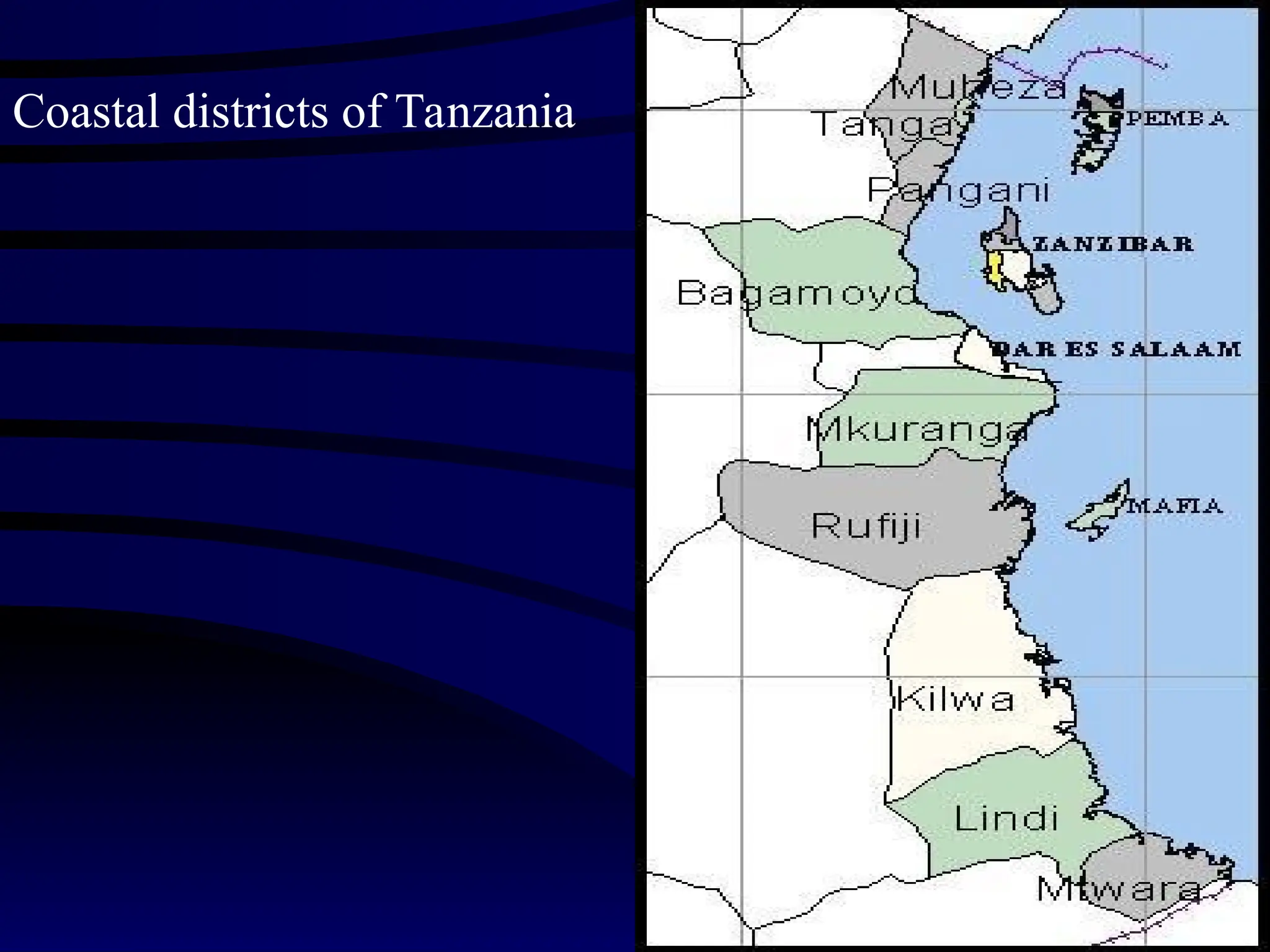
The document discusses the importance of coastal tourism in Tanzania, highlighting its economic benefits and the need for sustainable practices to protect the environment. It outlines challenges such as environmental degradation, inadequate infrastructure, and socio-economic issues faced by local communities. To address these, various initiatives and guidelines have been proposed to promote responsible tourism development while improving livelihoods in coastal areas.










![Problem Analysis [cont]
• Social-economic problems:
– Rural coastal communities are still poor,
depend on smallholder farming, small-
scale trade, livestock husbandry etc.
– Low level of participation by local
communities in tourism planning and
management processes
– Unemployment and lack of sufficient
knowledge about tourism business](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcmp-250103073225-f4de9ad9/75/TCMP-pptkjlkjlkjlkjsdaasddd-sdfda-asddda-12-2048.jpg)
![Problems[cont]
• Development Constraints:
– Inadequate access [International &
Internal flights]
– poor infrastructure esp. roads
– High costs of internal transport
– Poor services standard
– Poor quality tour and safari guides
– Lack of quality accommodation facilities](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tcmp-250103073225-f4de9ad9/75/TCMP-pptkjlkjlkjlkjsdaasddd-sdfda-asddda-13-2048.jpg)





