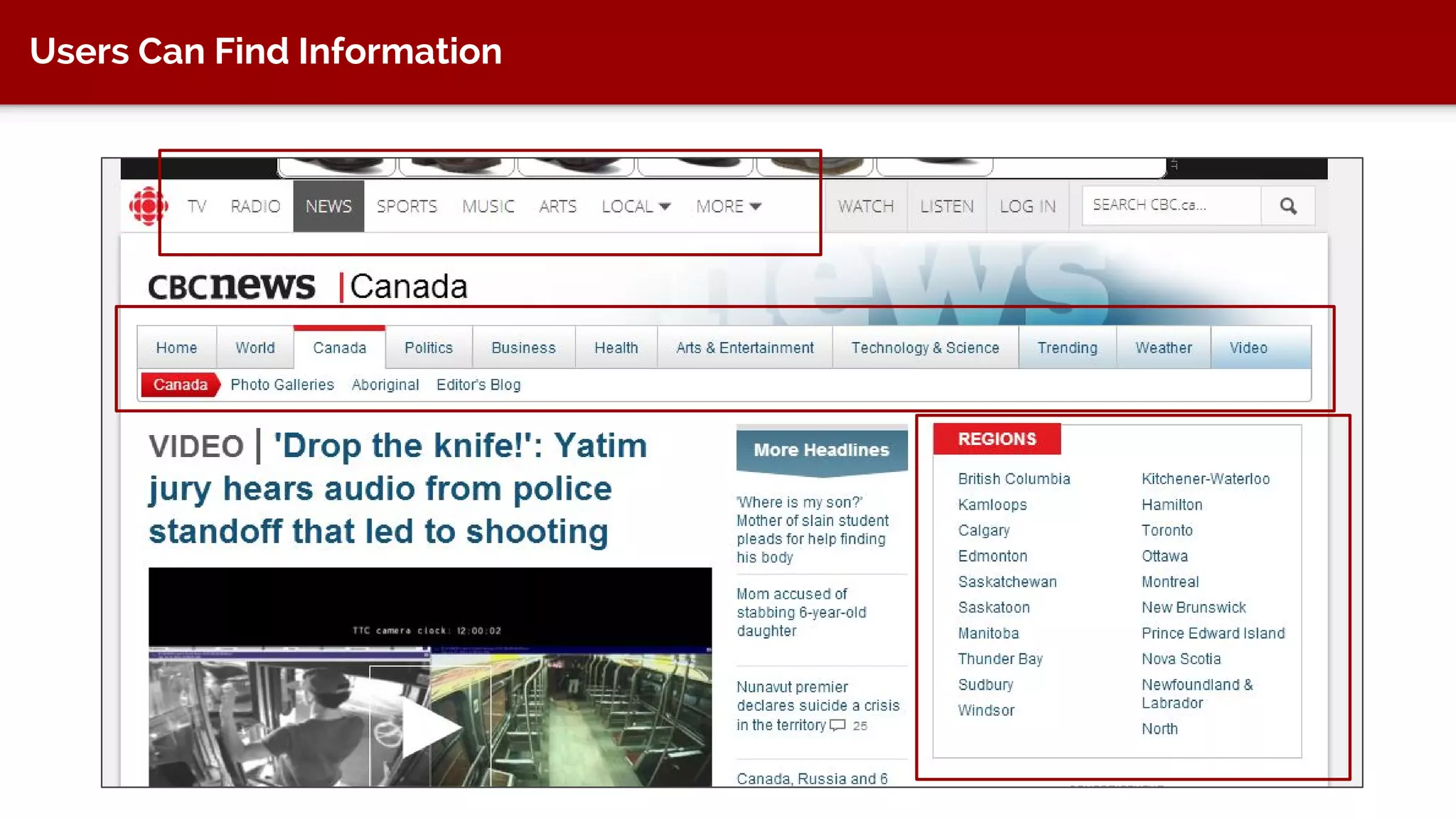
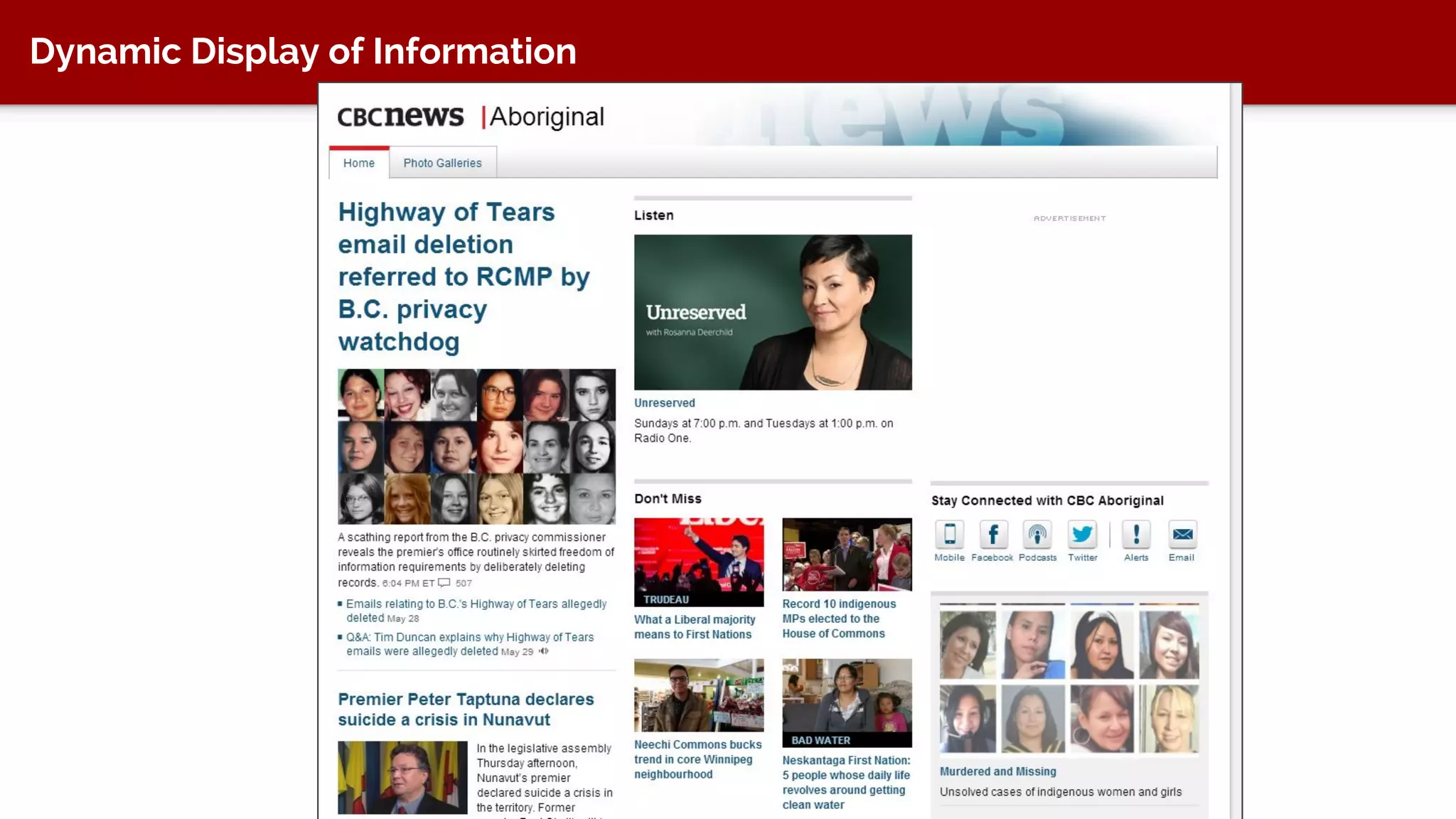
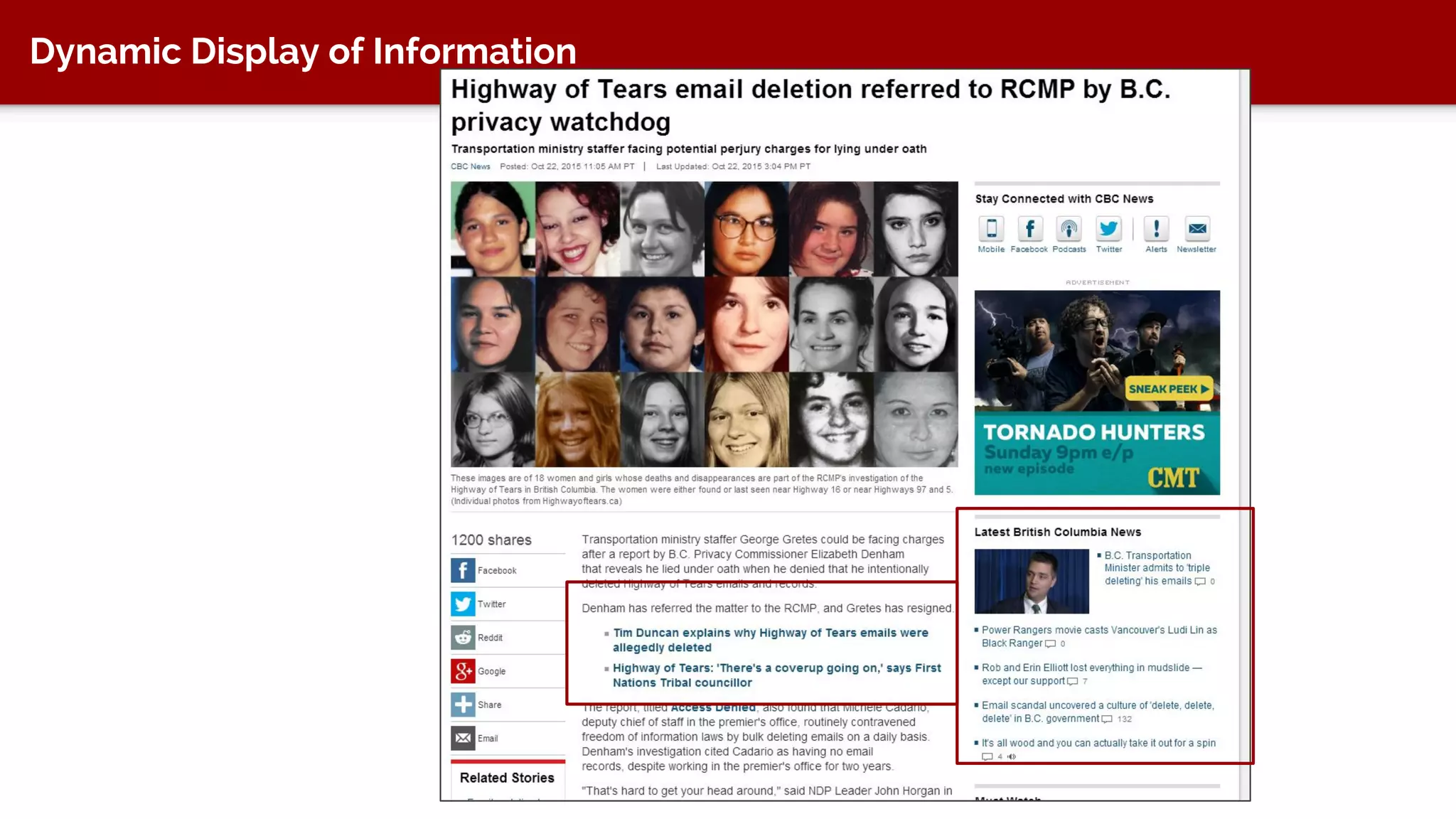
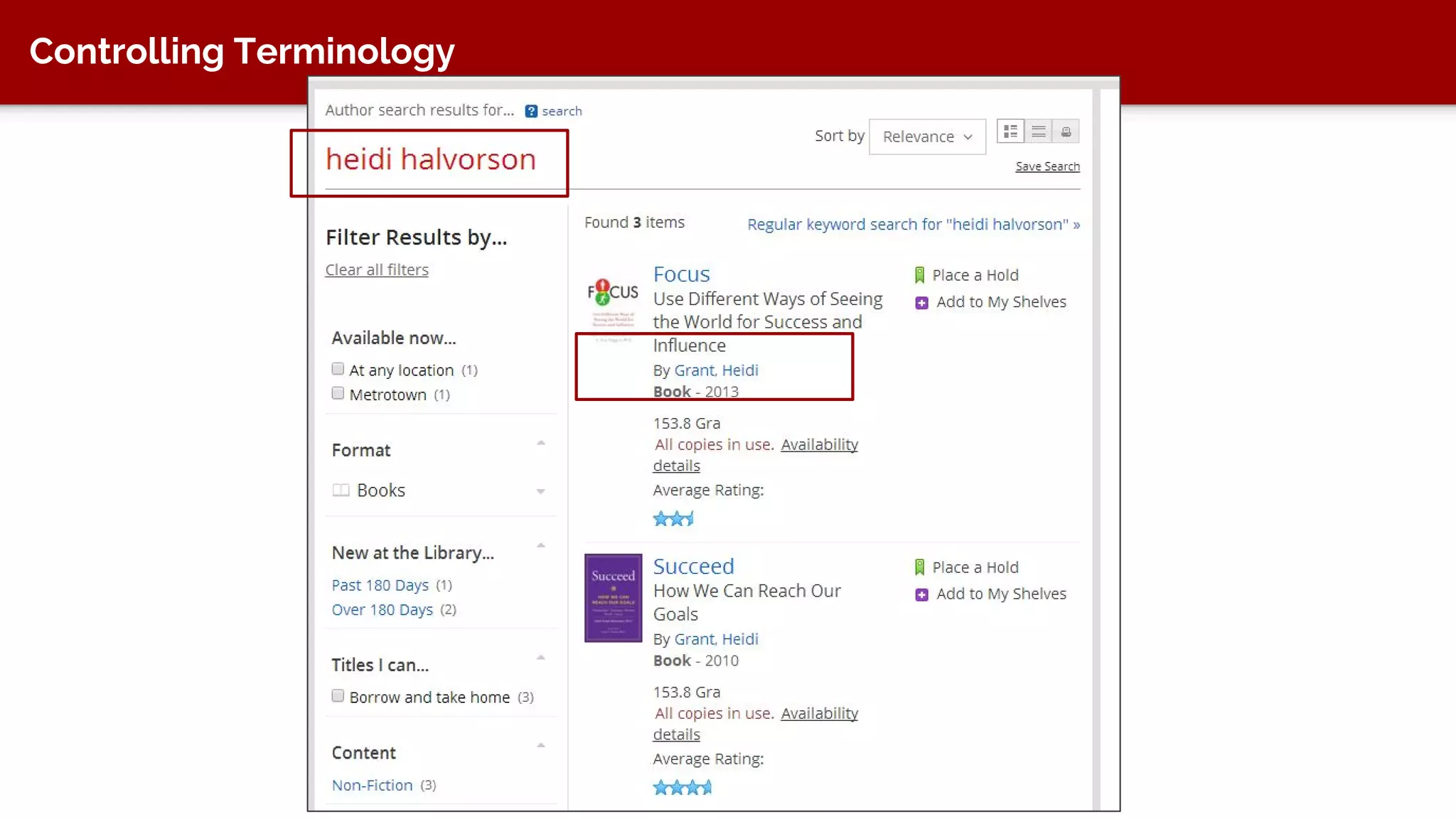
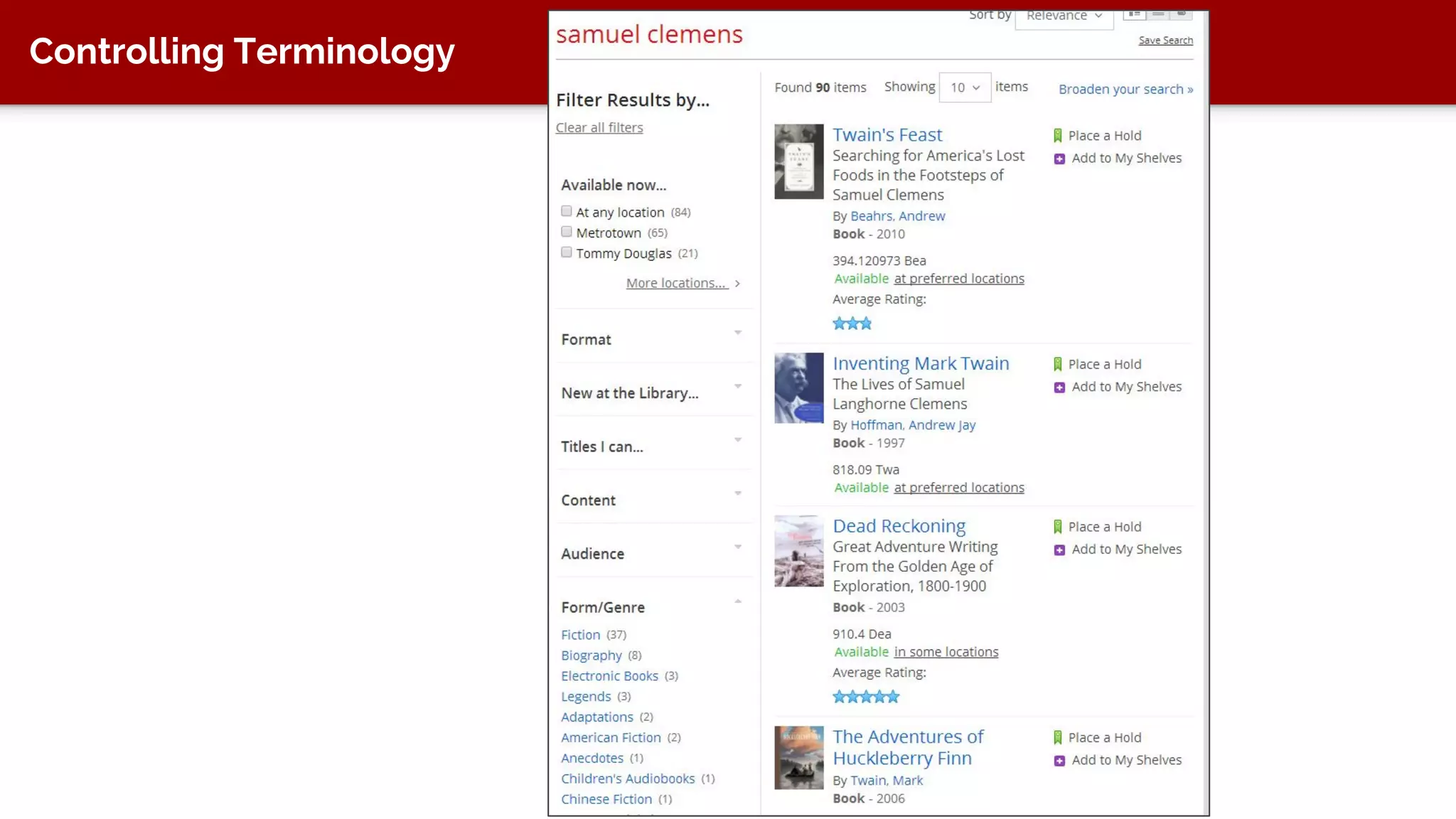
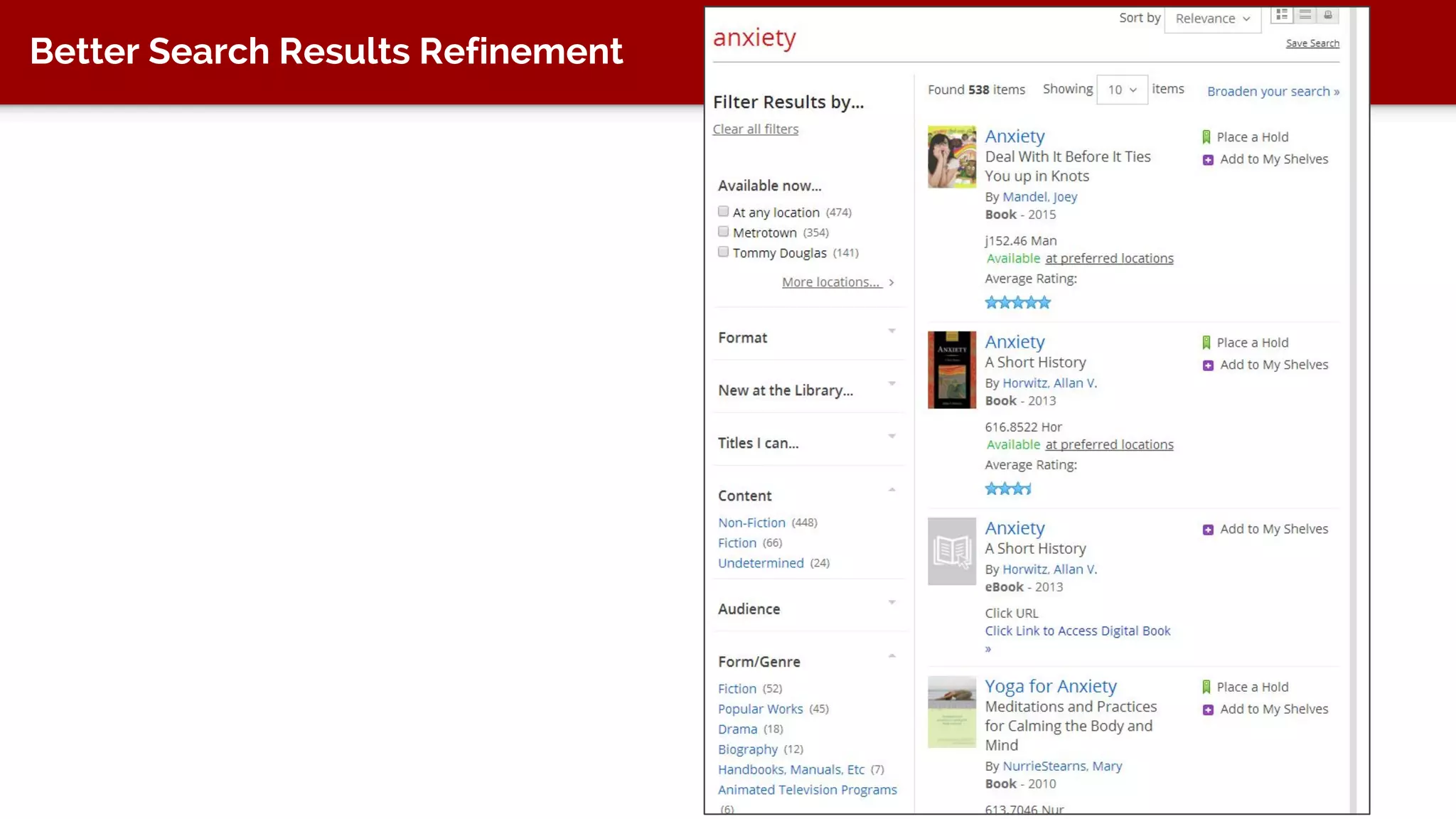
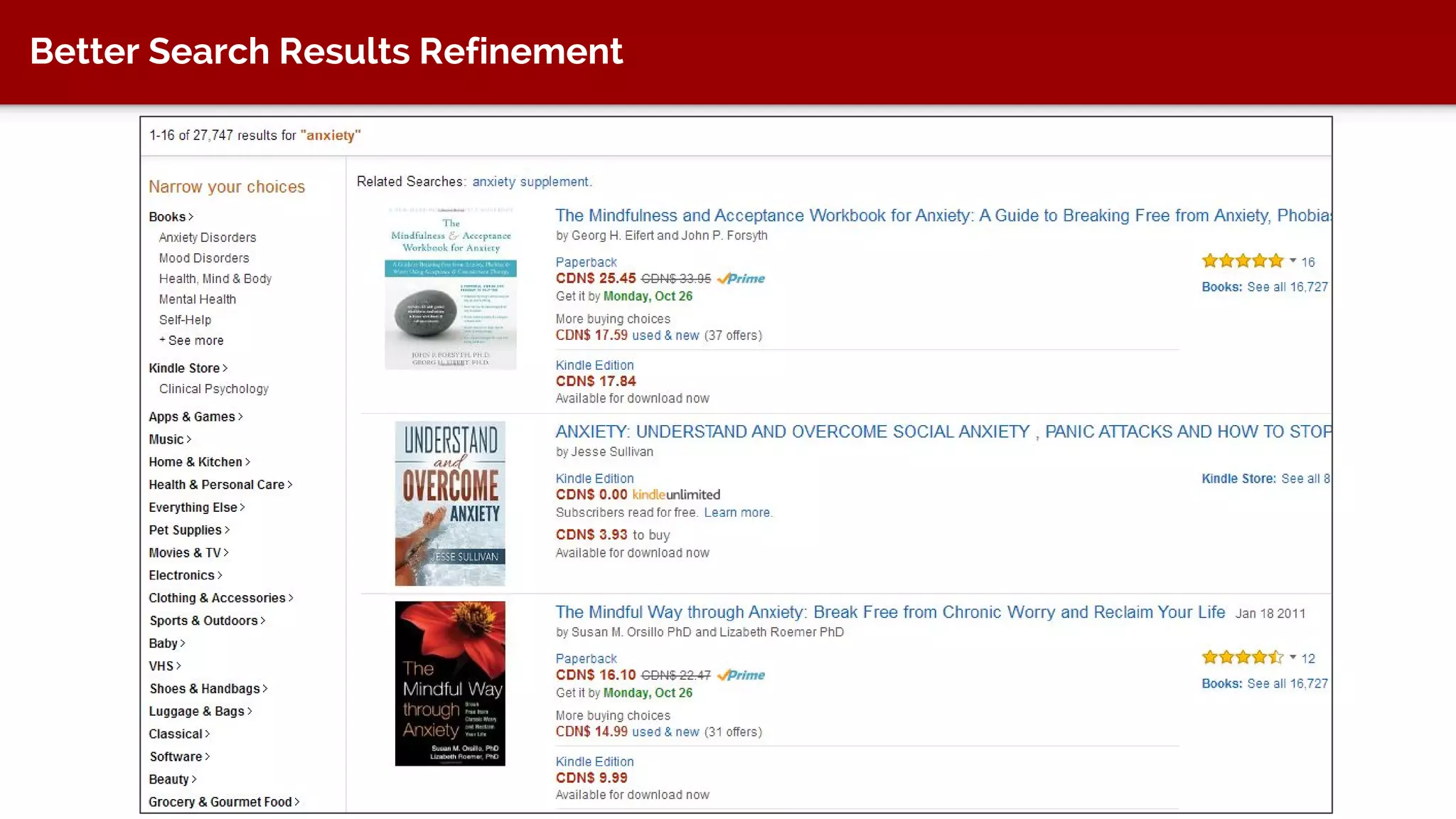
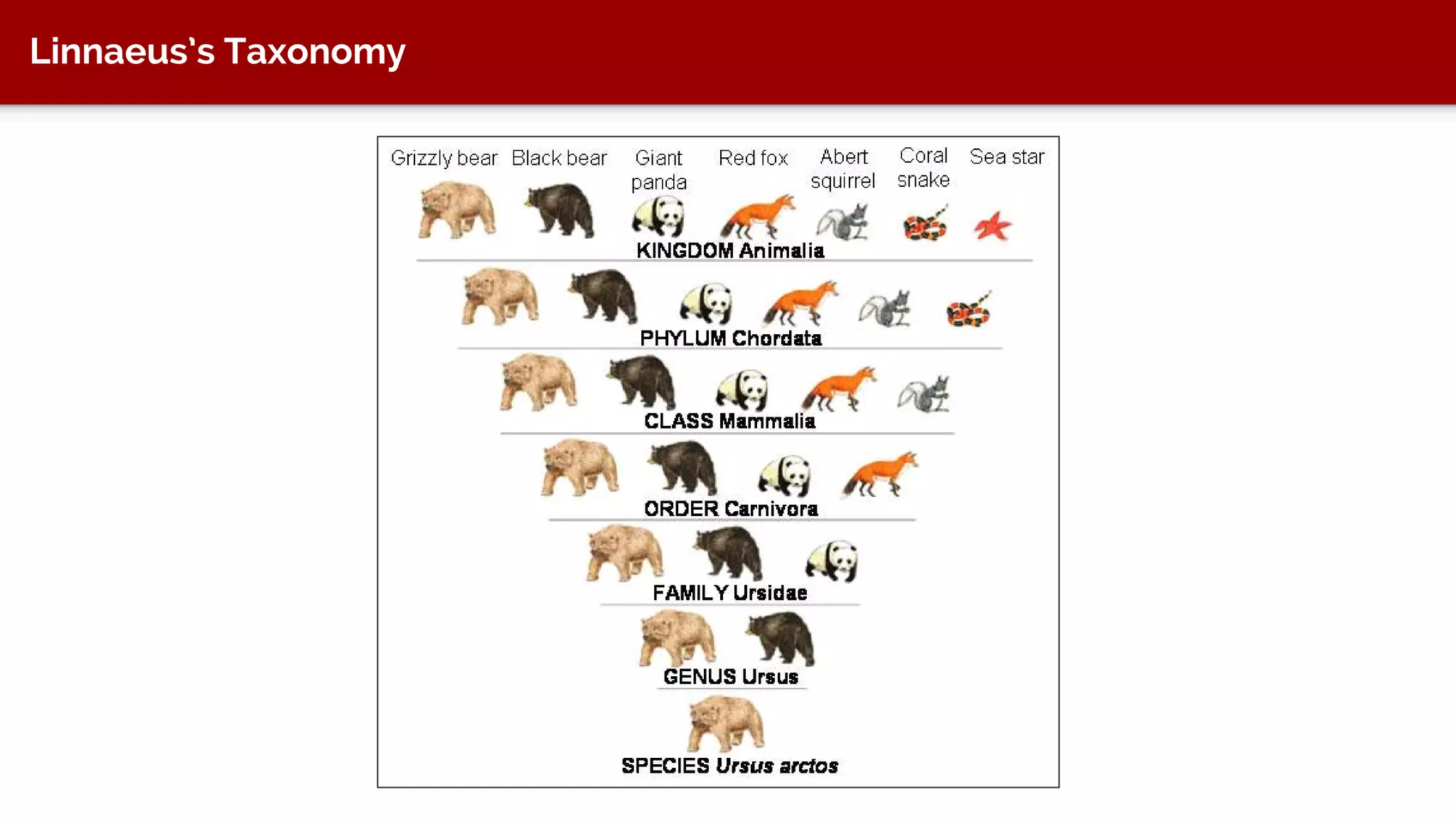
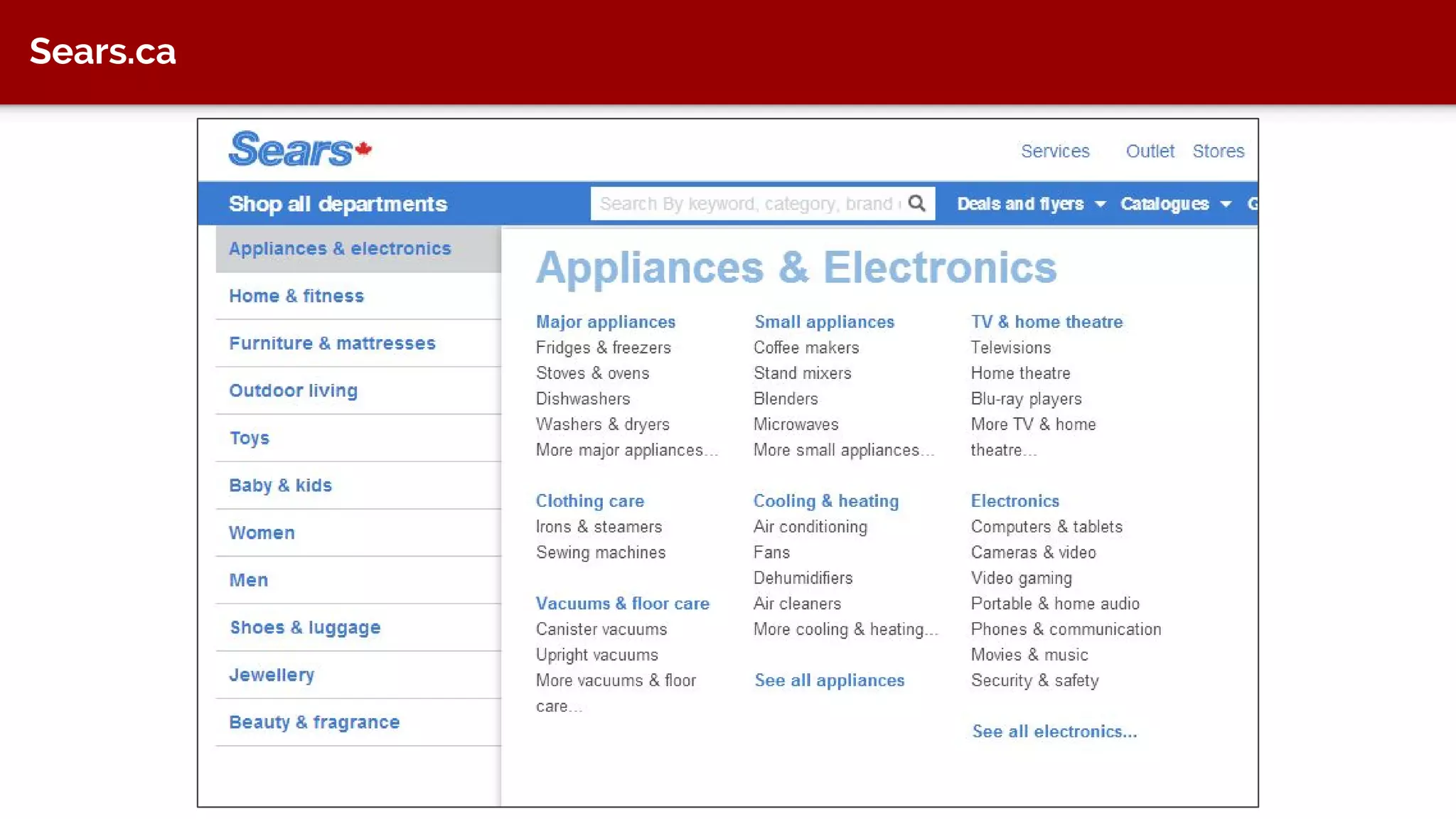
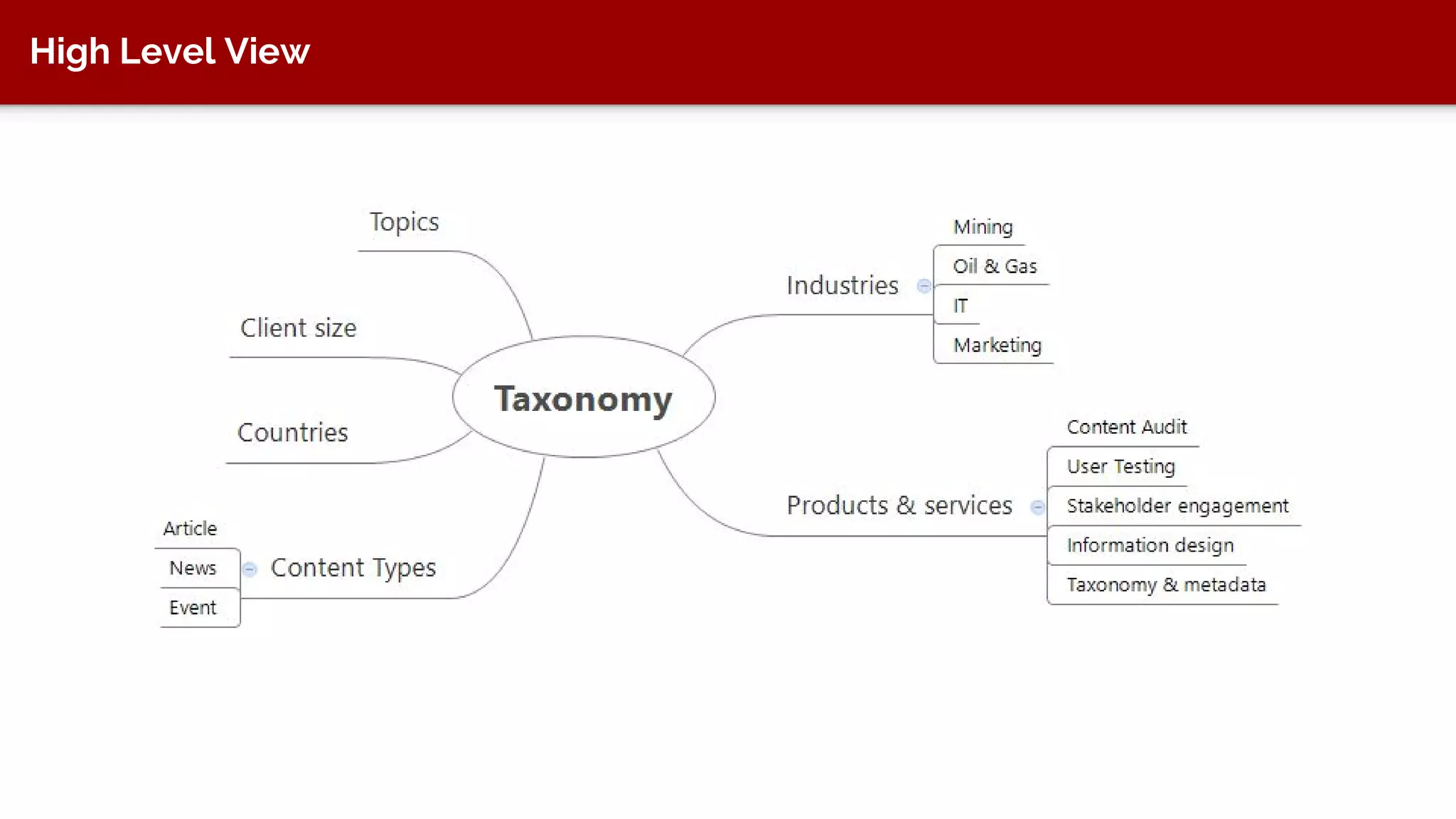
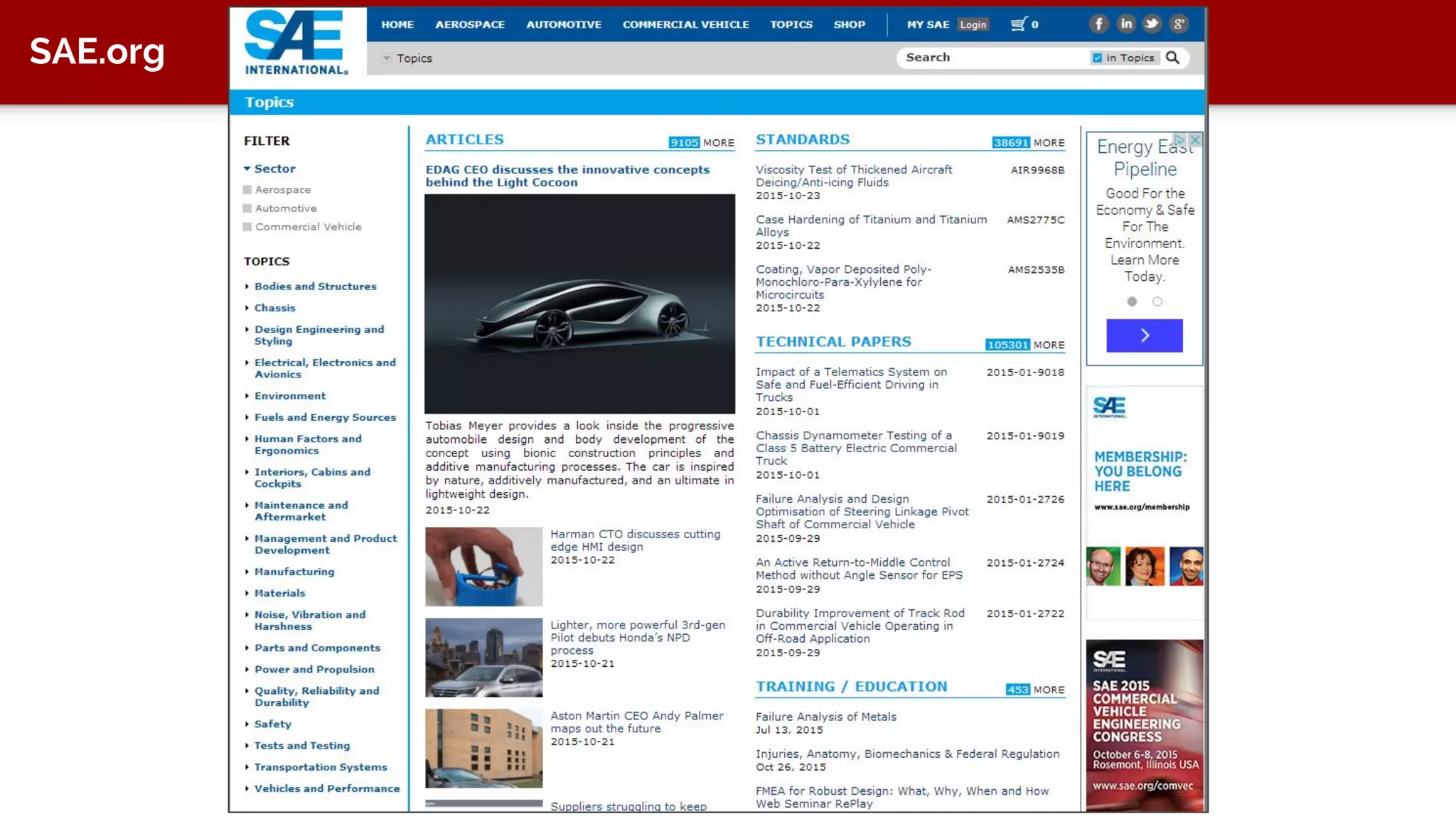
The document discusses taxonomy, an approach to categorizing untraditional information, particularly in the context of digital asset management (DAM) systems. It provides examples of how taxonomy can help organizations improve information organization, searchability, and user experience on websites. The document also outlines the importance of taxonomy development, auditing, and training for effective information management.