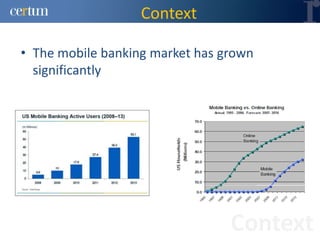
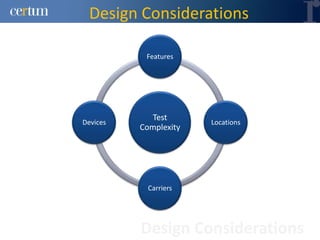
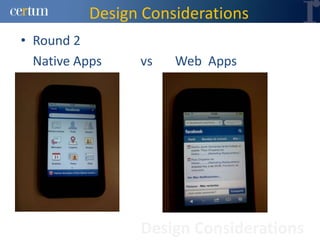
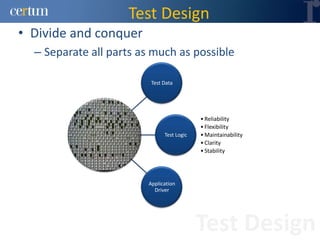
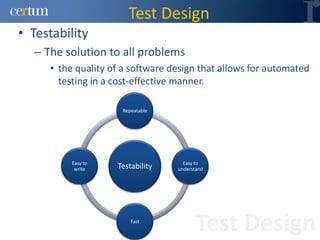
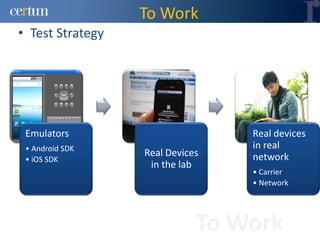
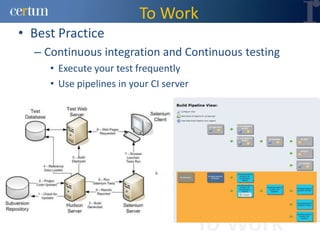
Christian Ramírez presented on software testing considerations for mobile banking applications. Key points included separating test logic from technical drivers, using test automation frameworks, and adopting test design approaches like TDD and BDD. Best practices involved continuous integration, model-based testing, and leveraging tools for code analysis and cross-browser testing. The presentation provided guidance on effective strategies for testing mobile apps across different platforms and environments.