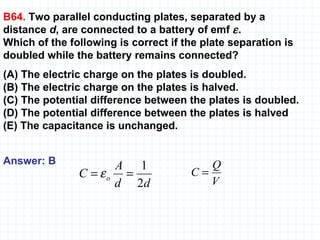
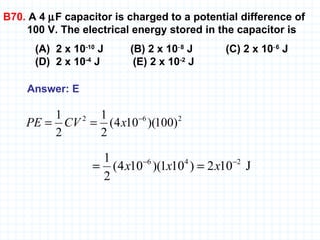
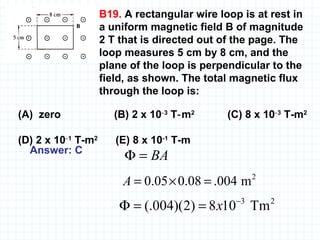
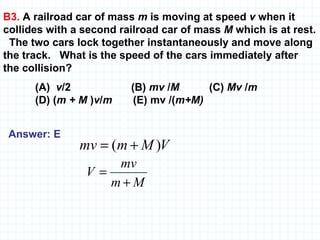
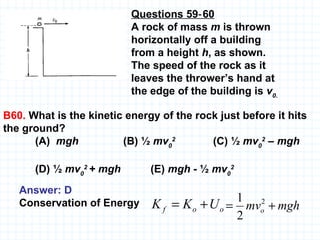
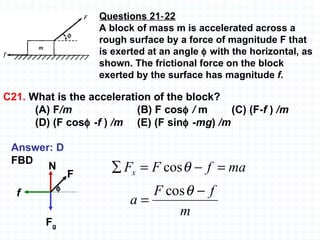
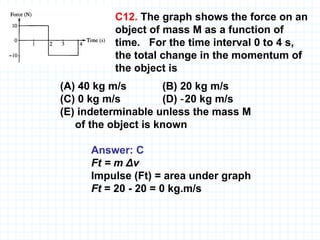
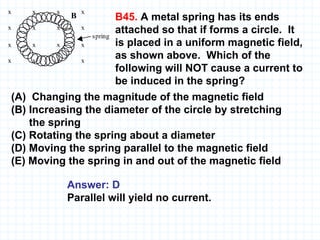
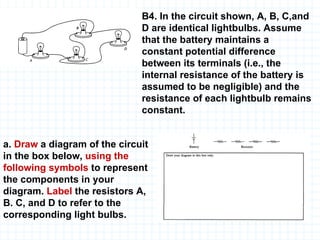
The document provides an overview of the AP Physics B exam, including the multiple choice and free response sections. It discusses the types of multiple choice questions asked, such as conceptual, computation, graph analysis, and diagram based. It provides examples of each type of question and explains the concepts and equations tested. The summary focuses on the key information about the exam format and question types to help students prepare.