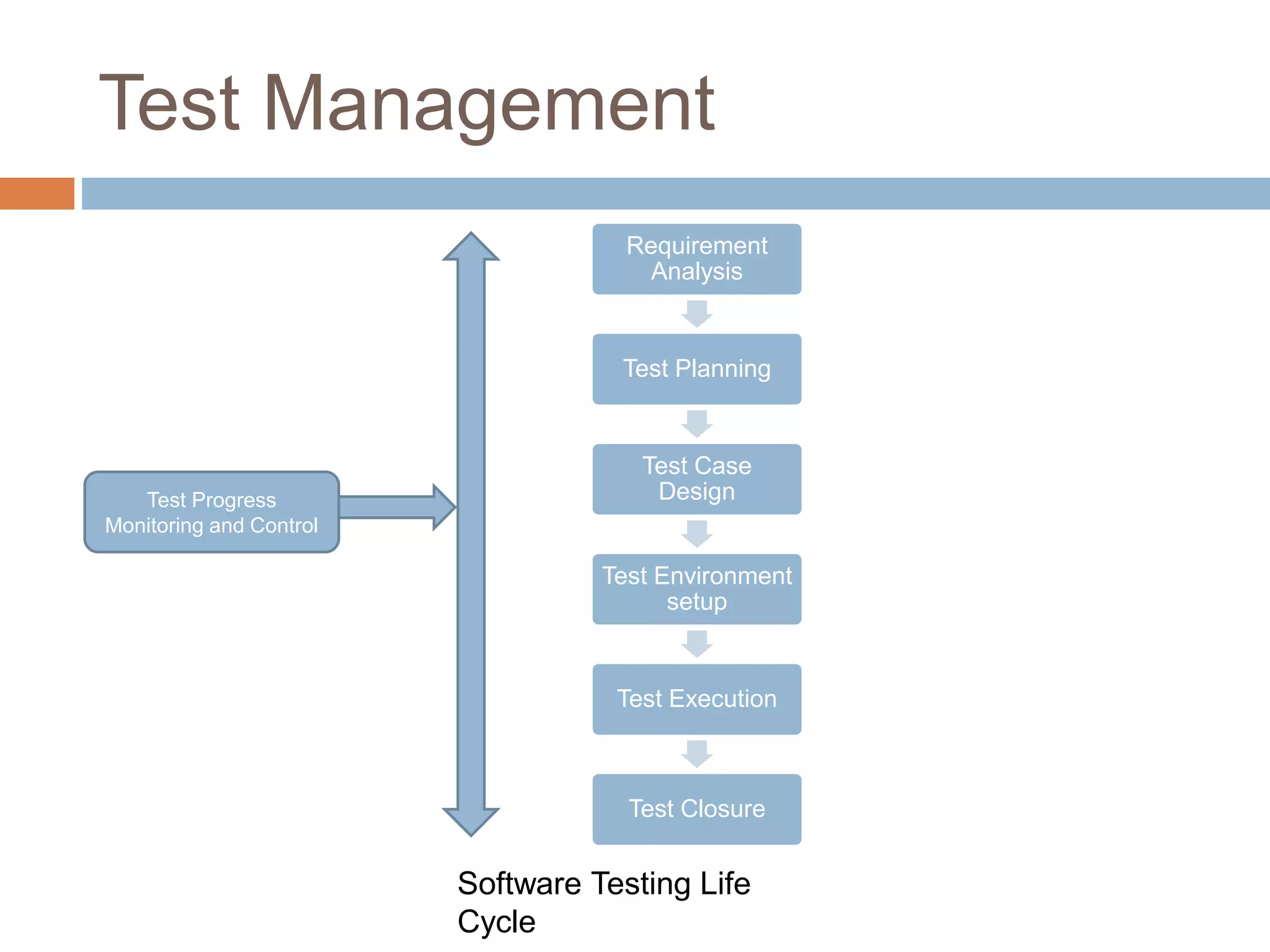
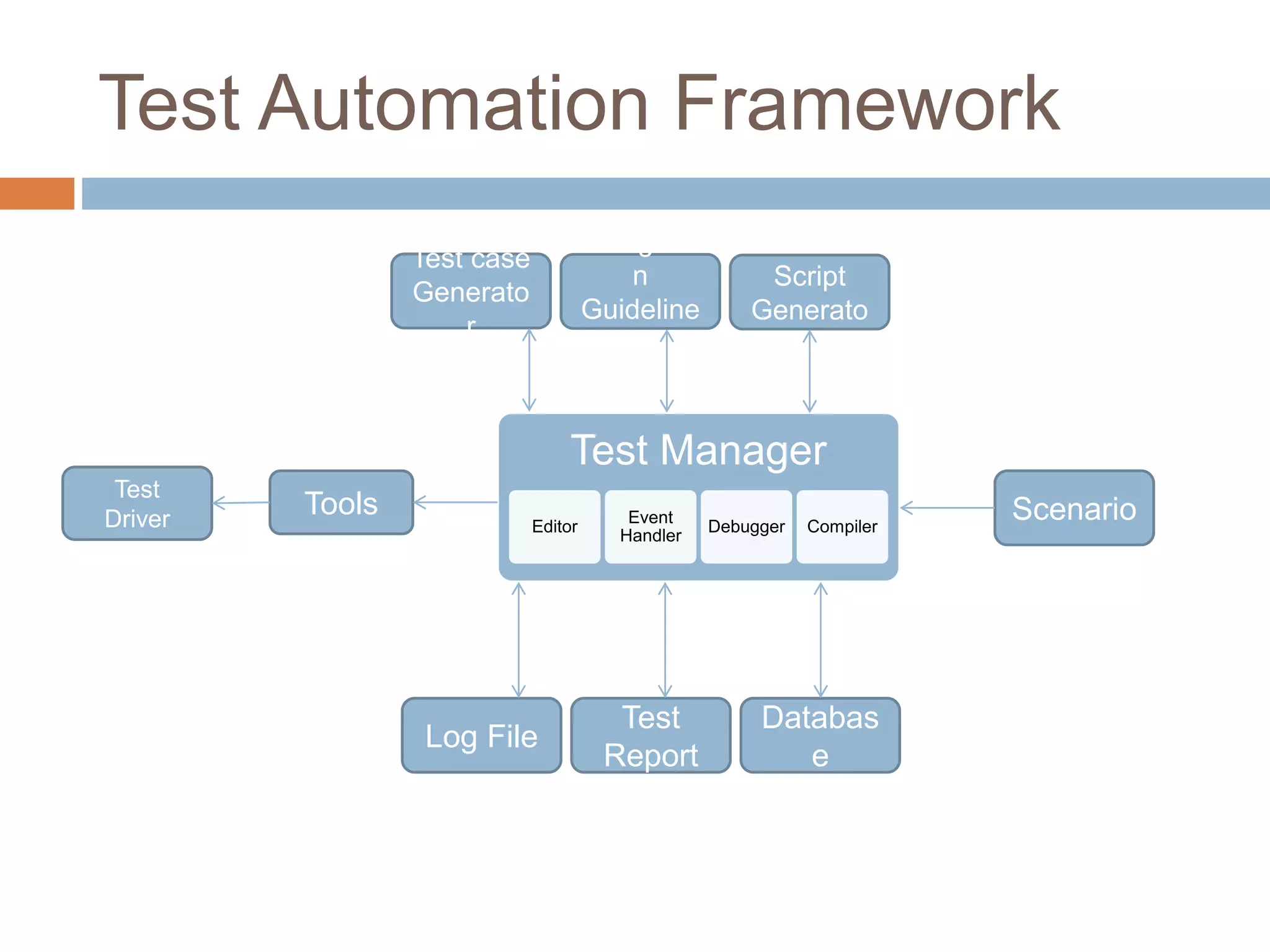
This document discusses software testing fundamentals. It defines key terms like testing, bugs, and defects. Testing is described as a quality control activity done throughout development to find defects before customers. There are different types of testing like unit, integration, and system level testing. Test management refers to planning testing activities and includes elements like test basis, test objects, and test conditions. Test automation involves automating manual testing processes using tools to replay test cases for comparison to expected results.