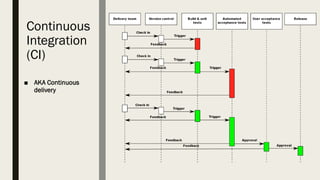
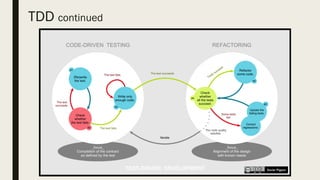
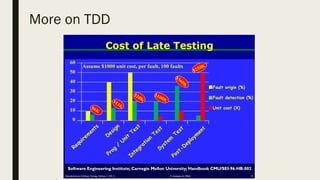
The document discusses various software development practices, focusing on methodologies such as Test Driven Development (TDD), Domain Driven Development (DDD), Continuous Integration (CI), and Extreme Programming (XP). It outlines the phases of the software development life-cycle and emphasizes the importance of effective testing strategies, including the advantages of TDD and Acceptance Test-Driven Development (ATDD). Additionally, it provides tips for writing and managing unit tests, highlighting best practices for maintaining code quality.