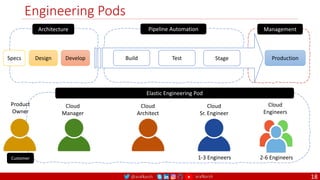
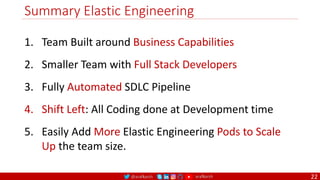
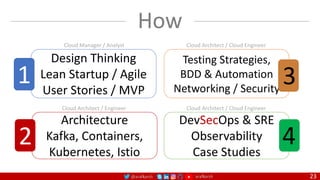
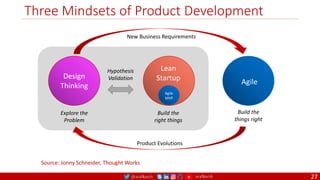
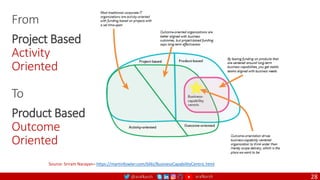
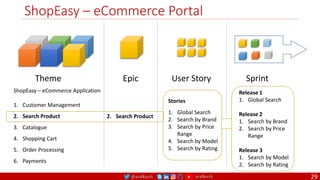
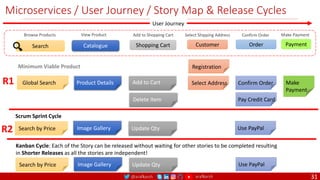
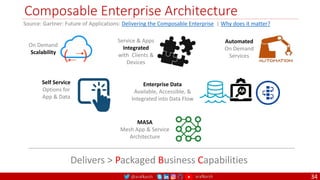
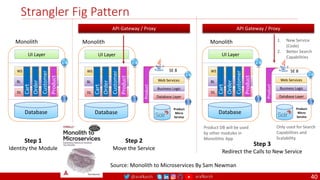
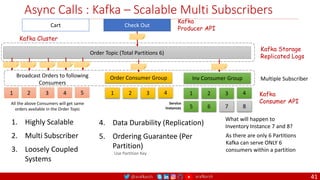
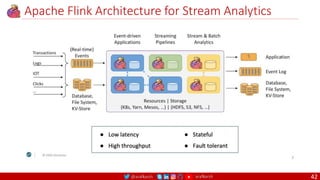
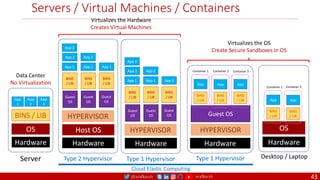
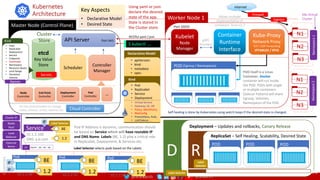
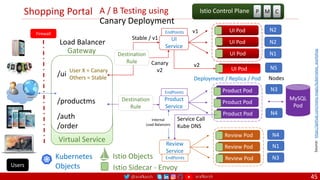
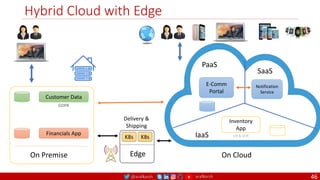
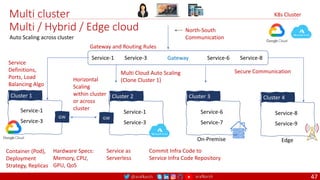
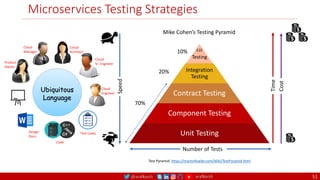
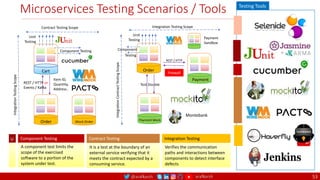
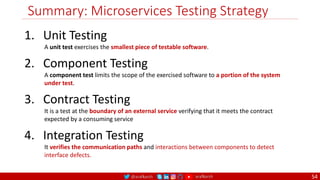
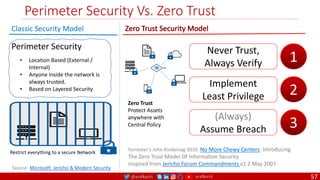
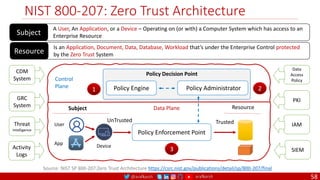
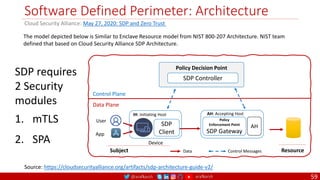
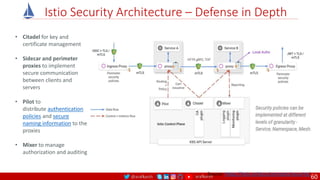
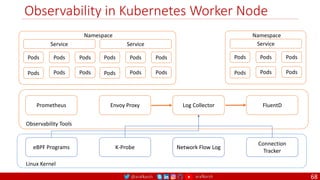
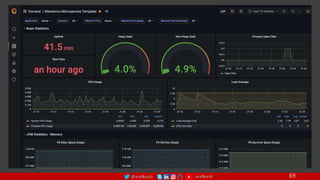
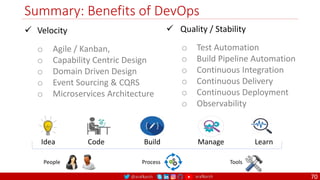
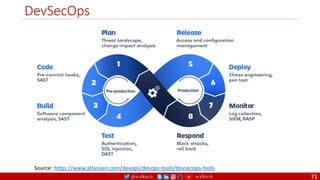
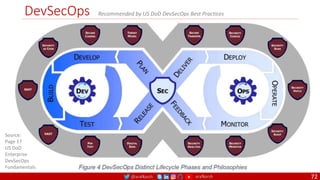
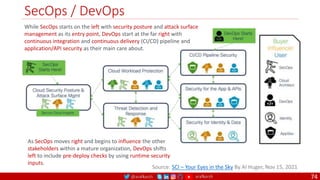
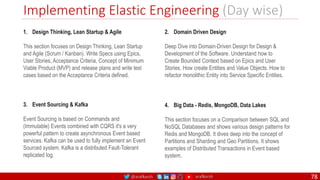
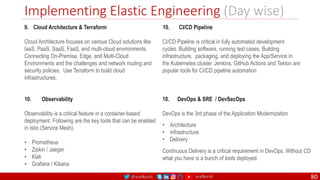
The document outlines a comprehensive approach to creating elastic engineering teams for cloud-native application development, emphasizing a business capability-centric design. It discusses the roles, objectives, and architectural frameworks (such as microservices and event sourcing) necessary for facilitating faster market entry and continuous delivery in software development. Additionally, the document explores the evolution of cloud technology and the importance of DevSecOps as a cultural approach to unite development, security, and operations.



![@arafkarsh arafkarsh
Agile
Scrum (4-6 Weeks)
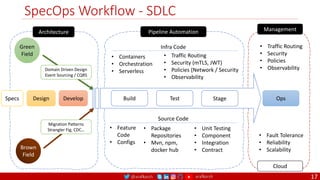
Developer (Migration – Brown Field or Green Field) Journey
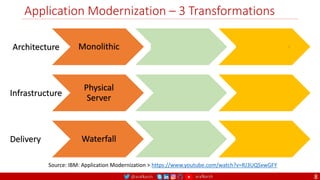
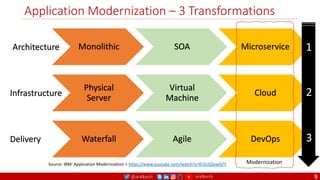
Monolithic
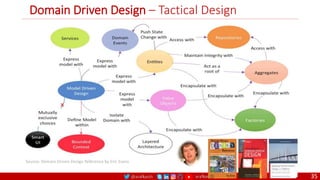
Domain Driven Design
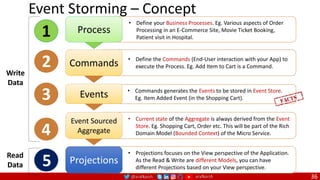
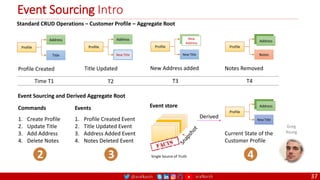
Event Sourcing and CQRS
Waterfall
Optional
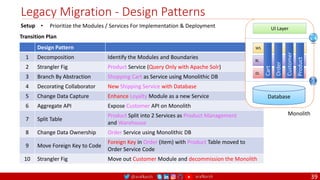
Design
Patterns
Continuous Integration (CI)
6/12+ Months
Enterprise Service Bus
Relational Database [SQL] / NoSQL
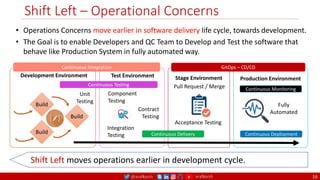
Development QA / QC Ops
7
Microservices
Domain Driven Design
Event Sourcing and CQRS
Scrum / Kanban (1-5 Days)
Mandatory
Design
Patterns
Infrastructure Design Patterns
Continuous Integration - CI
DevOps
Event Streaming / Replicated Logs
SQL NoSQL
Continuous Delivery - CD
Container Orchestrator Service Mesh](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/elastic-engineering-v06-m-proposal-220407081906/85/Elastic-Engineering-7-320.jpg)