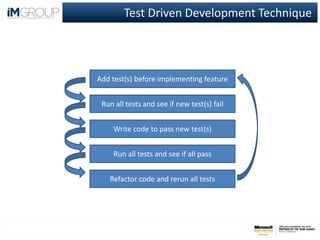
Unit testing is a software development method that involves writing small pieces of code called units to test individual functions or components. This helps ensure code works as intended and finds bugs early. Key benefits of unit testing include keeping code simple, making code more maintainable and robust, and providing regression tests. However, developers sometimes avoid unit testing due to perceptions that it is tedious or not valuable. Tools like NUnit and Visual Studio support automating unit tests. Test-driven development is a technique where tests are written before code to specify desired behavior.









![NUnit Attributes
• [TestFixture]
• [Test]
• [TestFixtureSetUp]
• [TestFixtureTearDown]
• [Setup]
• [TearDown]
• [ExpectedException]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/137c943d-47d7-4a90-afae-565c807418a5-151123214229-lva1-app6891/85/Testing-11-320.jpg)