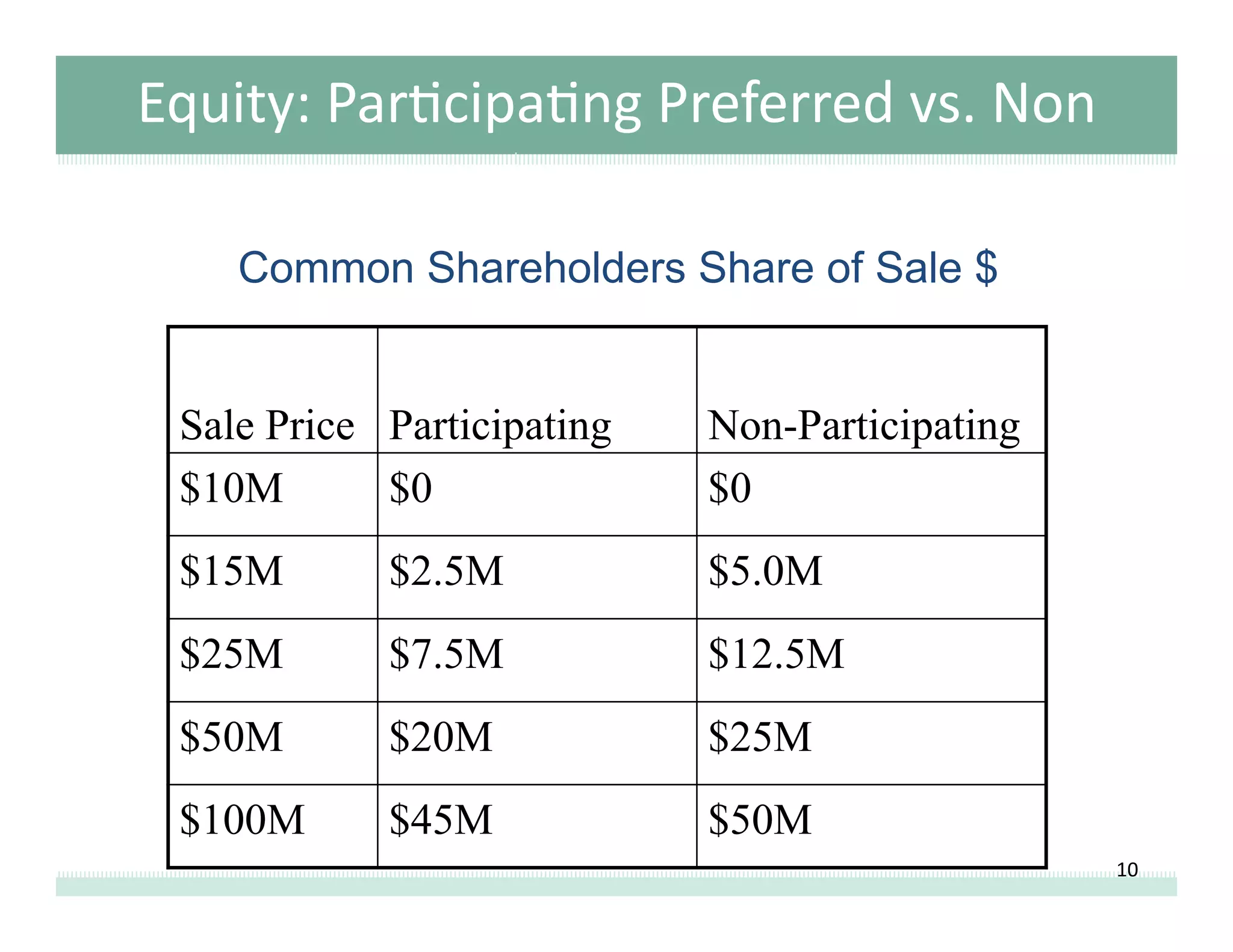
This document provides an overview of term sheets and common early-stage securities such as convertible debt and preferred stock. It discusses the key features and economic considerations of preferred stock, including liquidation preferences, anti-dilution provisions, and governance rights. Additionally, it outlines terms related to equity pricing, voting control, and stockholder rights.