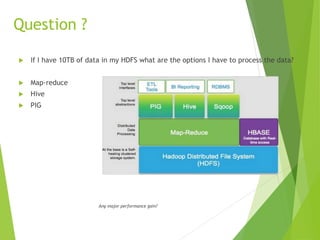
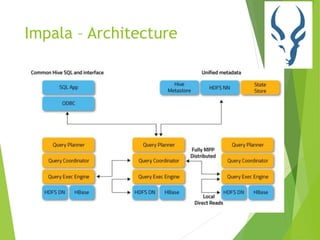
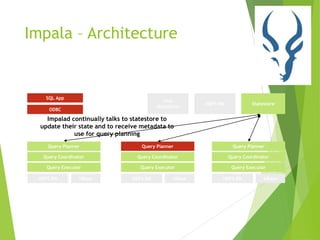
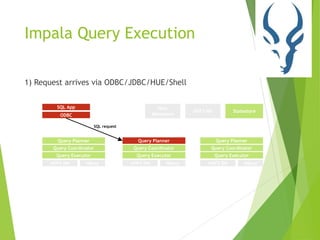
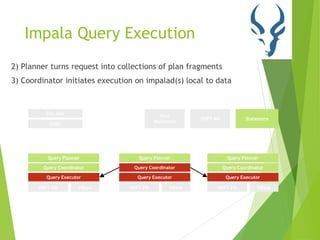
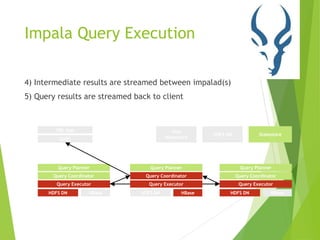
This document provides an overview of Cloudera Impala, which is an interactive SQL query engine for processing large datasets stored in HDFS. It discusses how Impala addresses the challenges of running analytical queries over petabytes of data in near real-time without much effort. The architecture of Impala is explained, which involves Impala daemons, a state store, and distributed query planning and execution. Key features and benefits of Impala like its scalability, low latency, and ease of use are also highlighted.