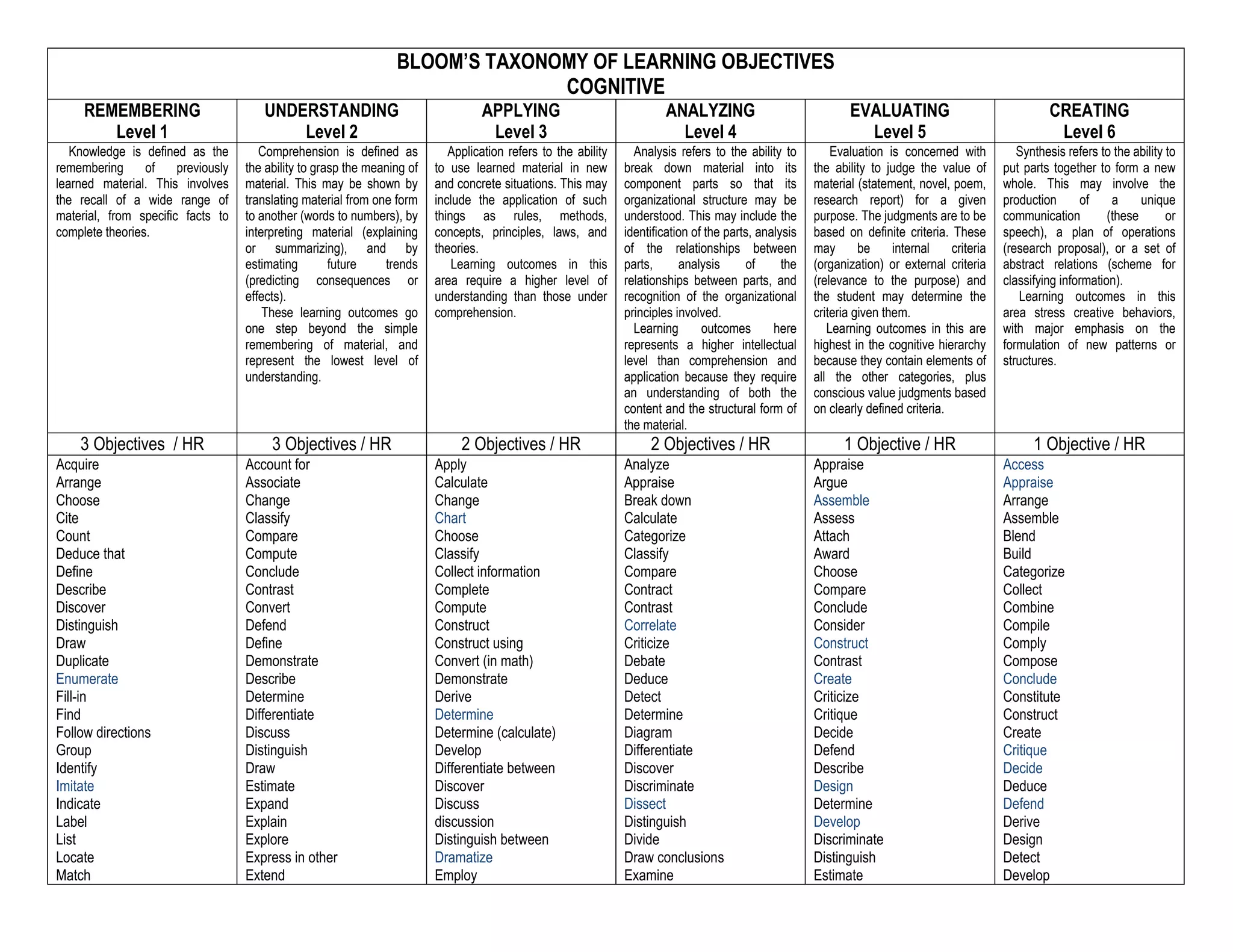
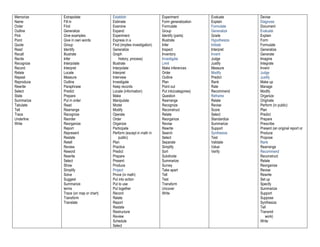
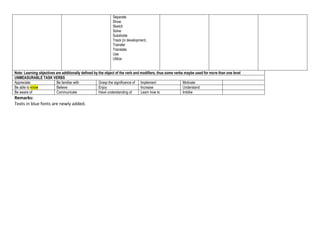
Bloom's Taxonomy categorizes learning objectives into six levels of cognitive complexity - Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Remembering involves recalling facts and theories. Understanding requires comprehending material by interpreting, explaining, and predicting. Applying refers to using learned material in concrete situations like applying rules or theories. Analyzing involves breaking down material into parts to understand organizational structures. Evaluating is judging material based on internal or external criteria. Creating involves putting parts together to form new wholes through activities like developing a research proposal.