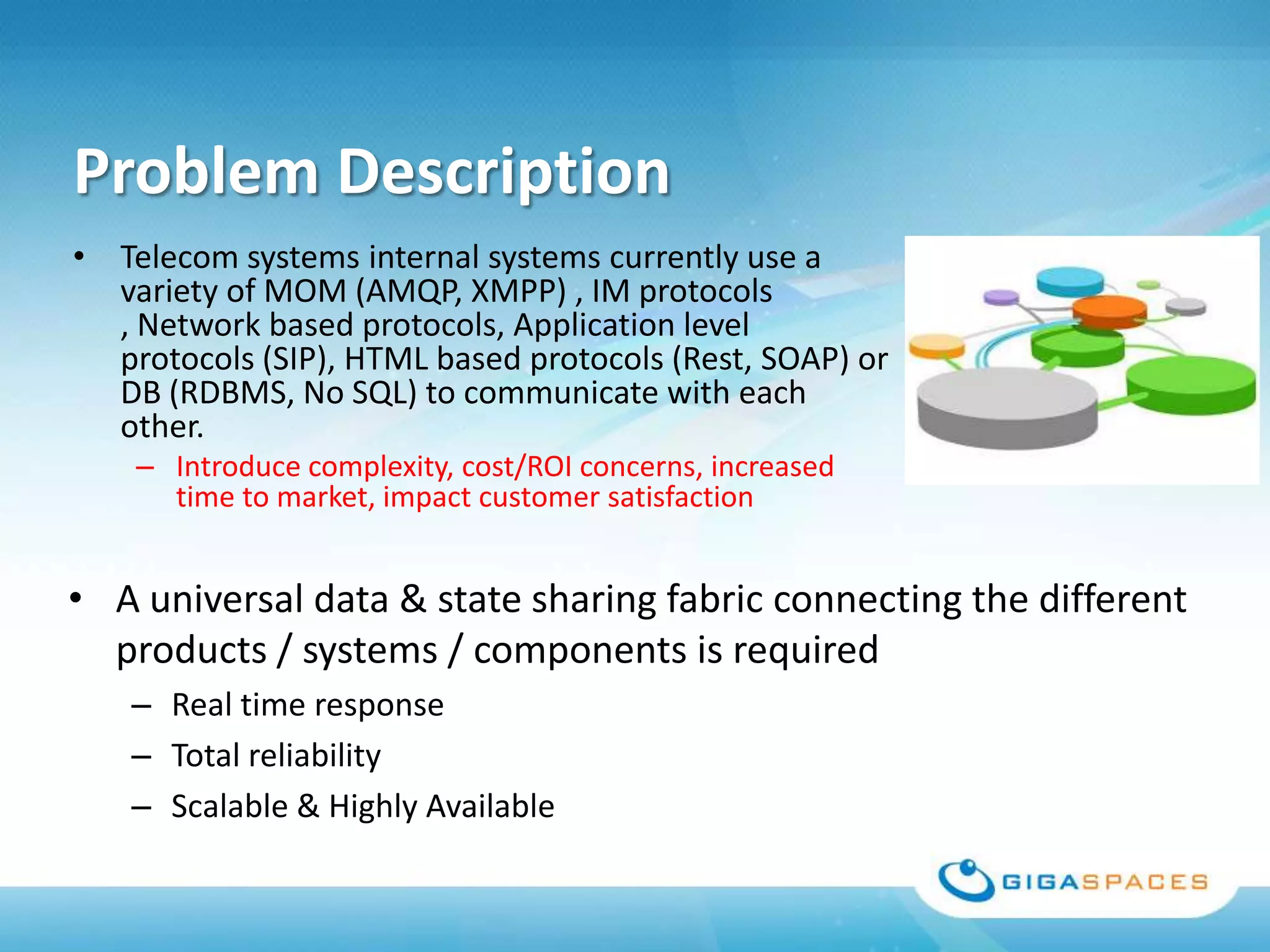
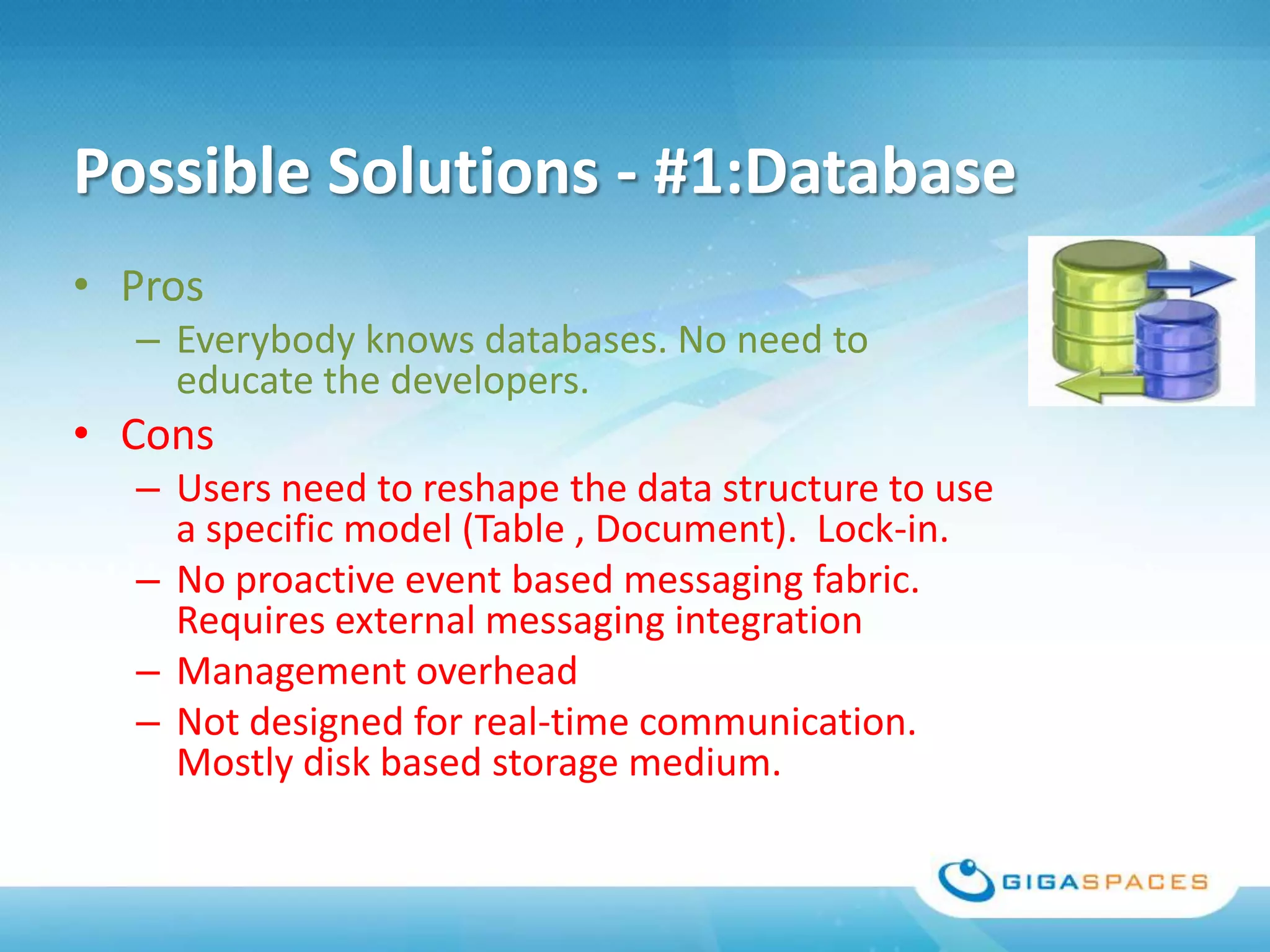
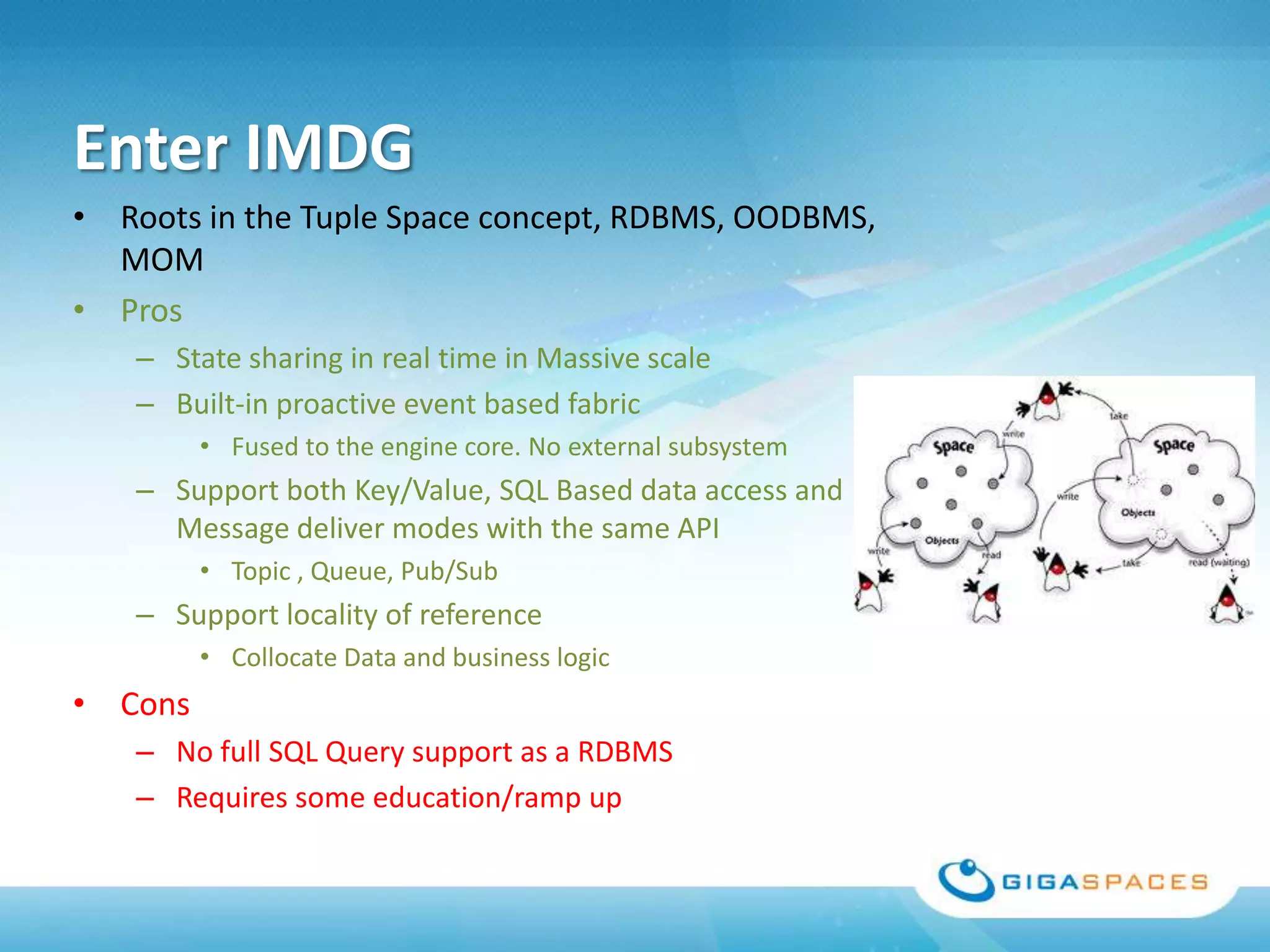
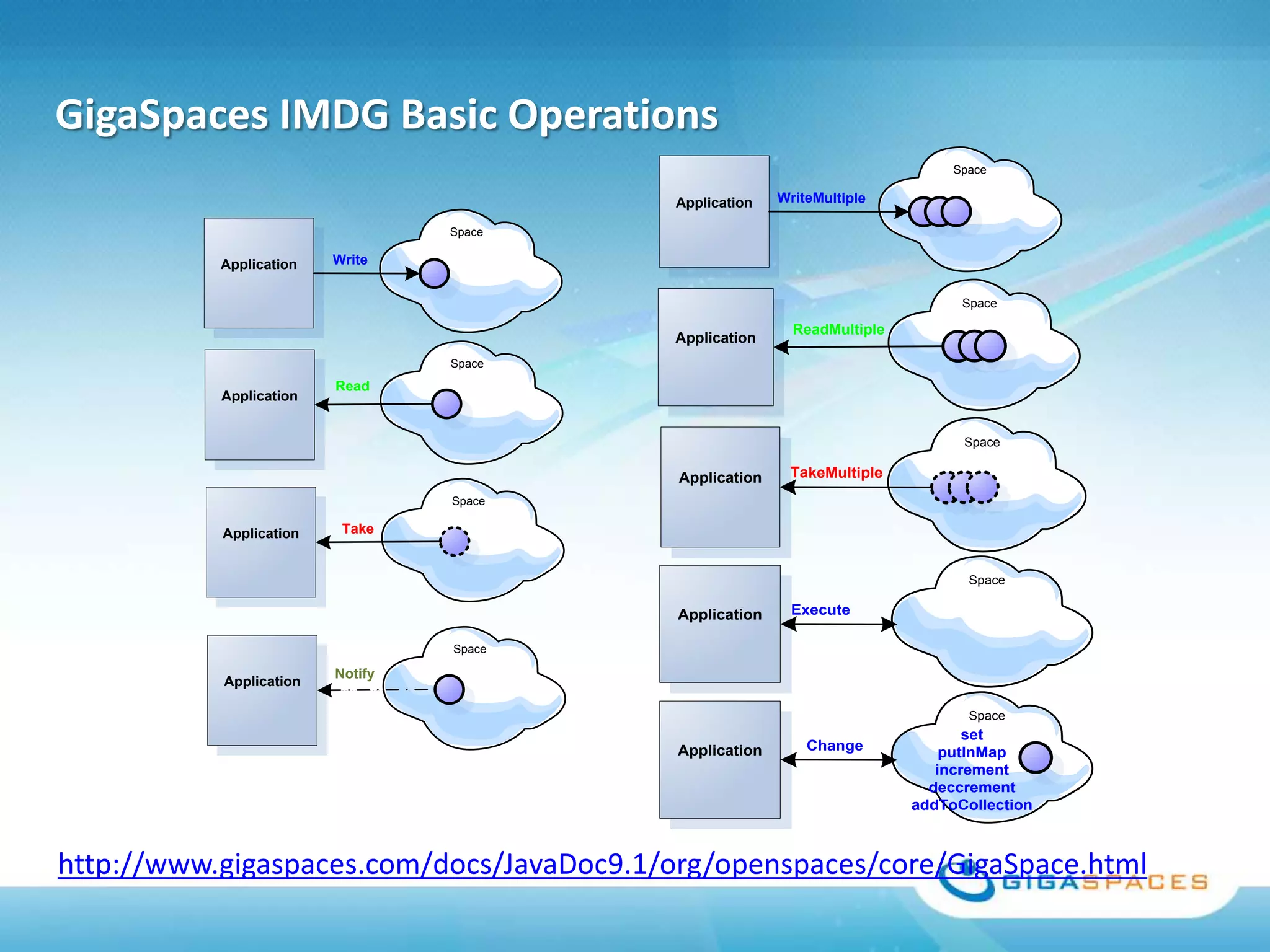
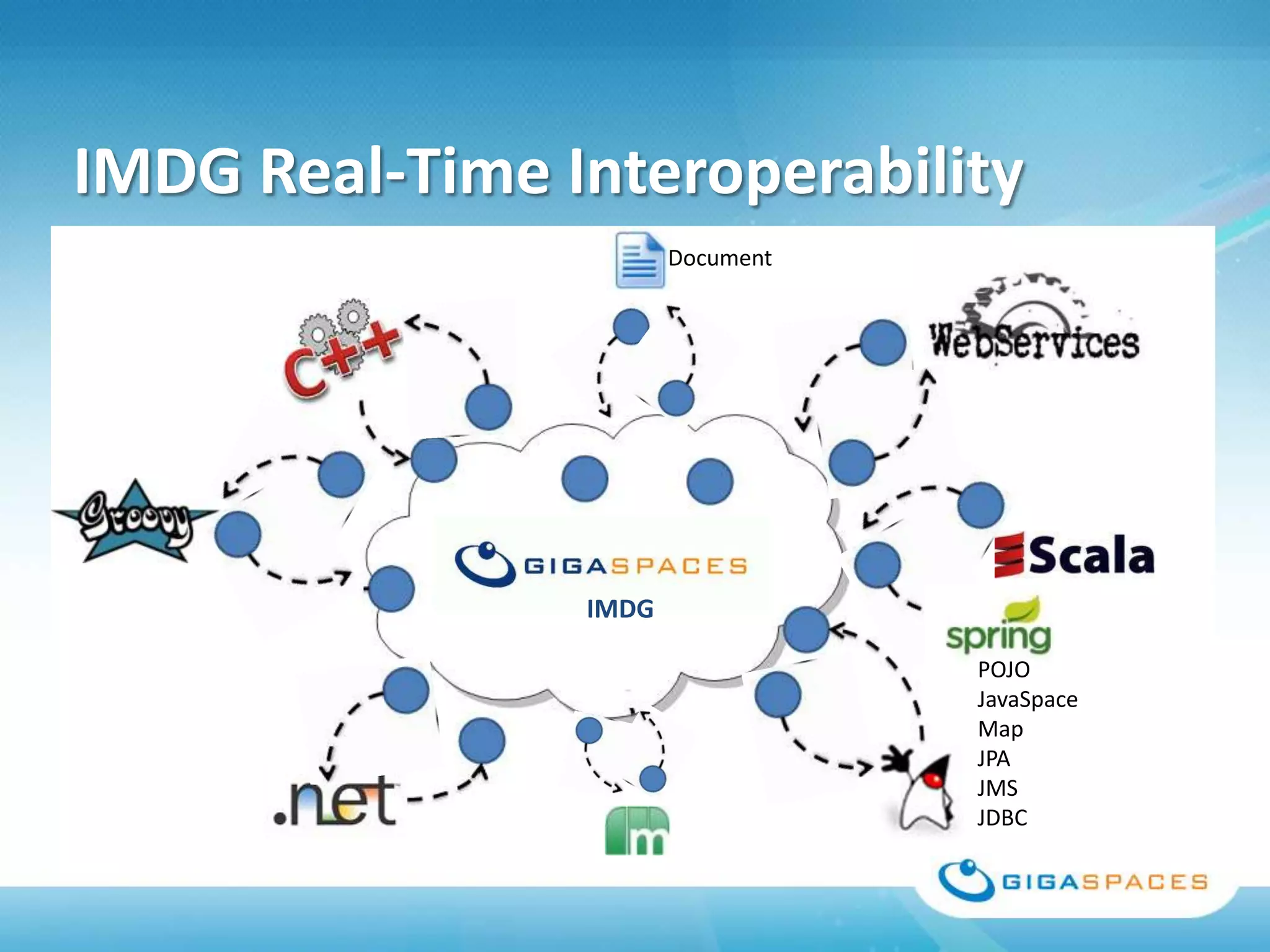
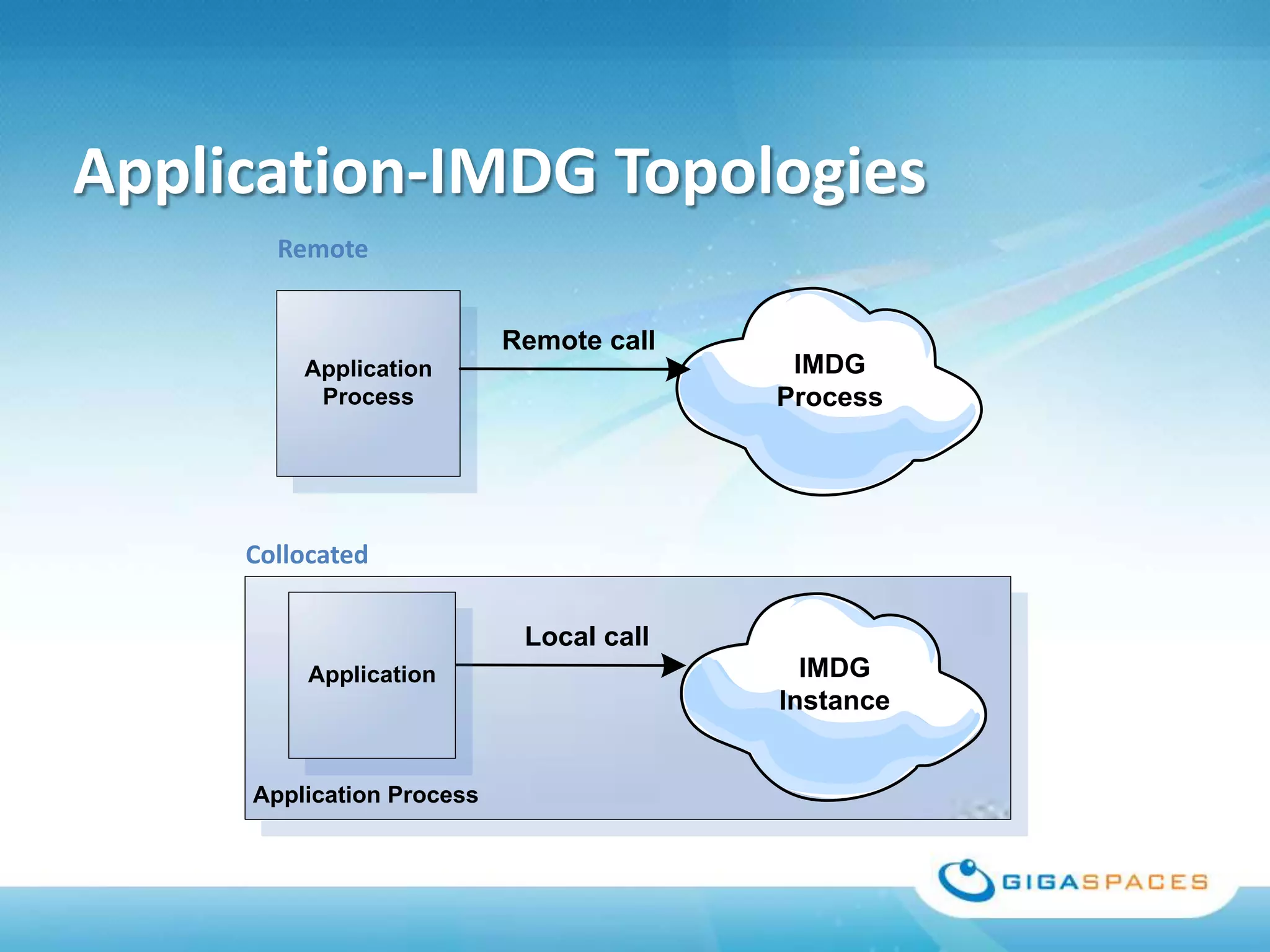
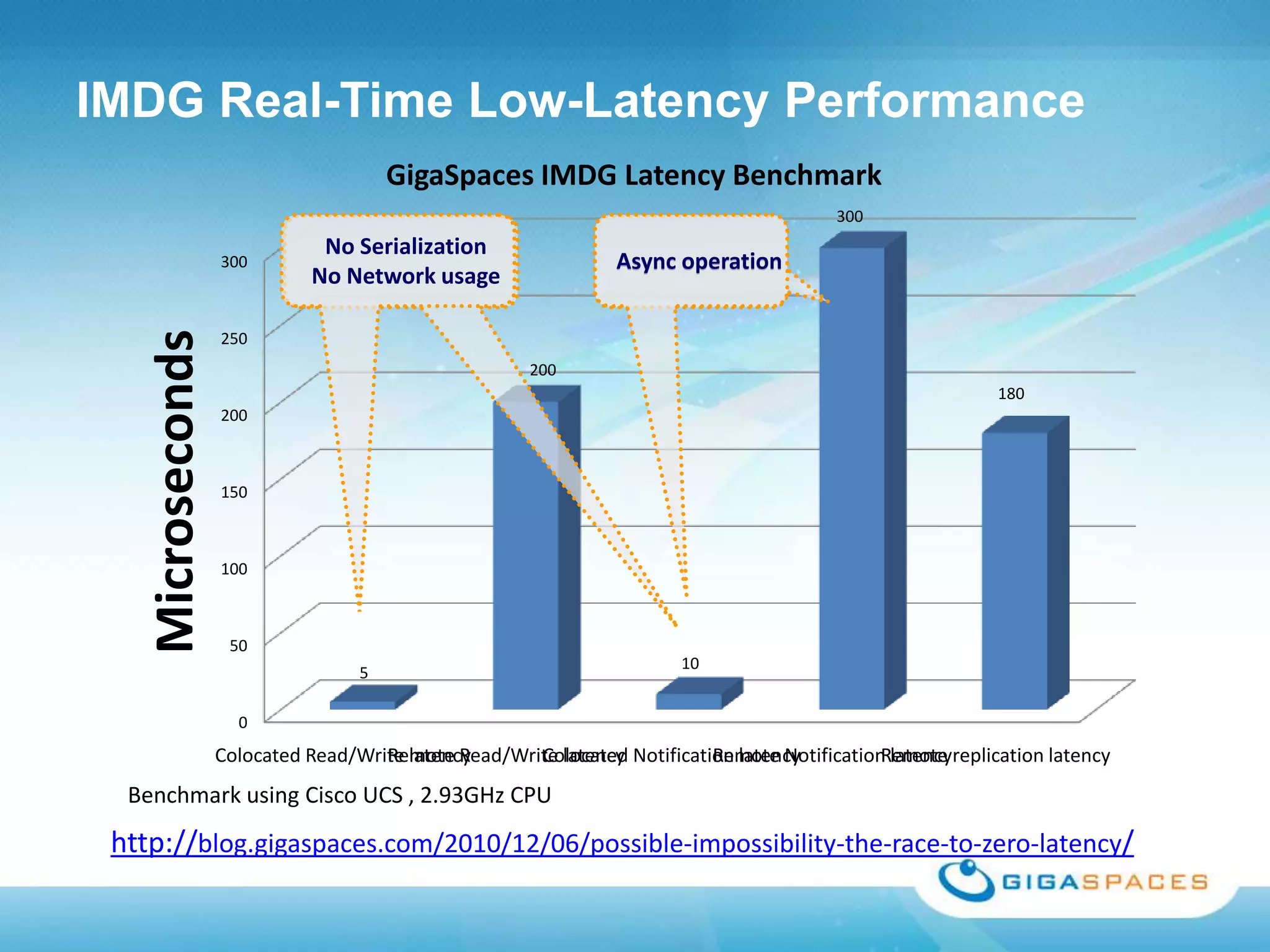
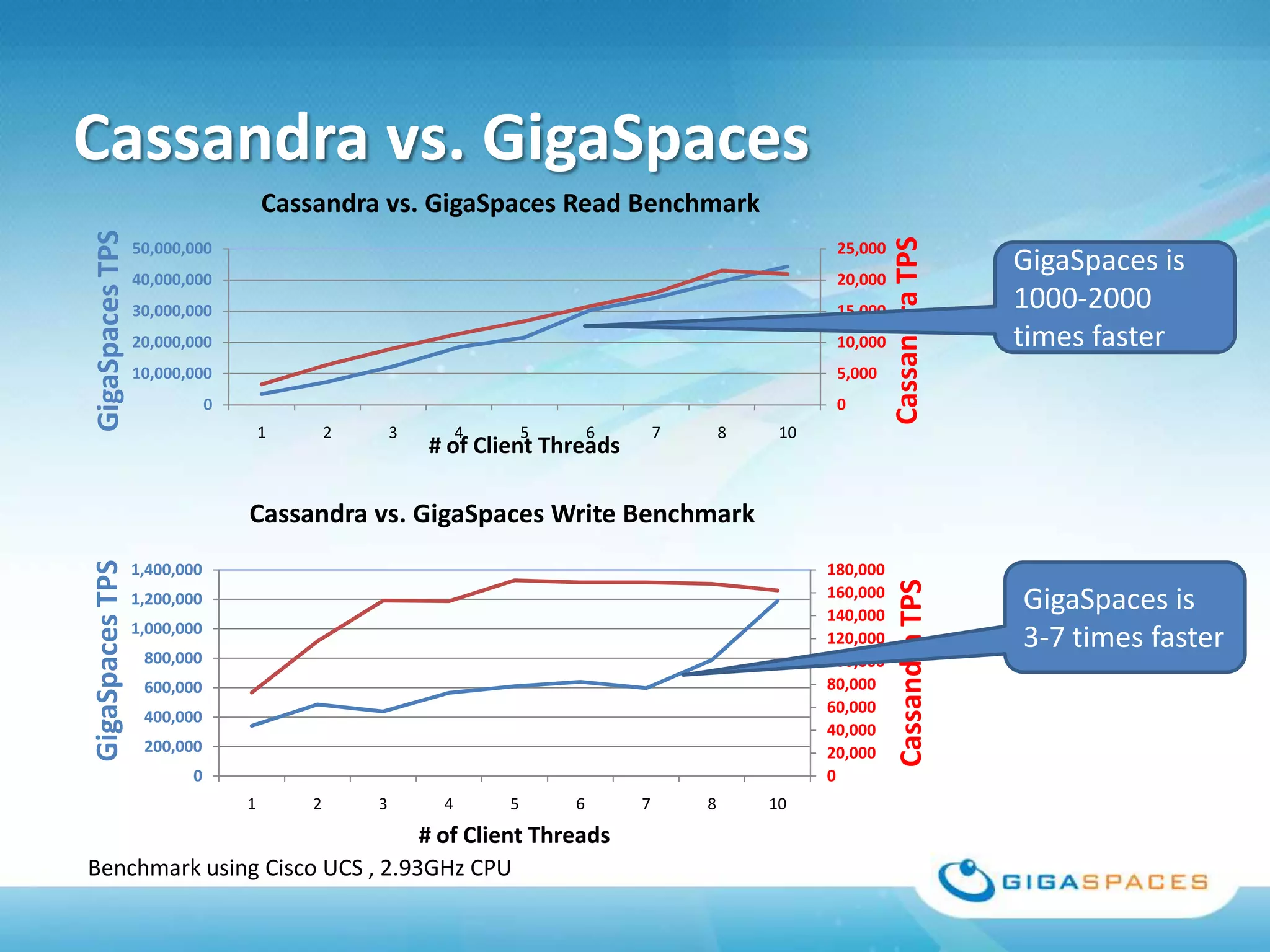
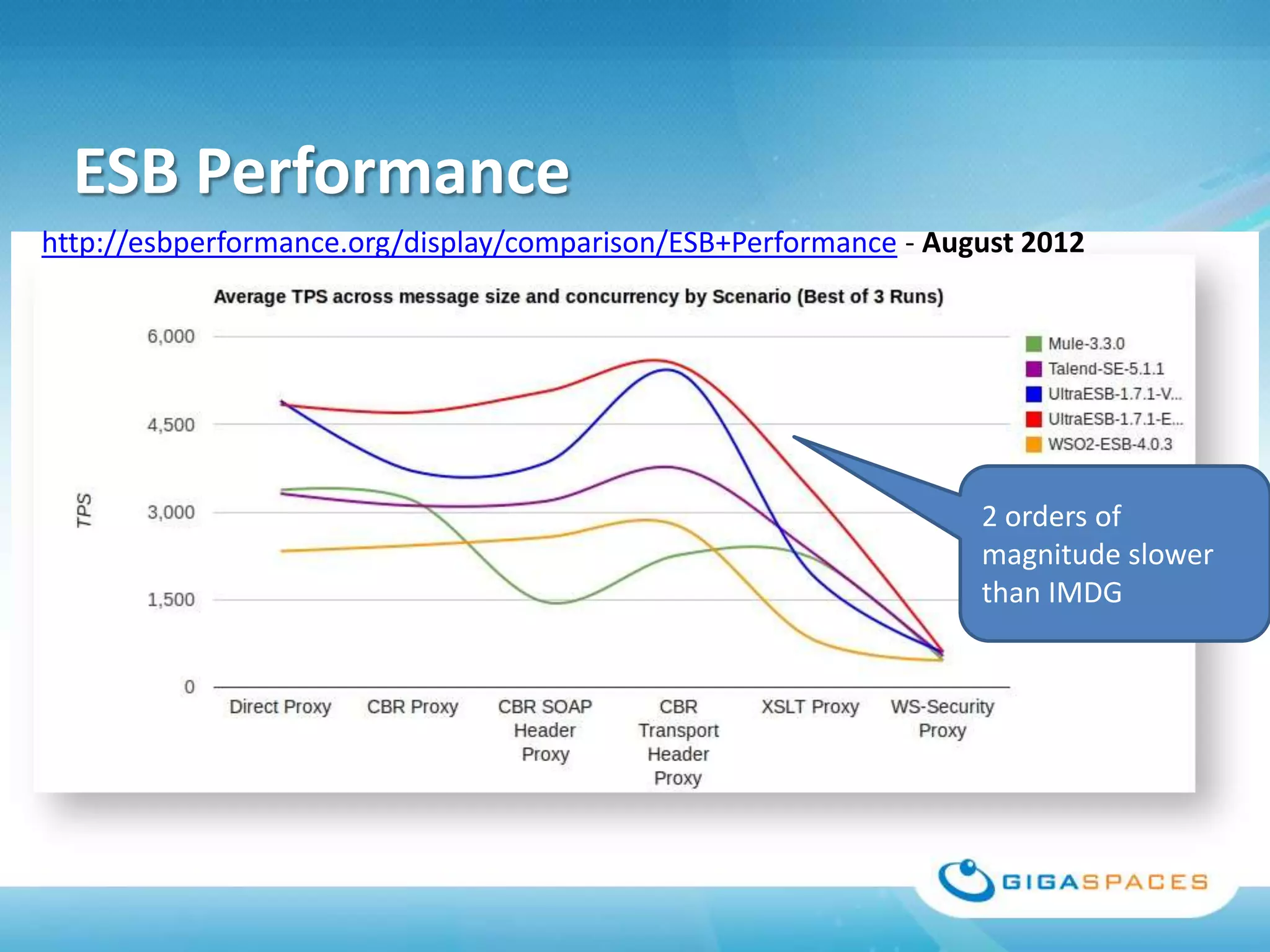
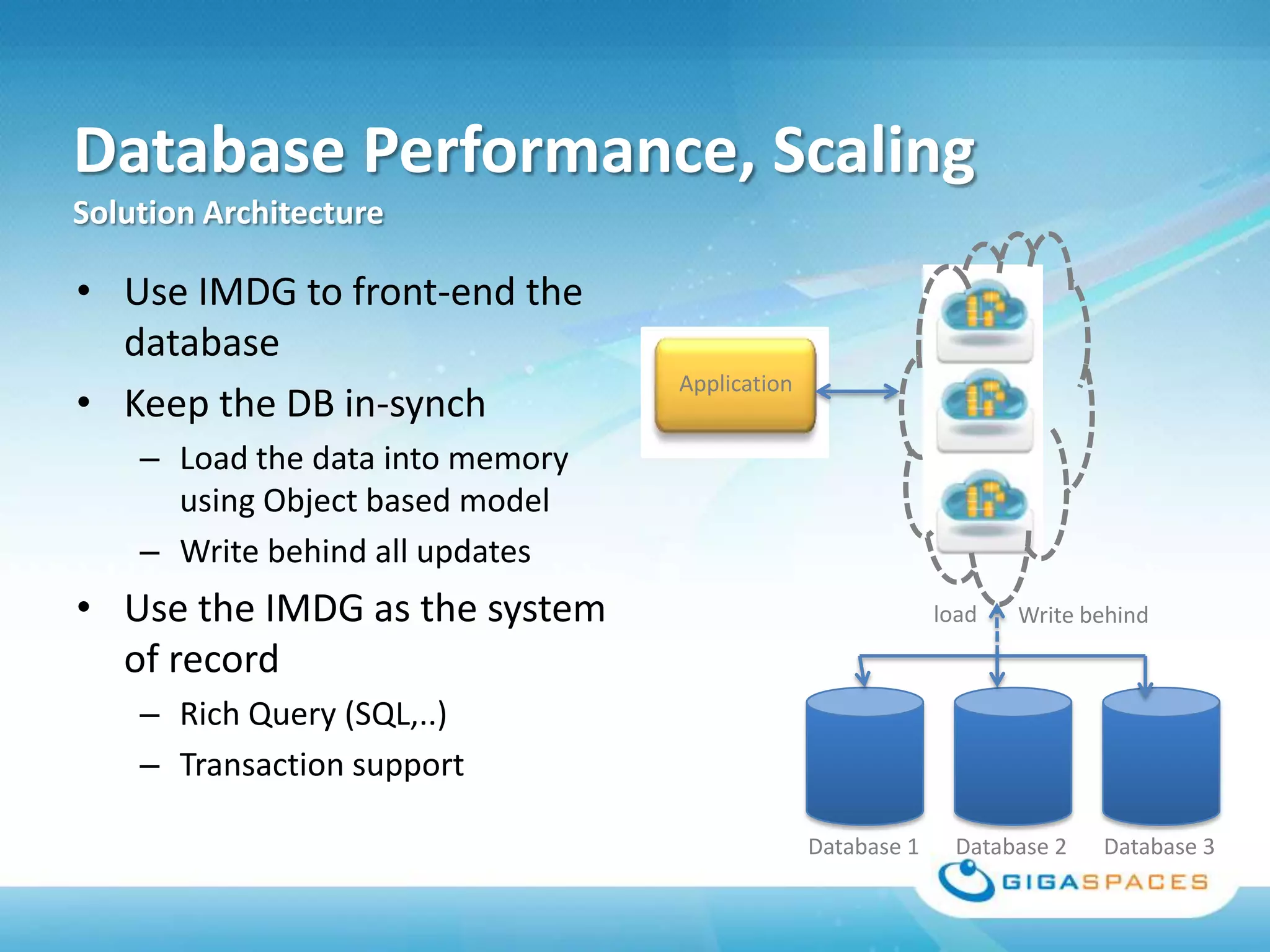
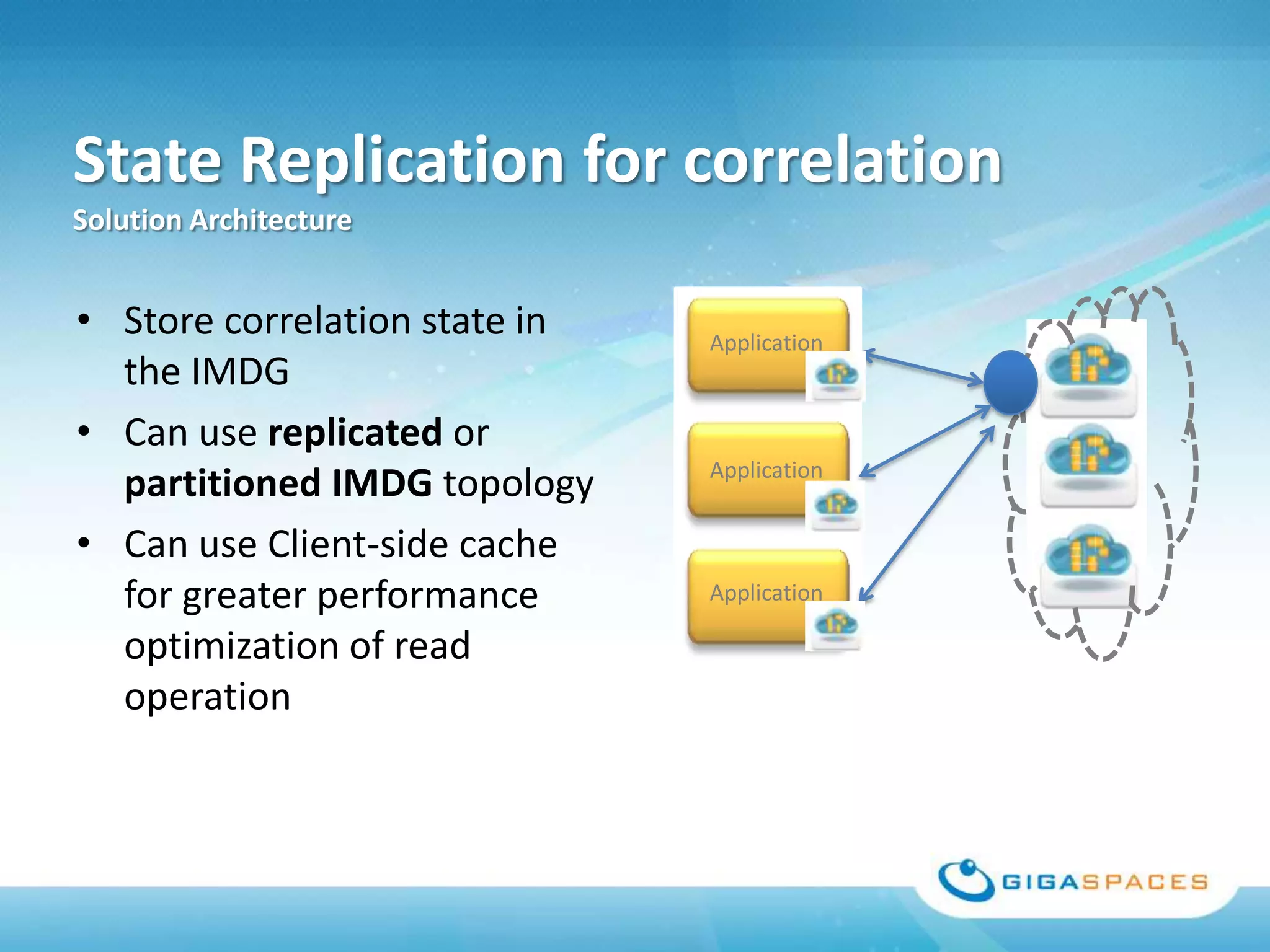
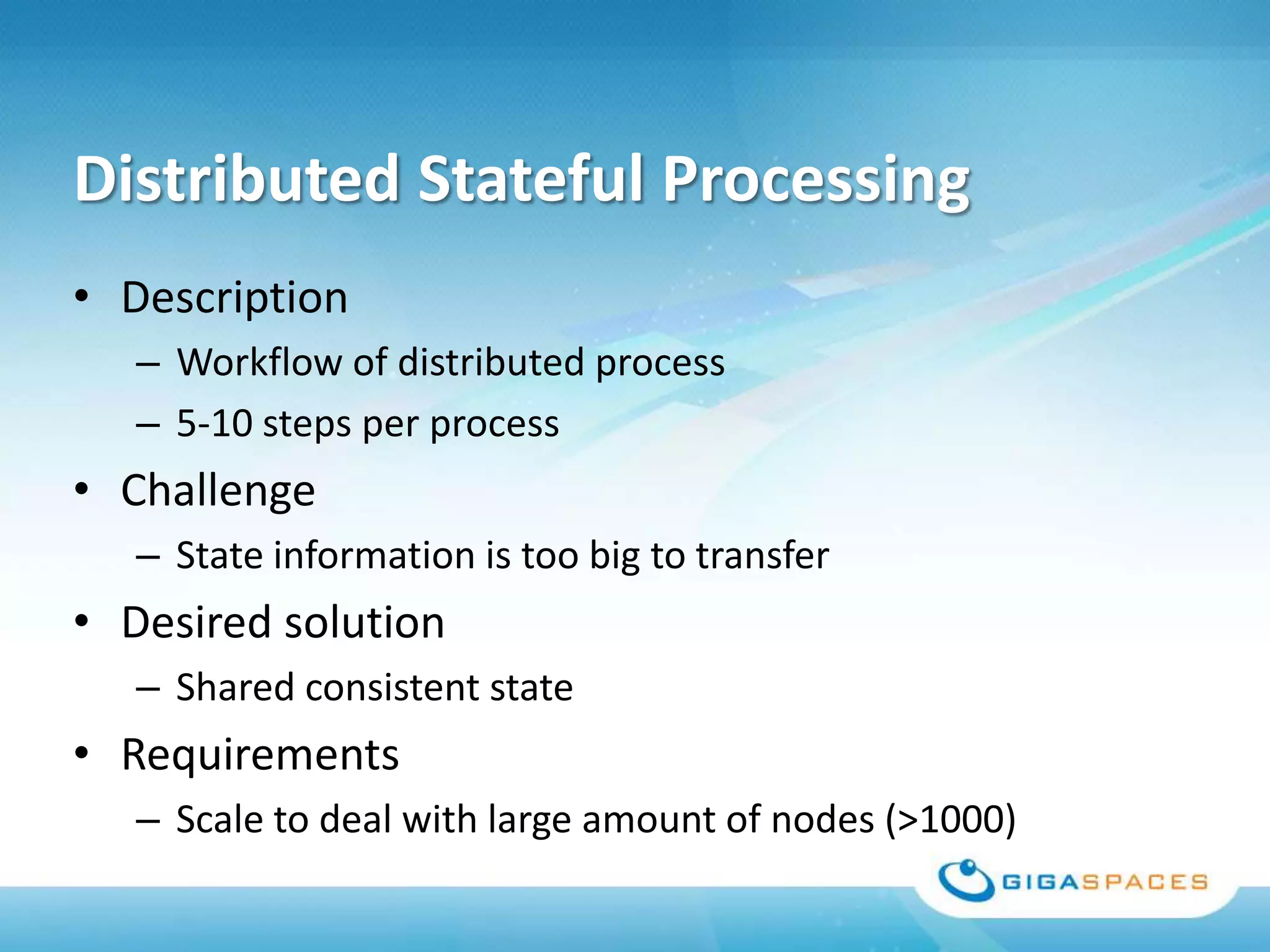
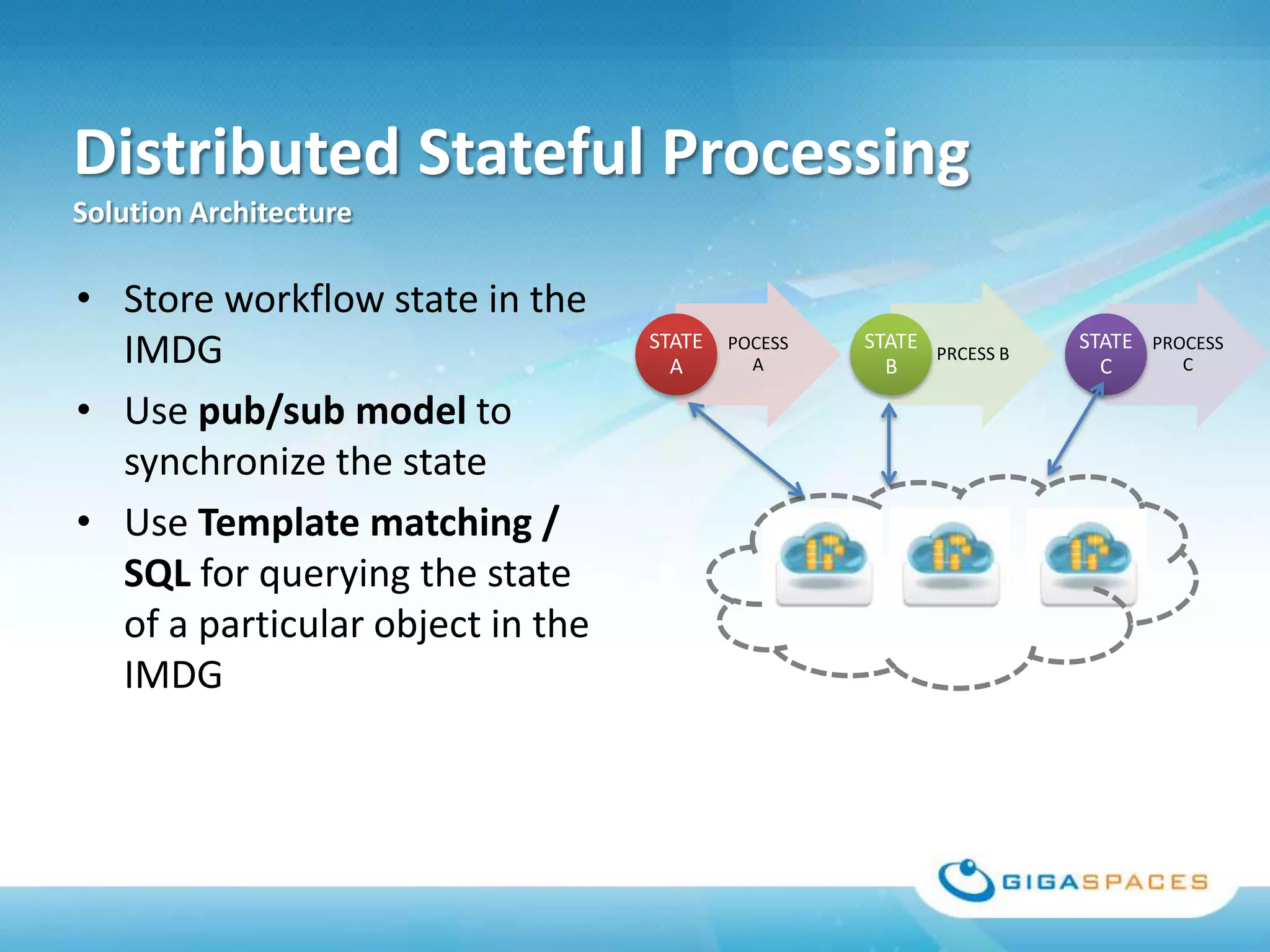
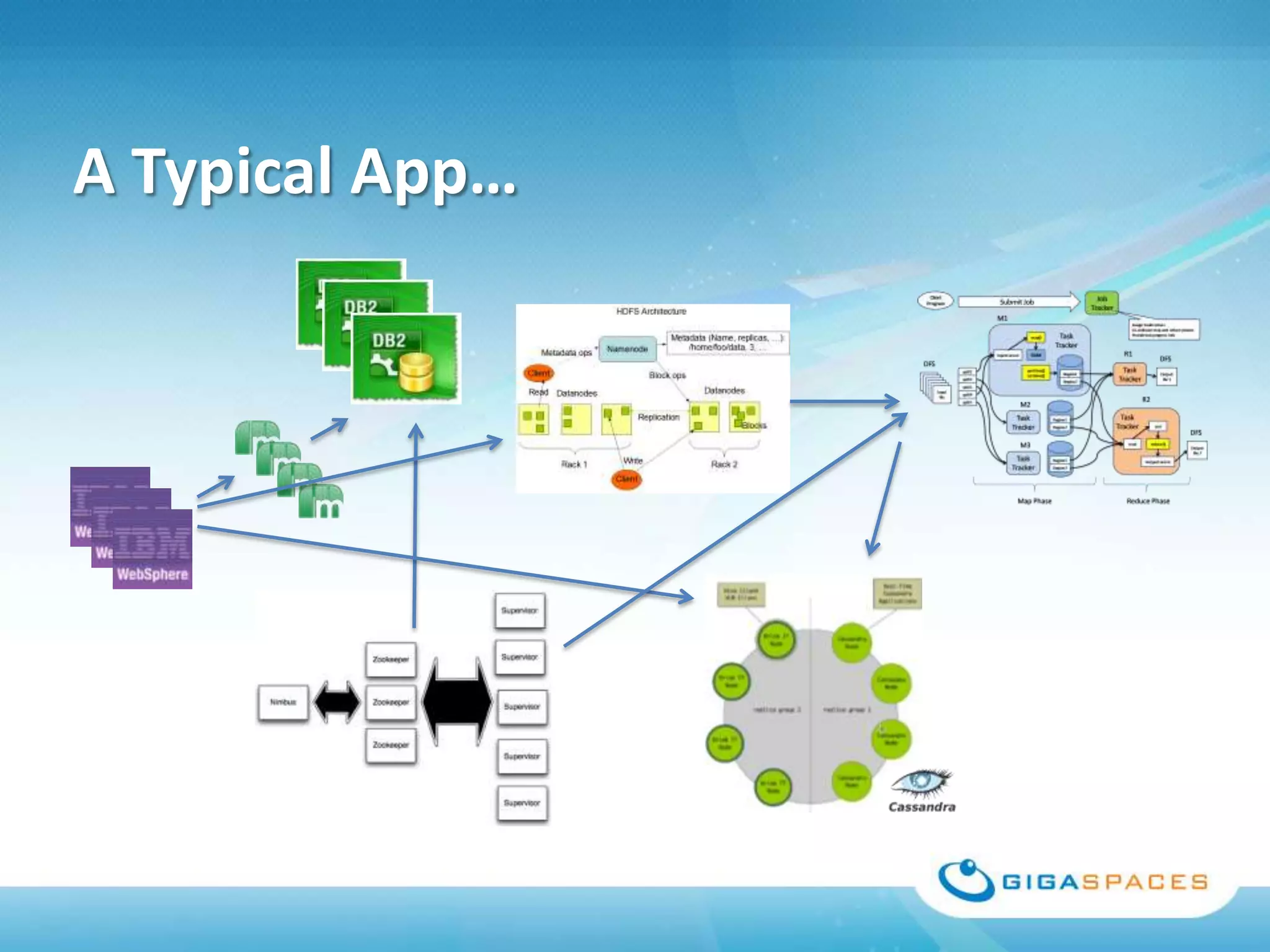
A universal Data & State sharing Fabric can help address the problem of different telecom systems using various protocols for communication by providing a shared fabric for real-time data and state sharing across systems. Existing solutions like databases and ESBs have drawbacks like being disk-based instead of real-time, lacking state sharing capabilities, and lower performance. IMDG provides a unified solution by combining the benefits of databases and ESBs while avoiding their limitations, allowing different systems and components to share data and state in real-time at massive scale with low latency.